Embed presentation
Downloaded 12 times

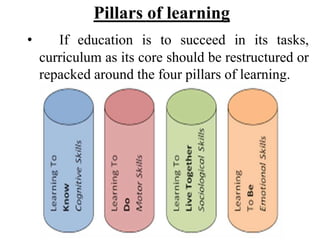







The document discusses restructuring curriculum around four pillars of learning: developing memory, imagination, reasoning, and problem-solving abilities. It argues curriculum should focus on learning to know through discovery and understanding, and learning to learn via concentration, memory, and thought. The goal is to provide equal opportunities for all students to learn, progress, and achieve their highest potential, while also promoting their social-cultural development and preparation for work and society. A varied curriculum incorporating subjects, libraries, labs, playgrounds, and co-curricular activities can increase learning.








