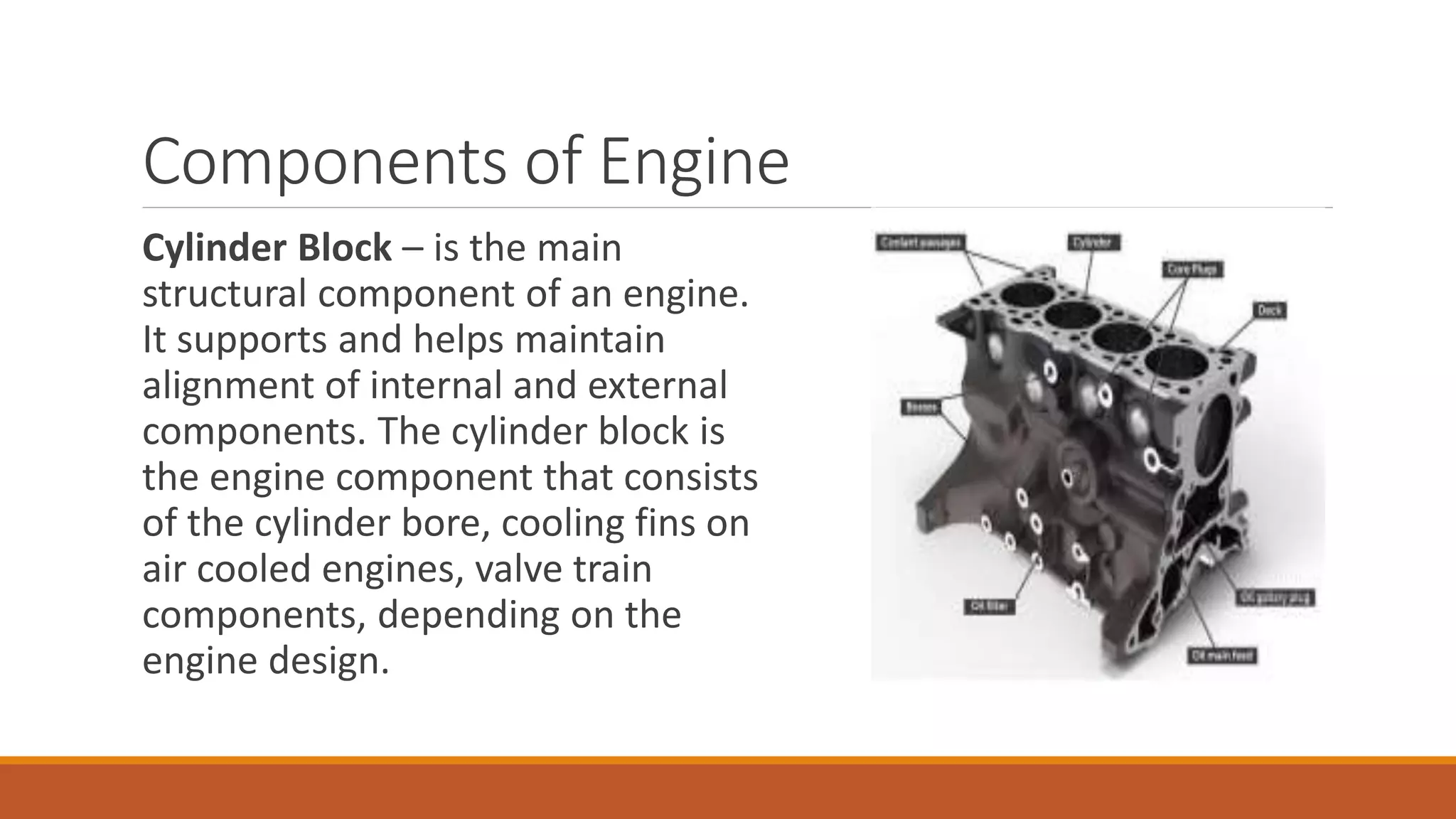
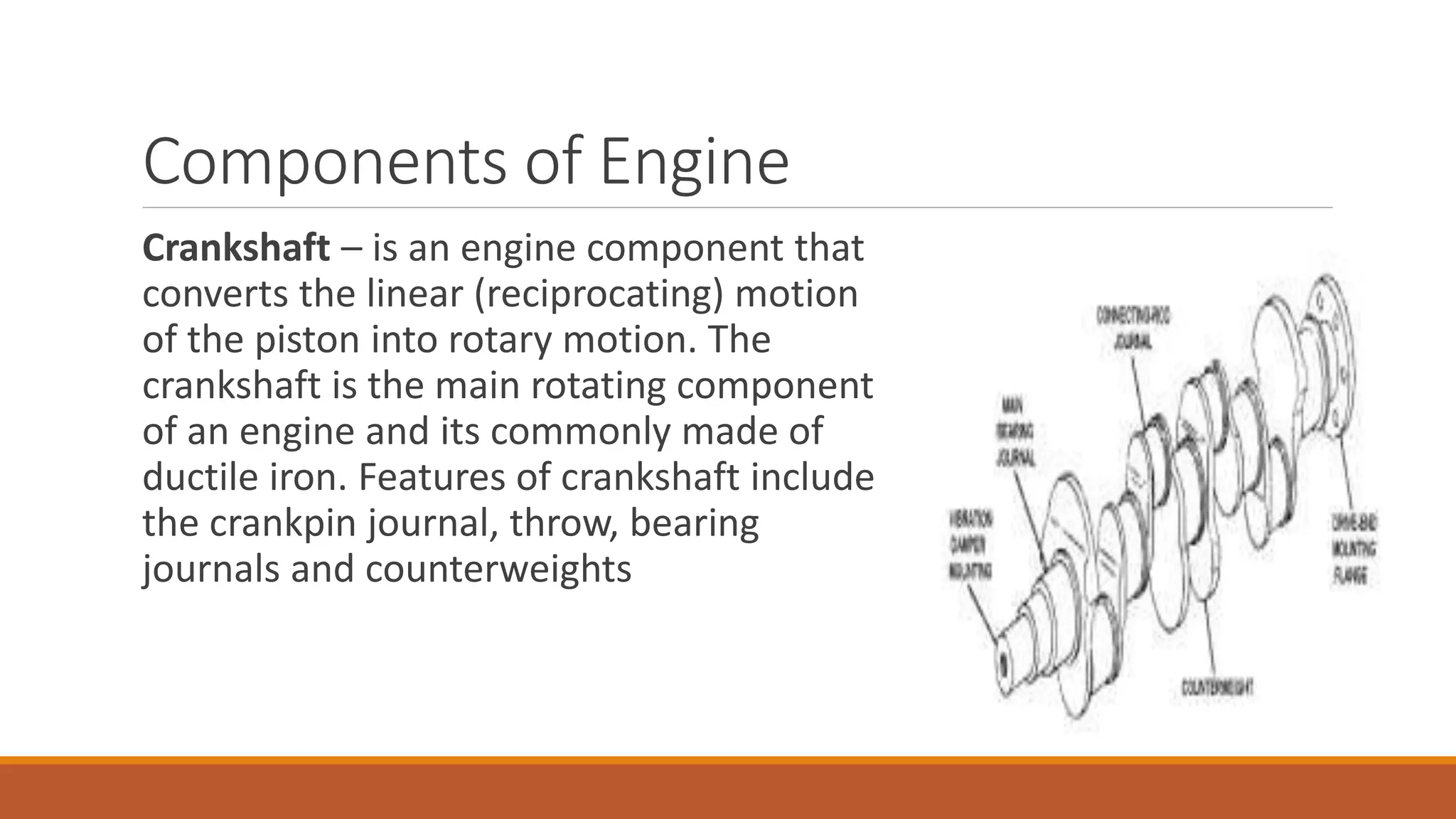
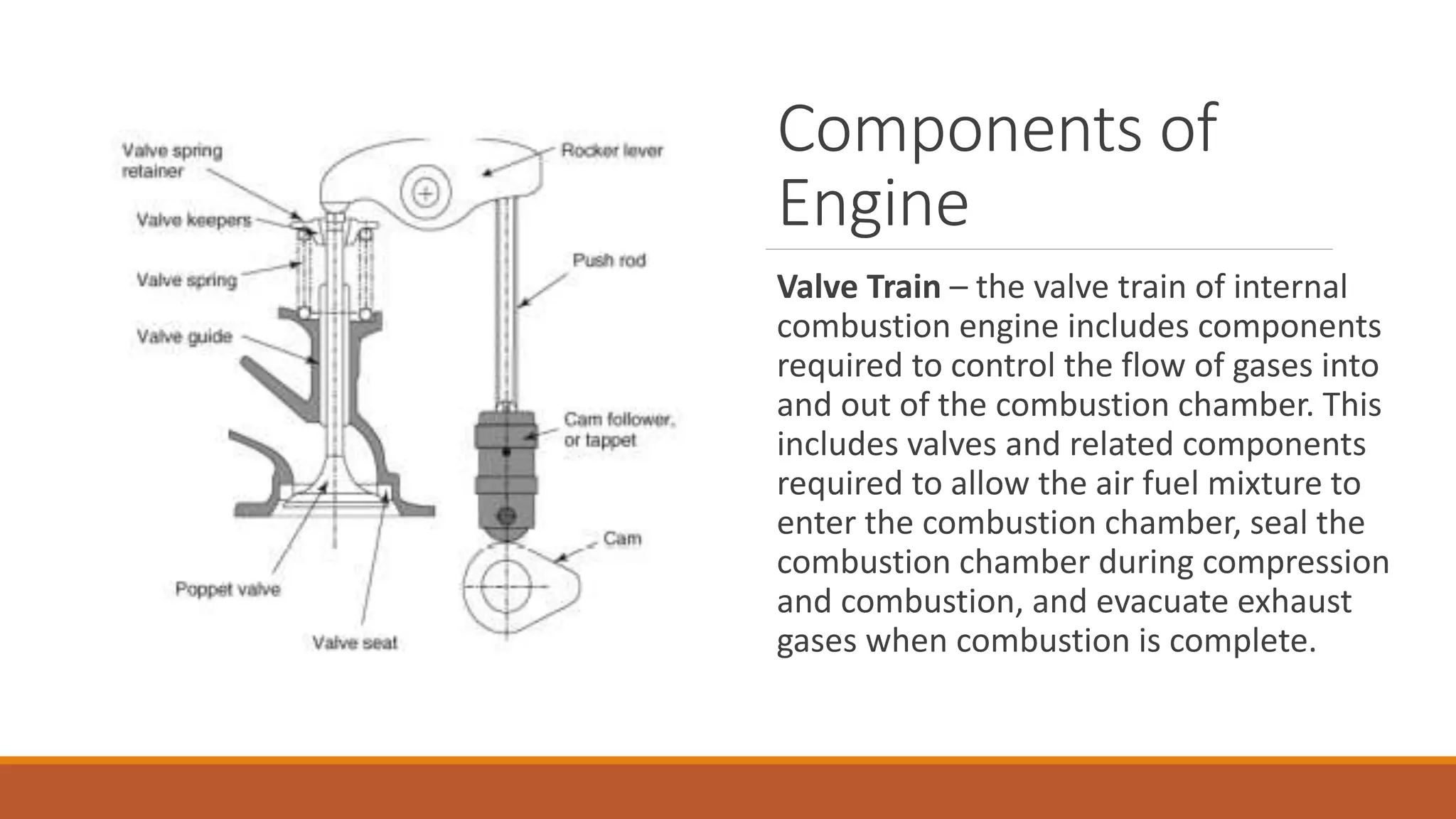
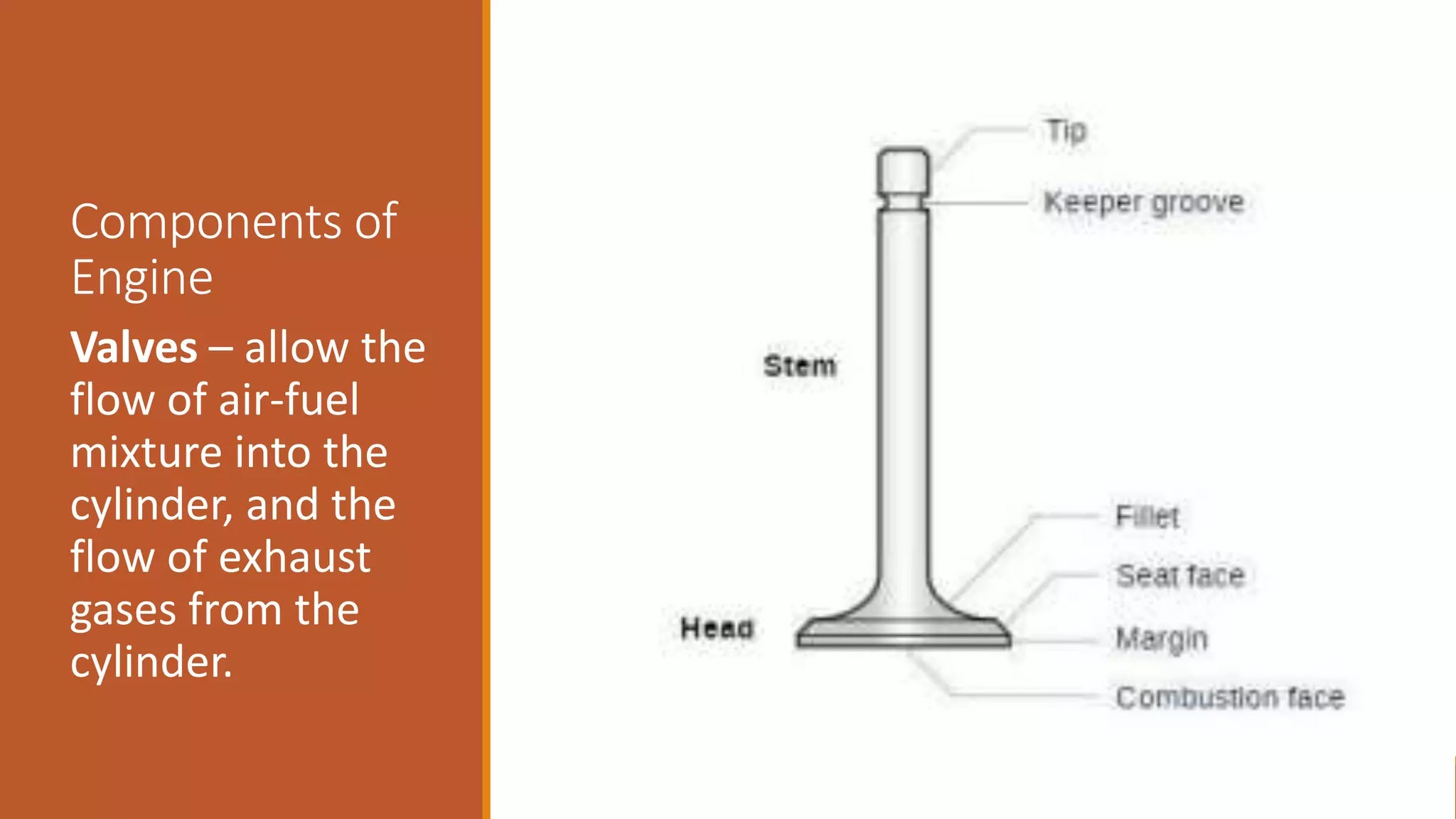
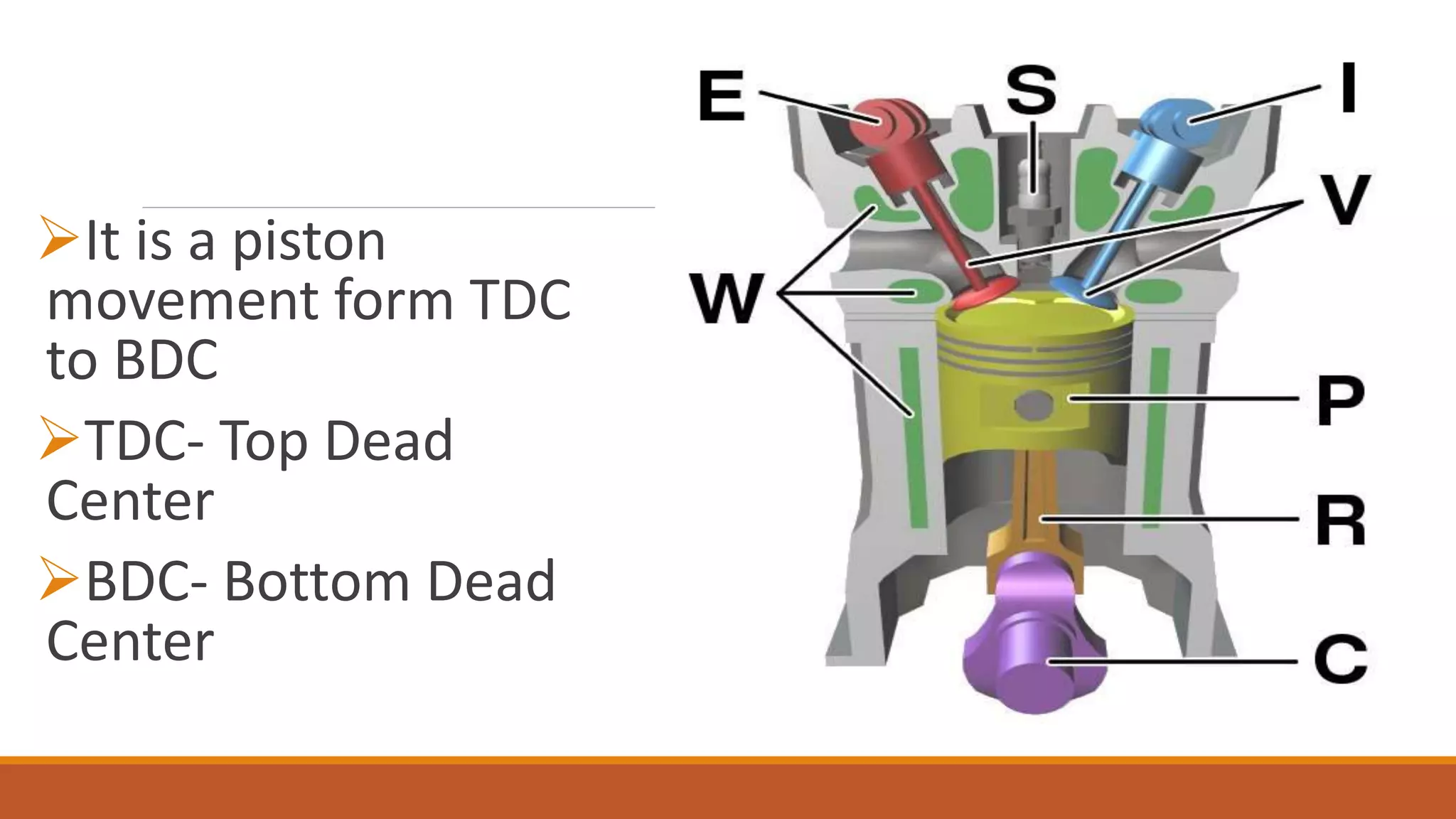
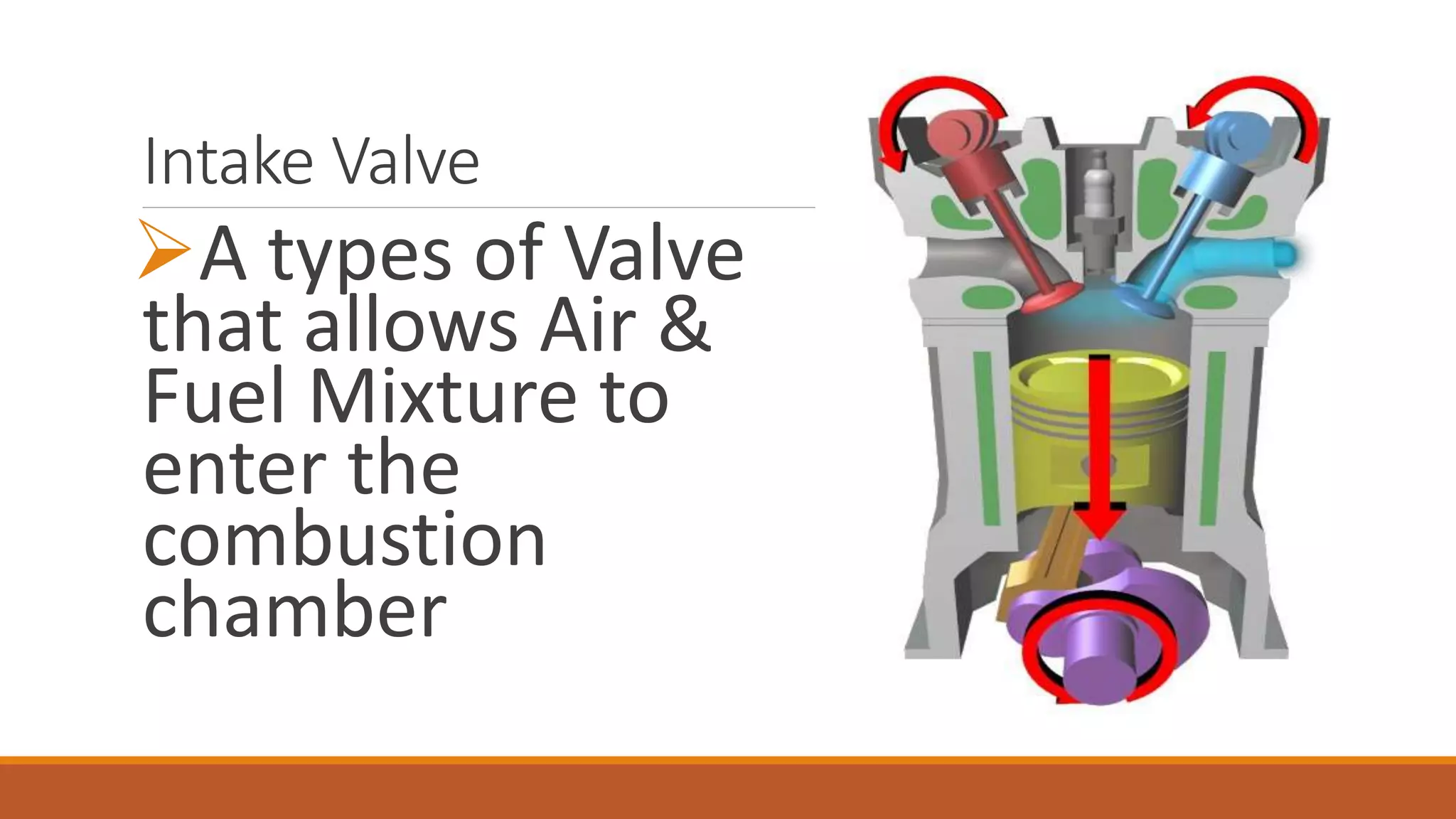
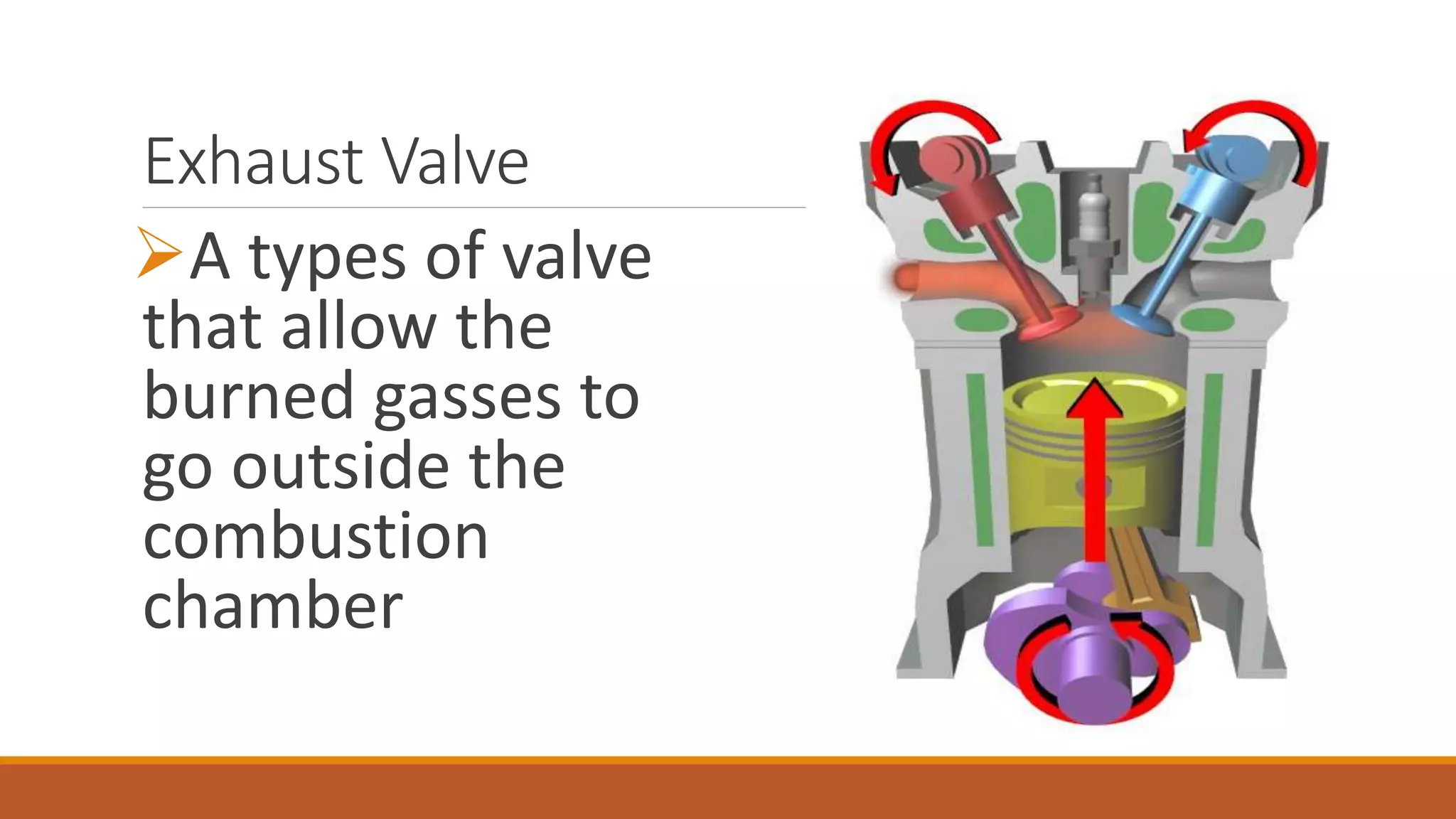
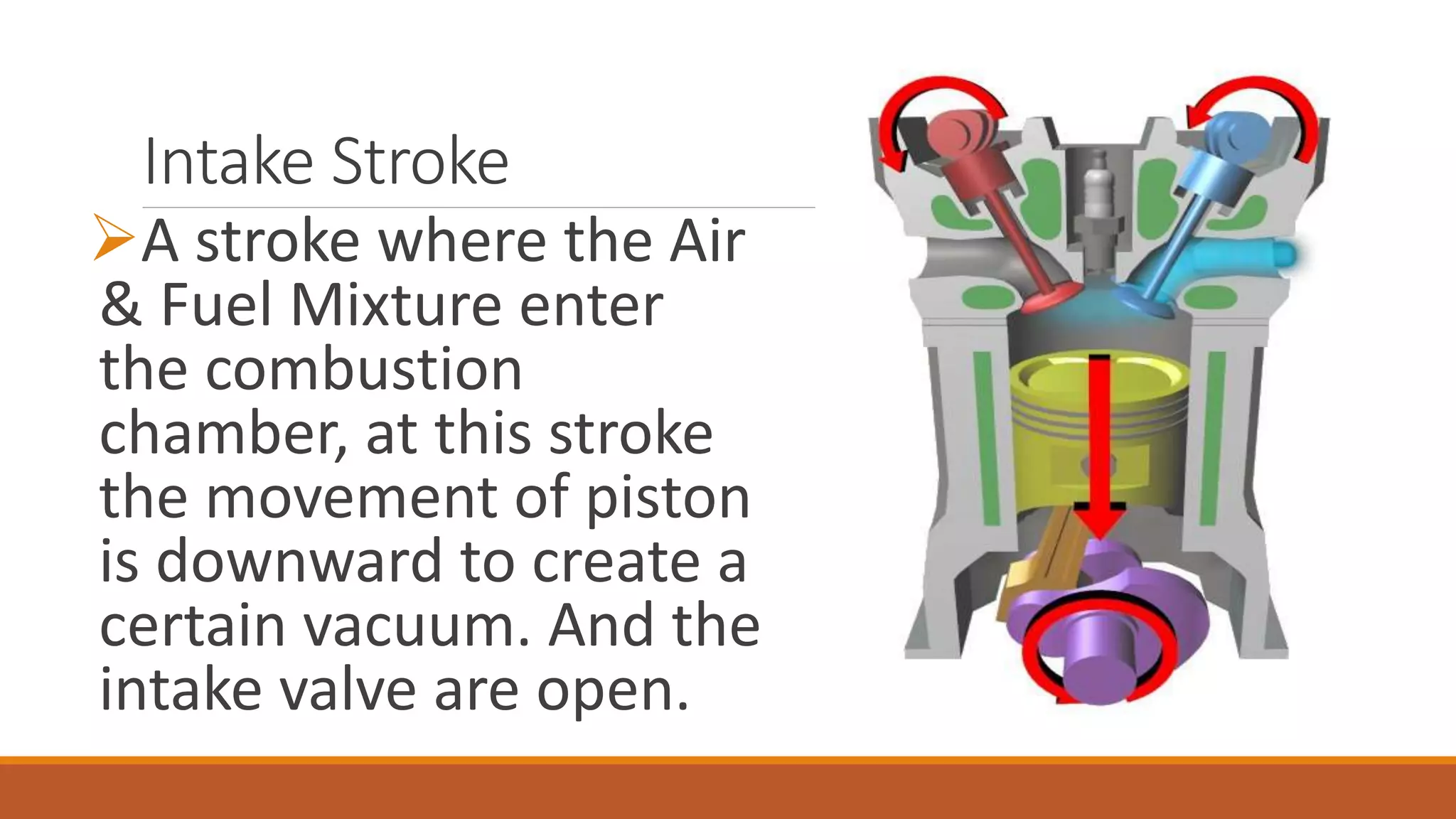
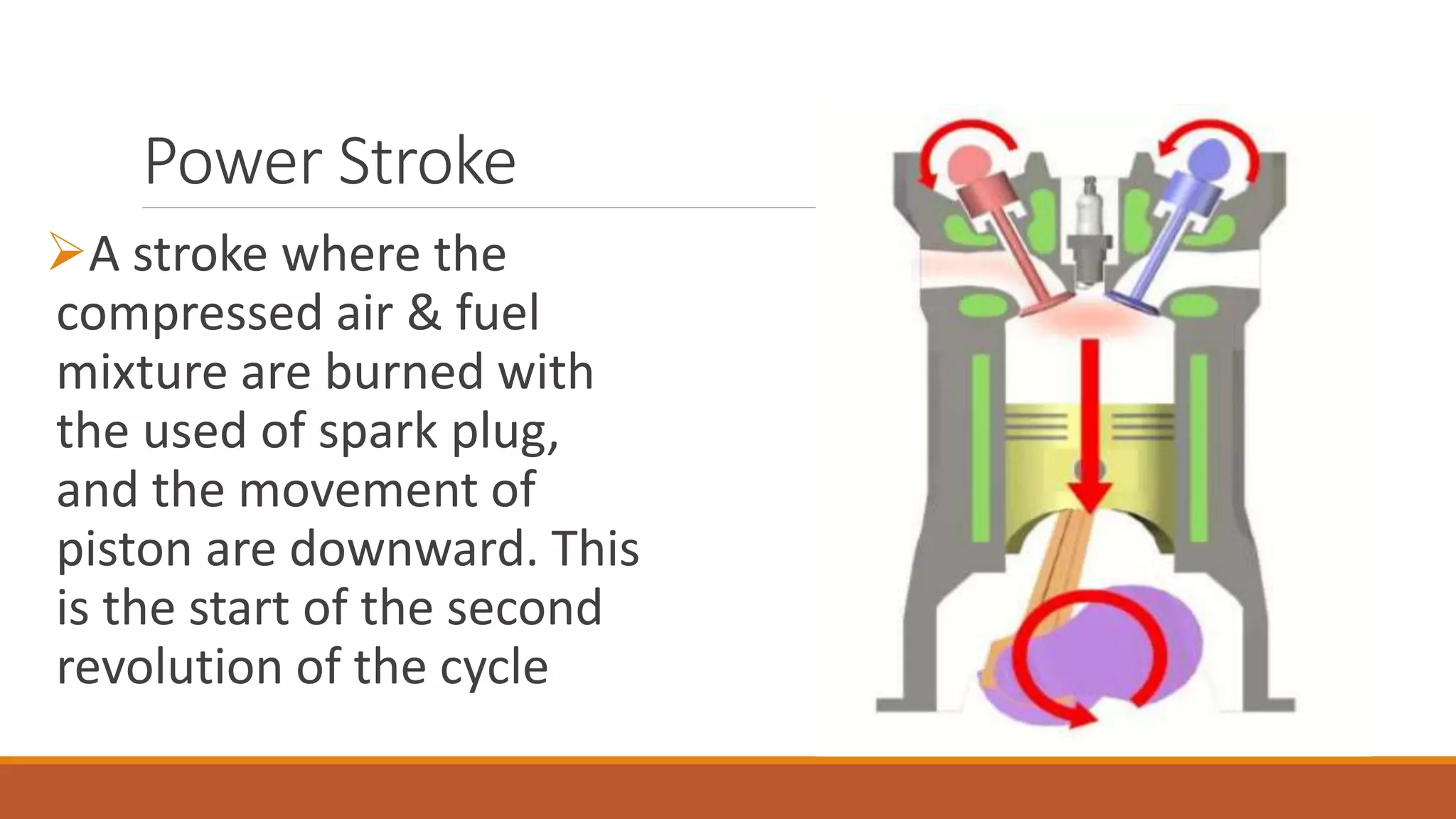
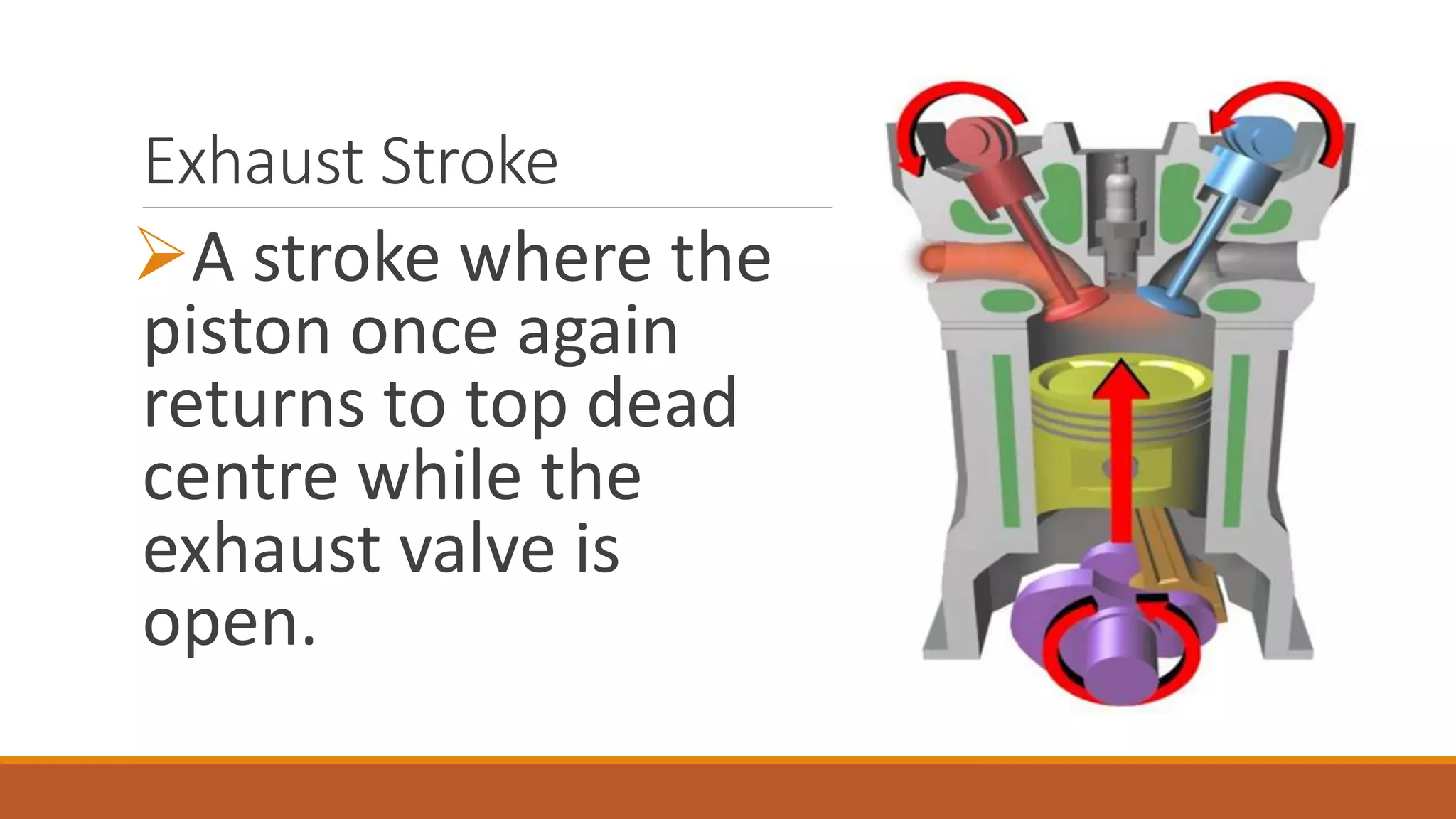
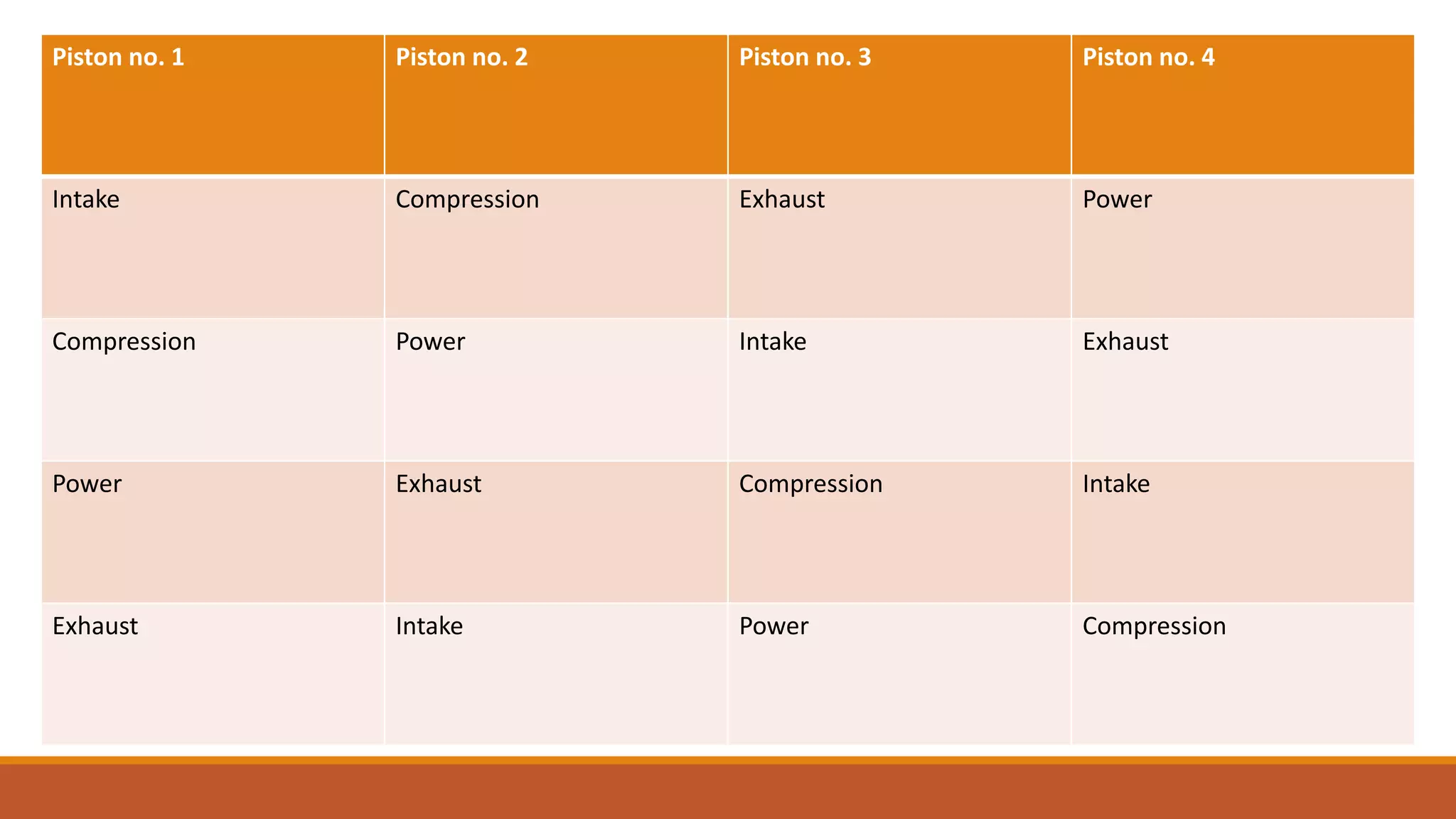
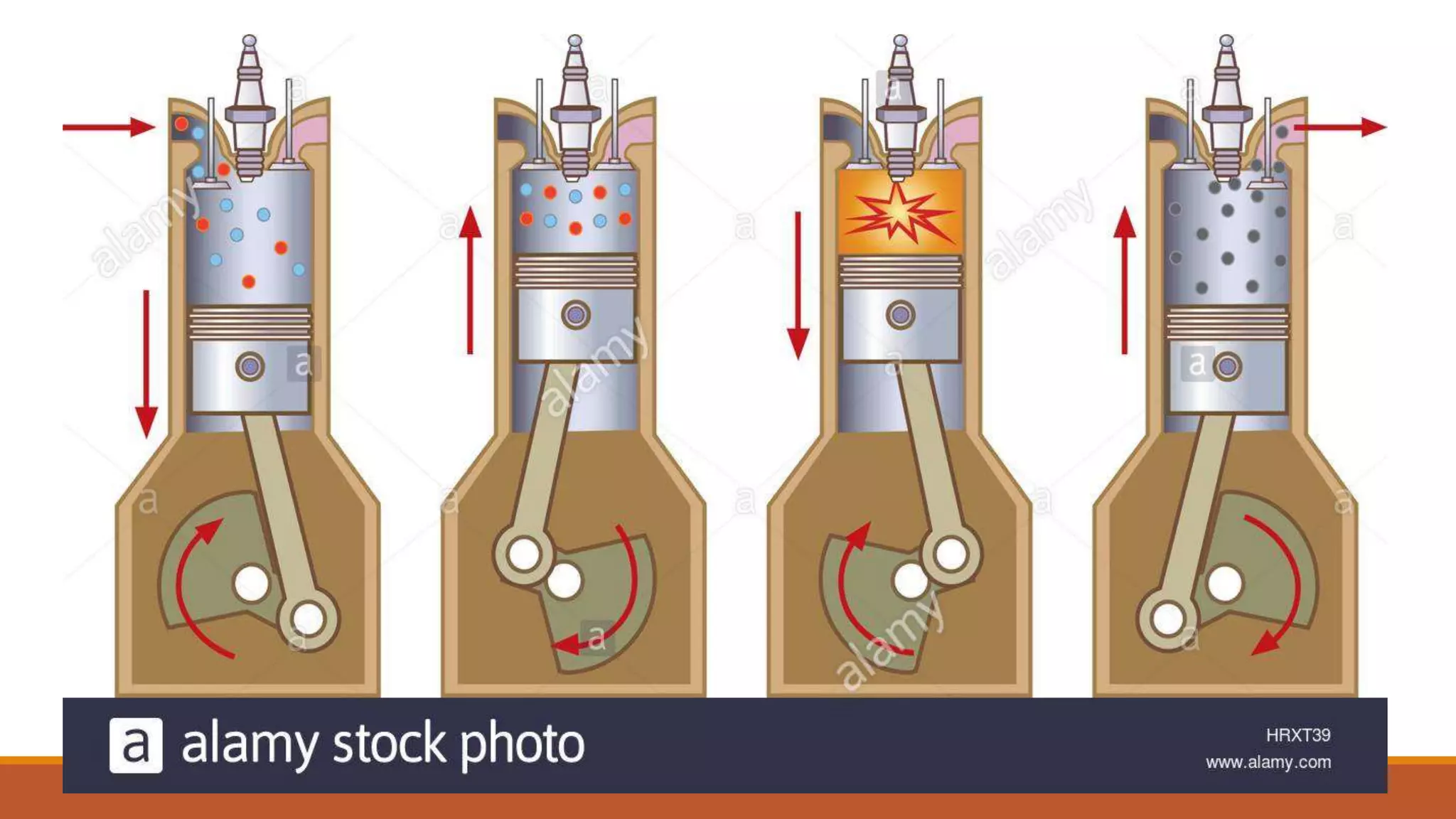
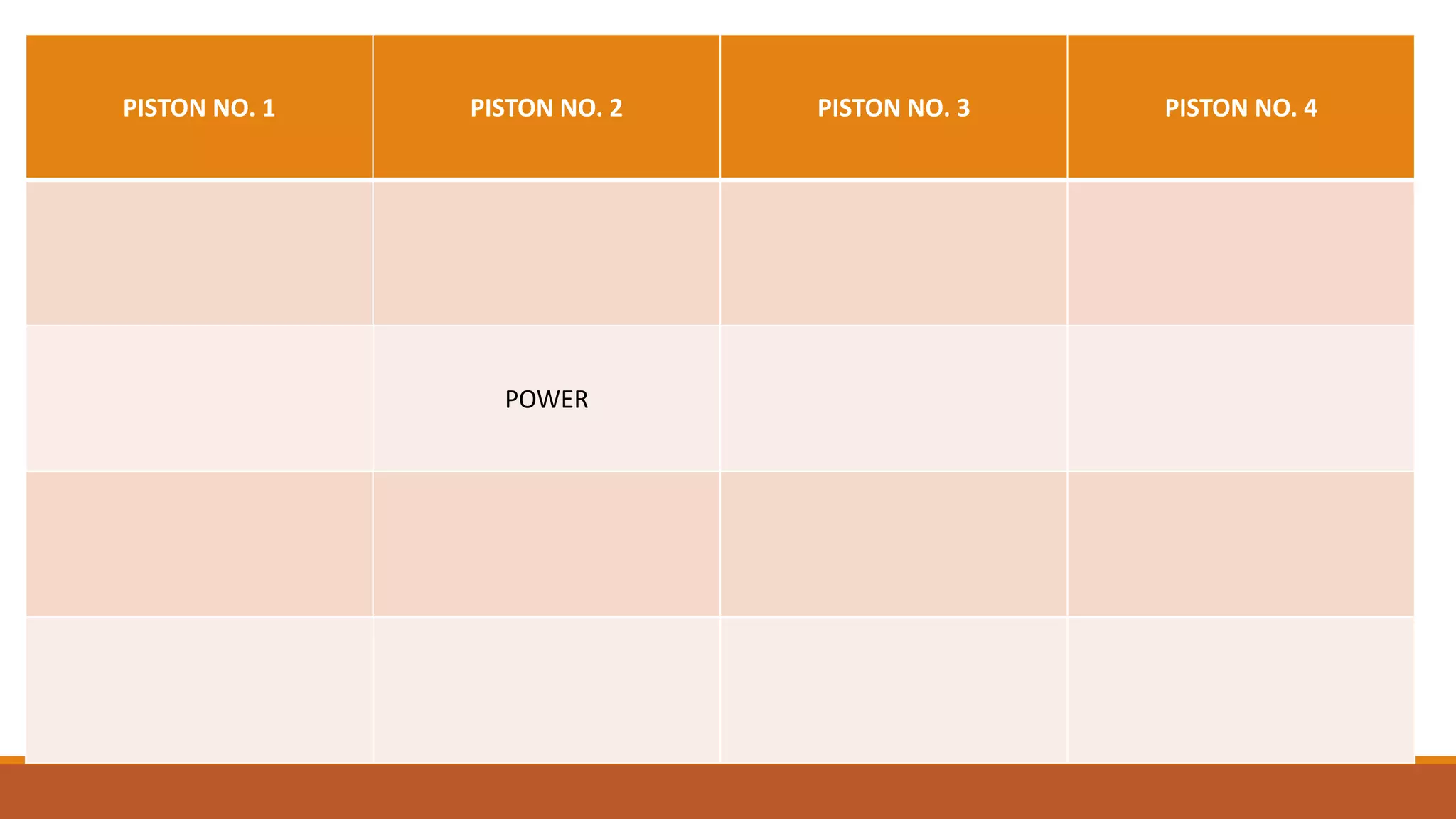
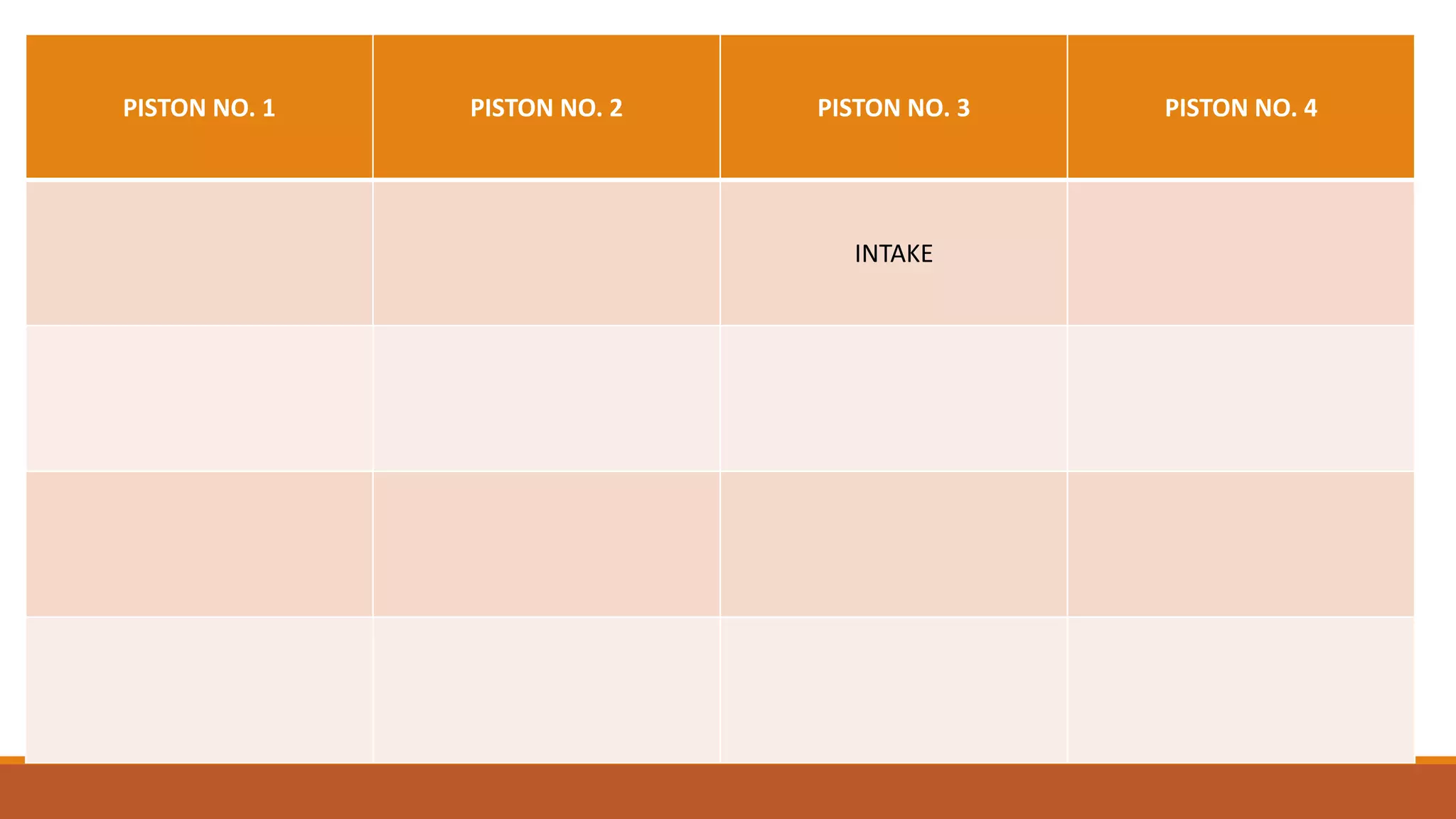
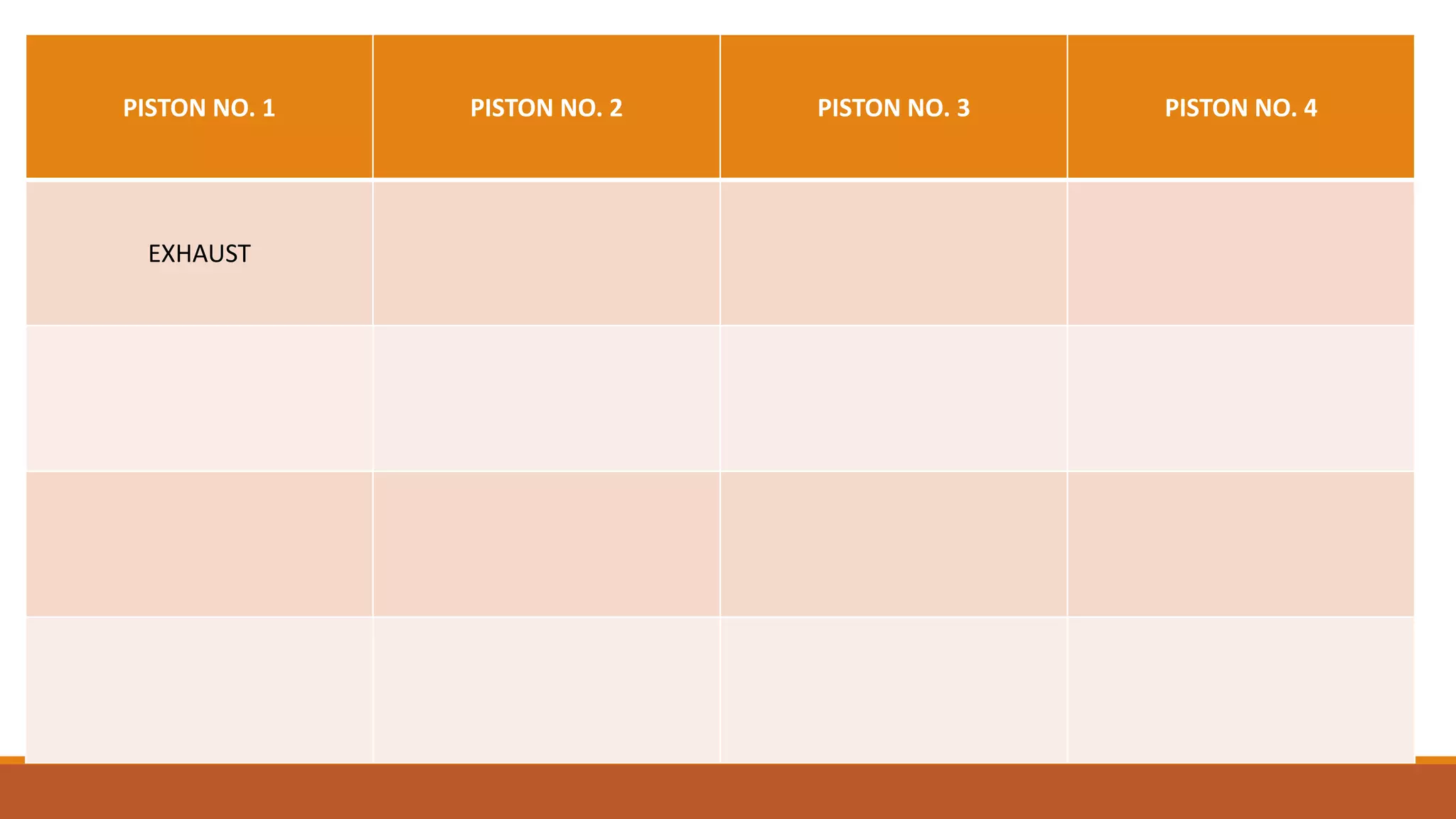
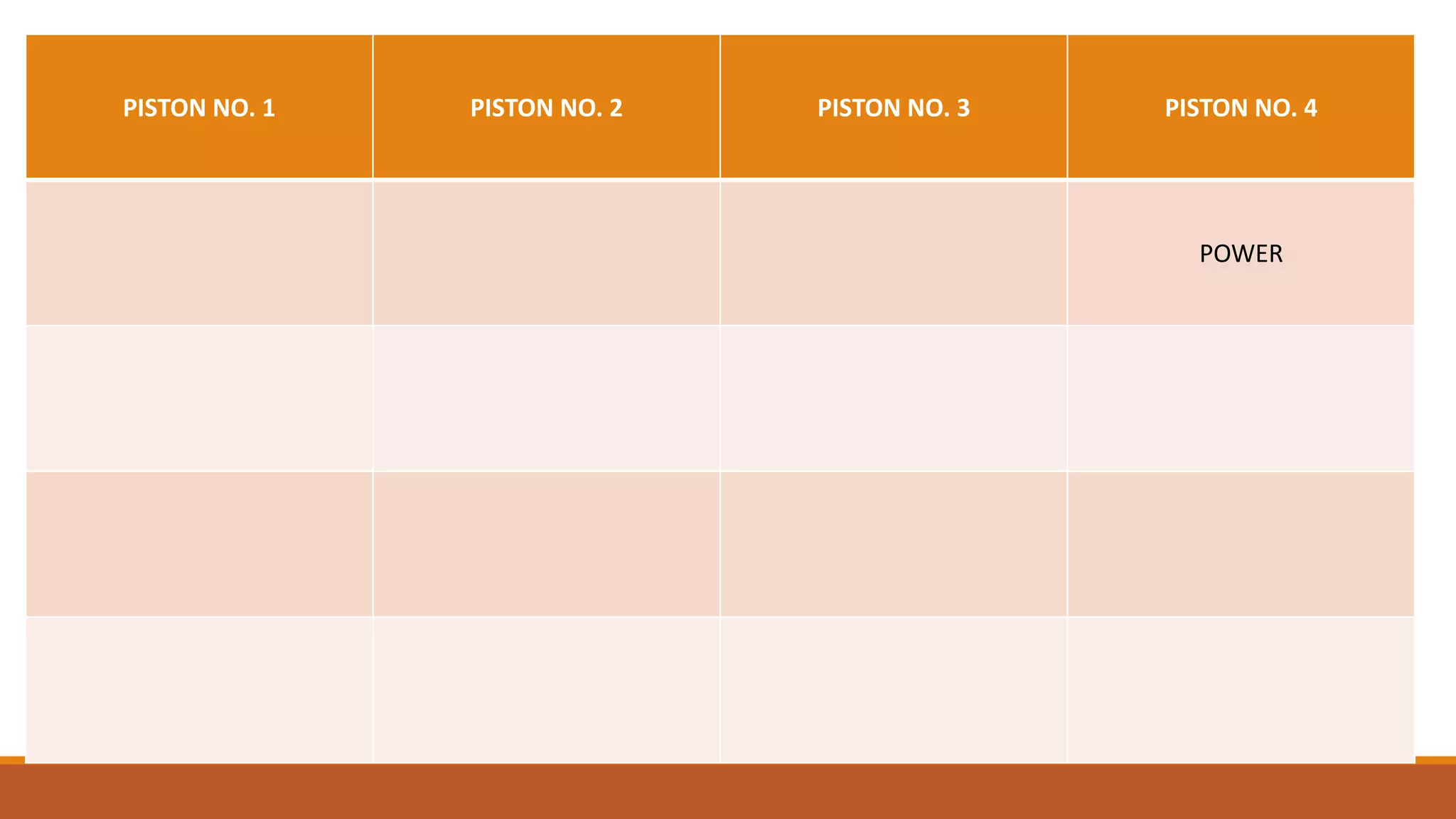
The document discusses the key components of an internal combustion engine and the 4-stroke cycle. It describes the cylinder block, cylinder head, crankshaft, piston and piston rings, connecting rod, bearings, flywheel, and valve train as the main components. It then explains the 4 strokes of the engine cycle: the intake stroke where air/fuel mixture enters; compression stroke where the mixture is compressed; power stroke where combustion provides energy; and exhaust stroke where burned gases exit. The 4 strokes occur sequentially in each cylinder, with all cylinders completing a stroke simultaneously so pistons work together like steps on an engine.