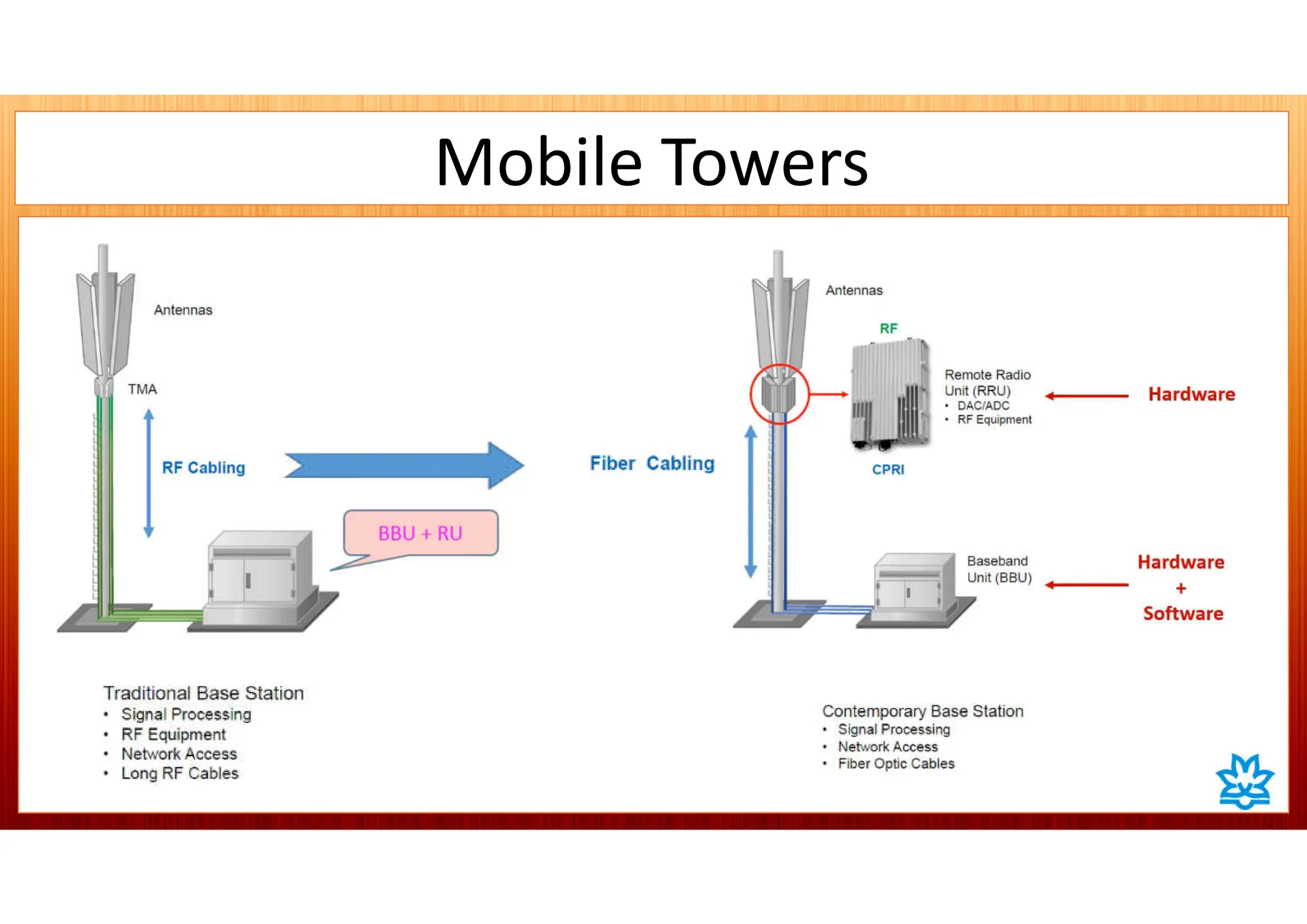
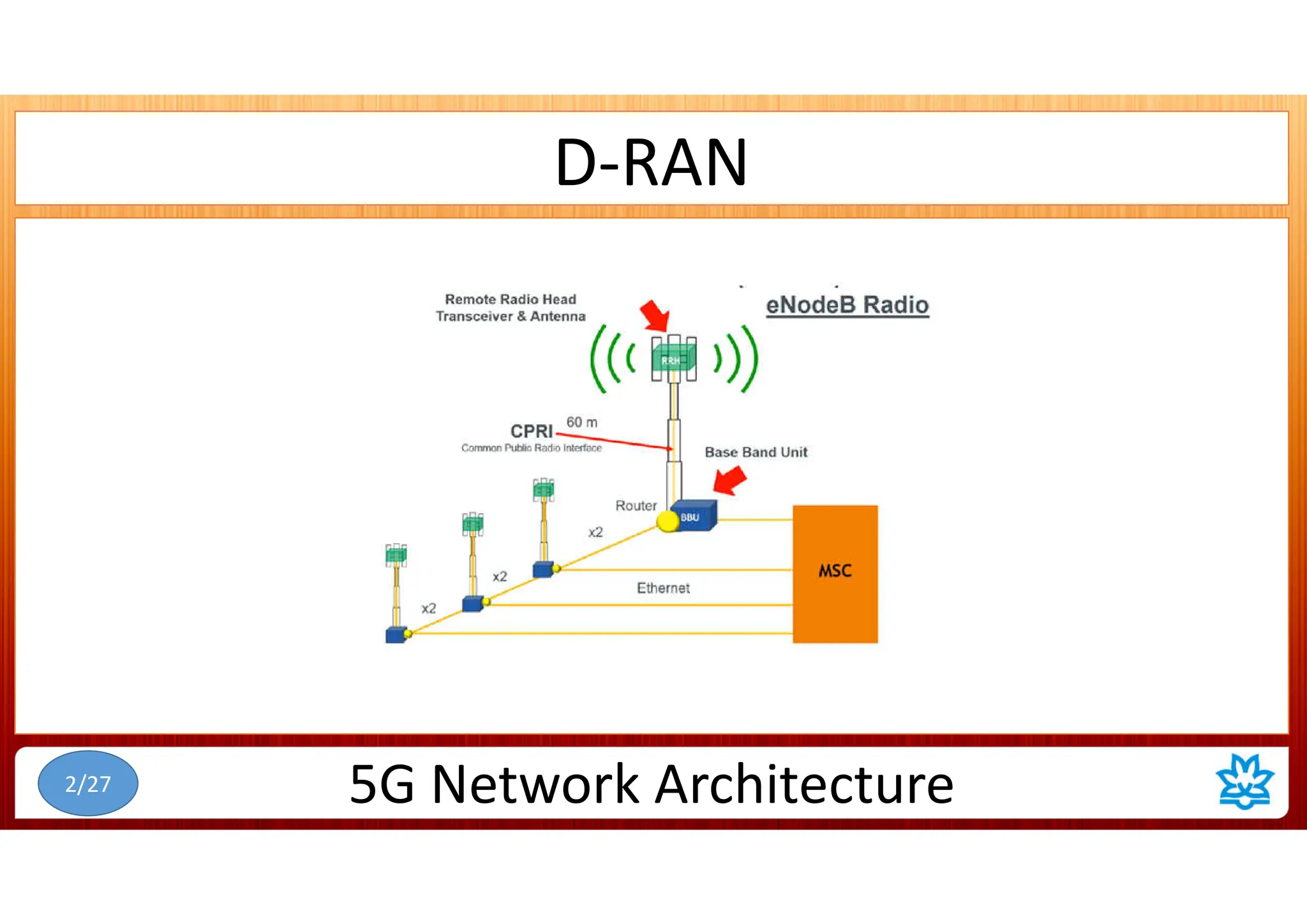
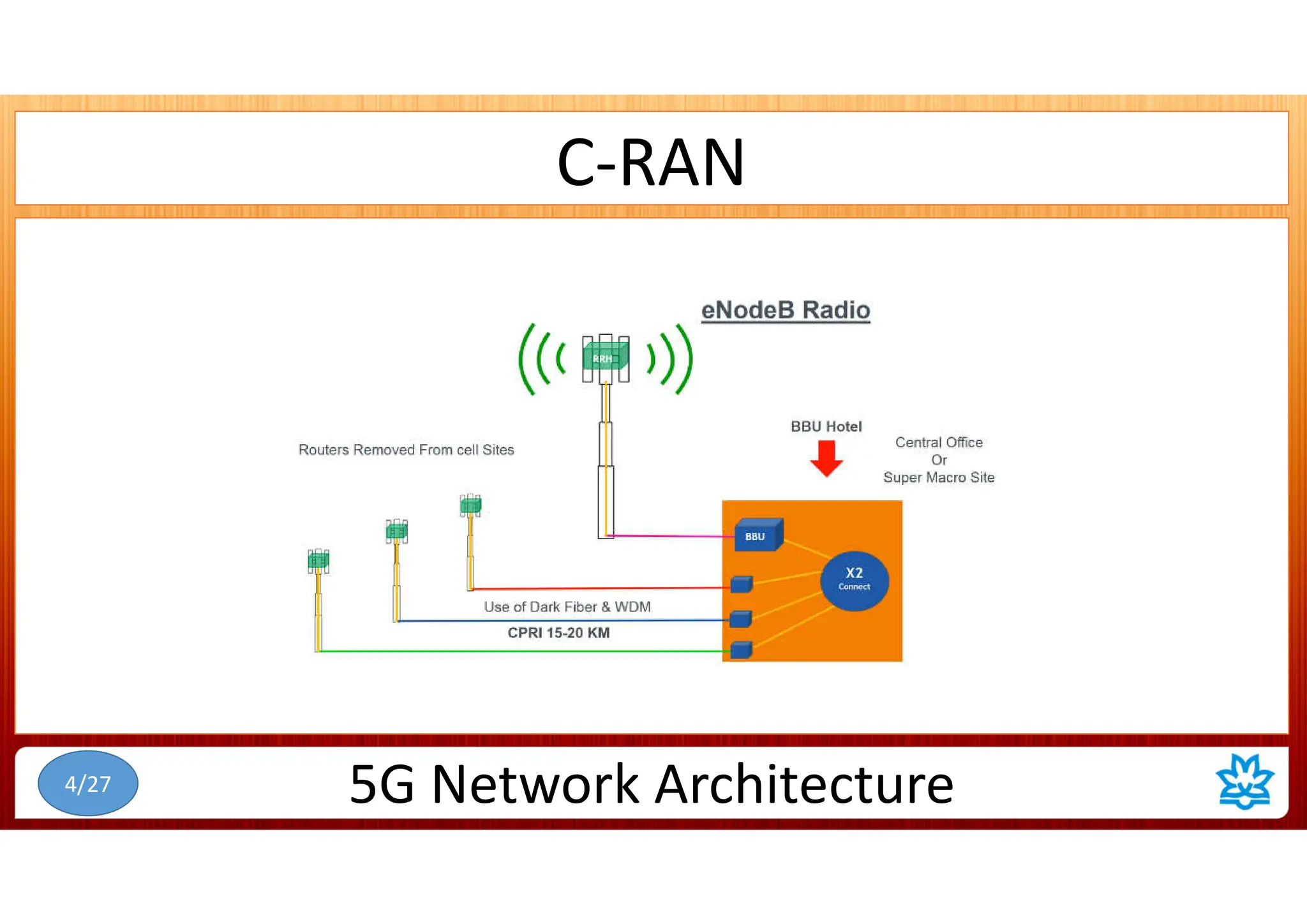
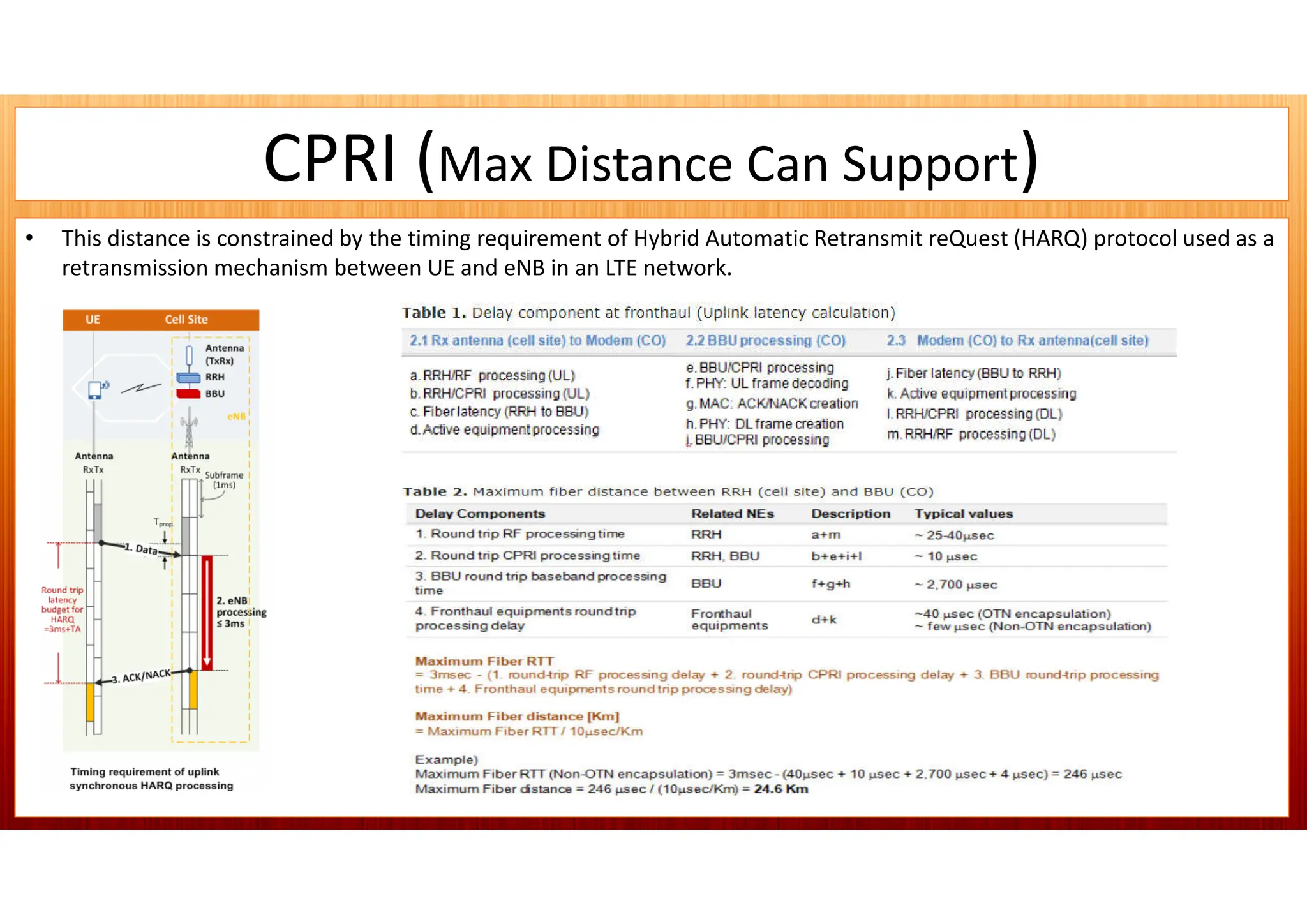
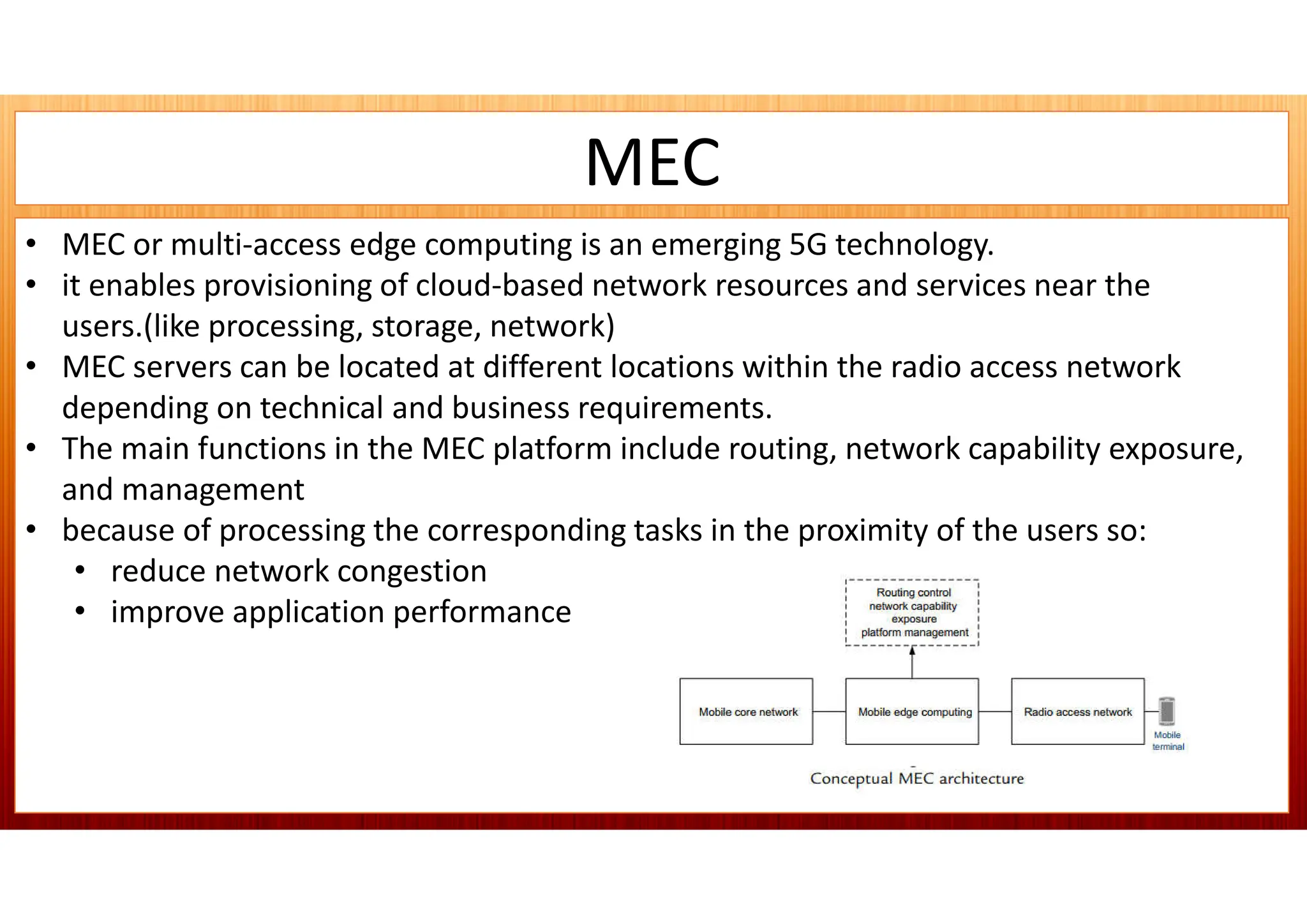
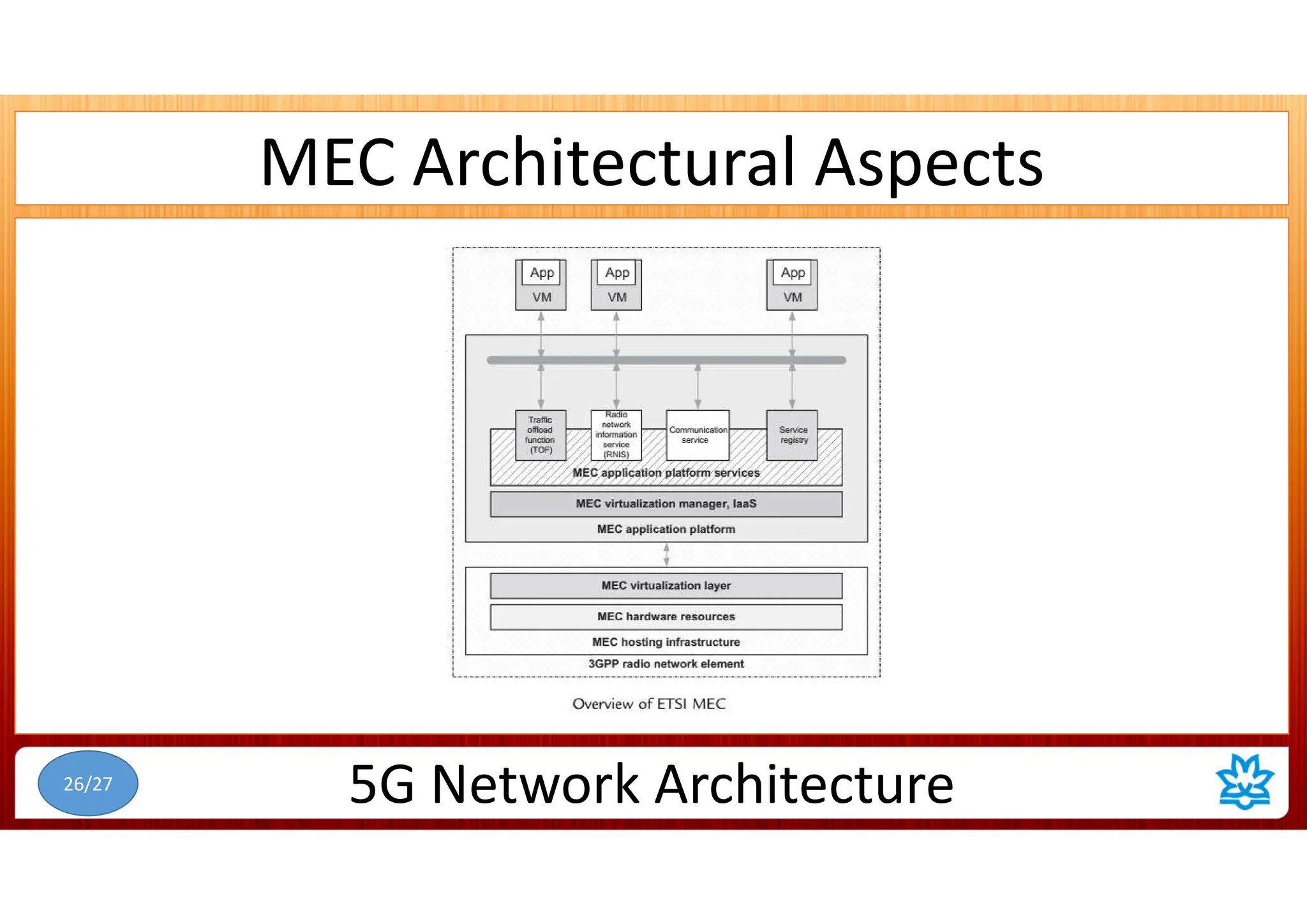
This document discusses 5G network architecture. It covers mobile towers, distributed and centralized radio access networks (D-RAN, C-RAN), virtualized RAN (V-RAN), fronthaul interfaces like CPRI and eCPRI, time-sensitive networking standards, mobile backhaul, and multi-access edge computing (MEC). Function splitting and different functional split options between baseband and radio units are described. Standards like IEEE 1914.1 for packet-based fronthaul are also summarized.