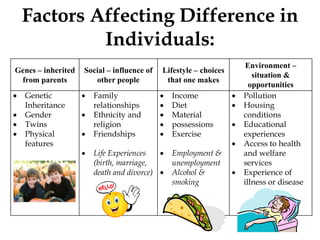
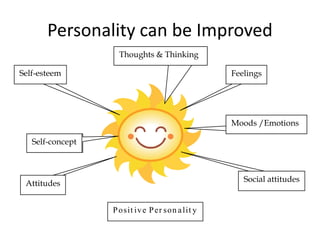
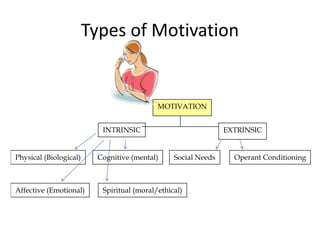
This document discusses individual differences and motivation. It covers factors that influence individual differences such as genes, environment, gender and life experiences. These differences impact learning in the classroom. Teachers need to employ varied teaching strategies like grouping students homogenously, pairing work, and individual teaching. The document also discusses personality development and theories. Self-esteem is influenced by self-concept and experiences. Motivation is influenced by internal and external factors and can be intrinsic or extrinsic.