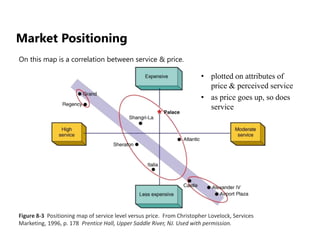
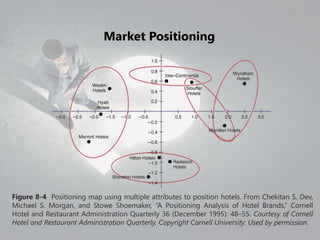
This document discusses market positioning and perceptual mapping. It provides examples of perceptual maps that plot brands based on attributes like price and service level, as well as maps using multiple attributes to position hotels. Perceptual maps can identify a competitive set and open spaces that may represent opportunities for repositioning away from competition. The positions on perceptual maps are neutral, with no spot inherently better than another. Perceptual mapping is a tool that can provide data to support the need for repositioning due to increased competition or ineffective strategies.
![SEKOLAH TINGGI
P A R I W I S A T A
T R I S A K T I
Welcome to
Market Positioning
Rina Suprina M.Hum, Msi, Par
Ivan Prasetya M.Par
[ ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-151025043227-lva1-app6892/85/4-market-positioning-pearson-1-320.jpg)