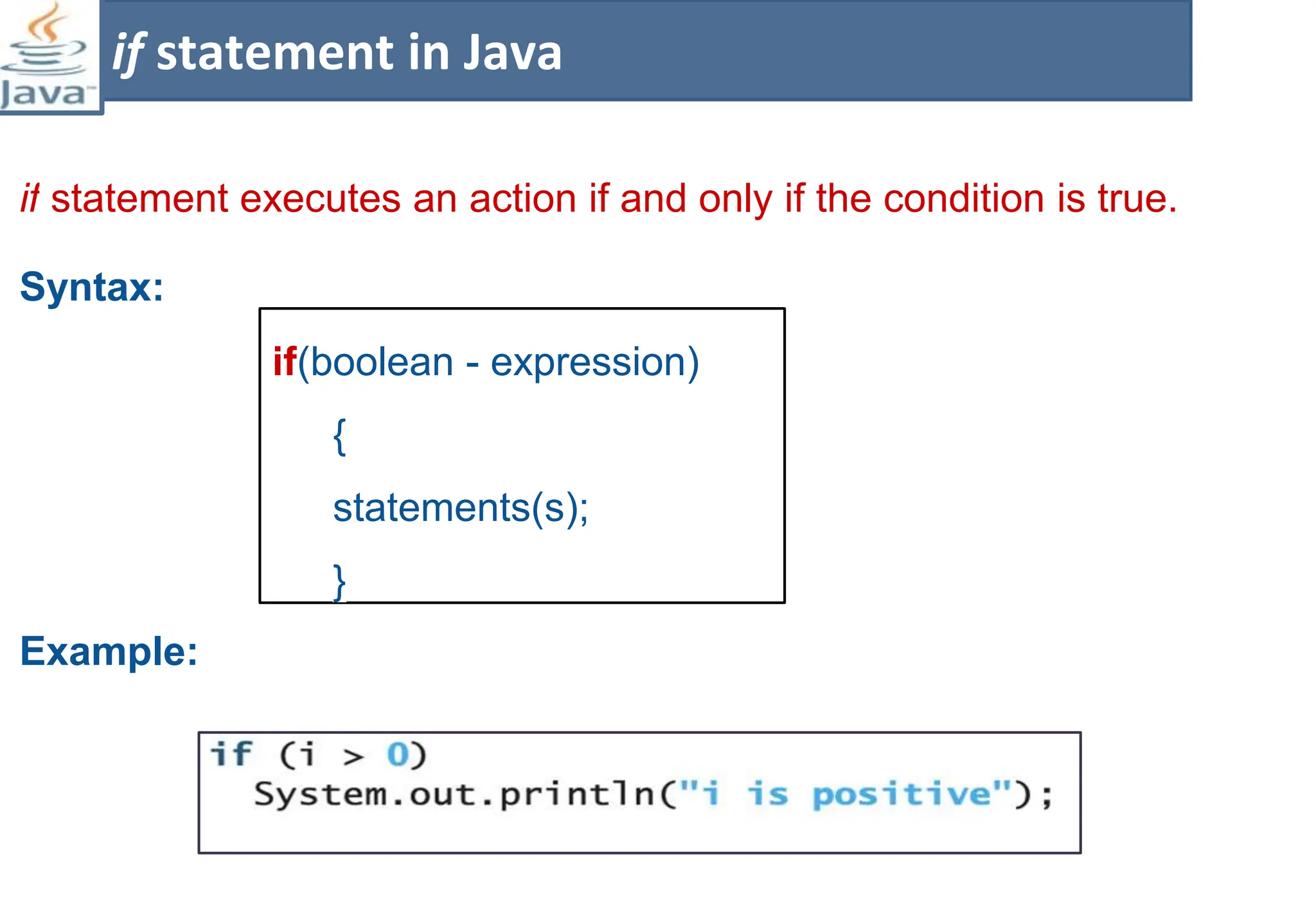
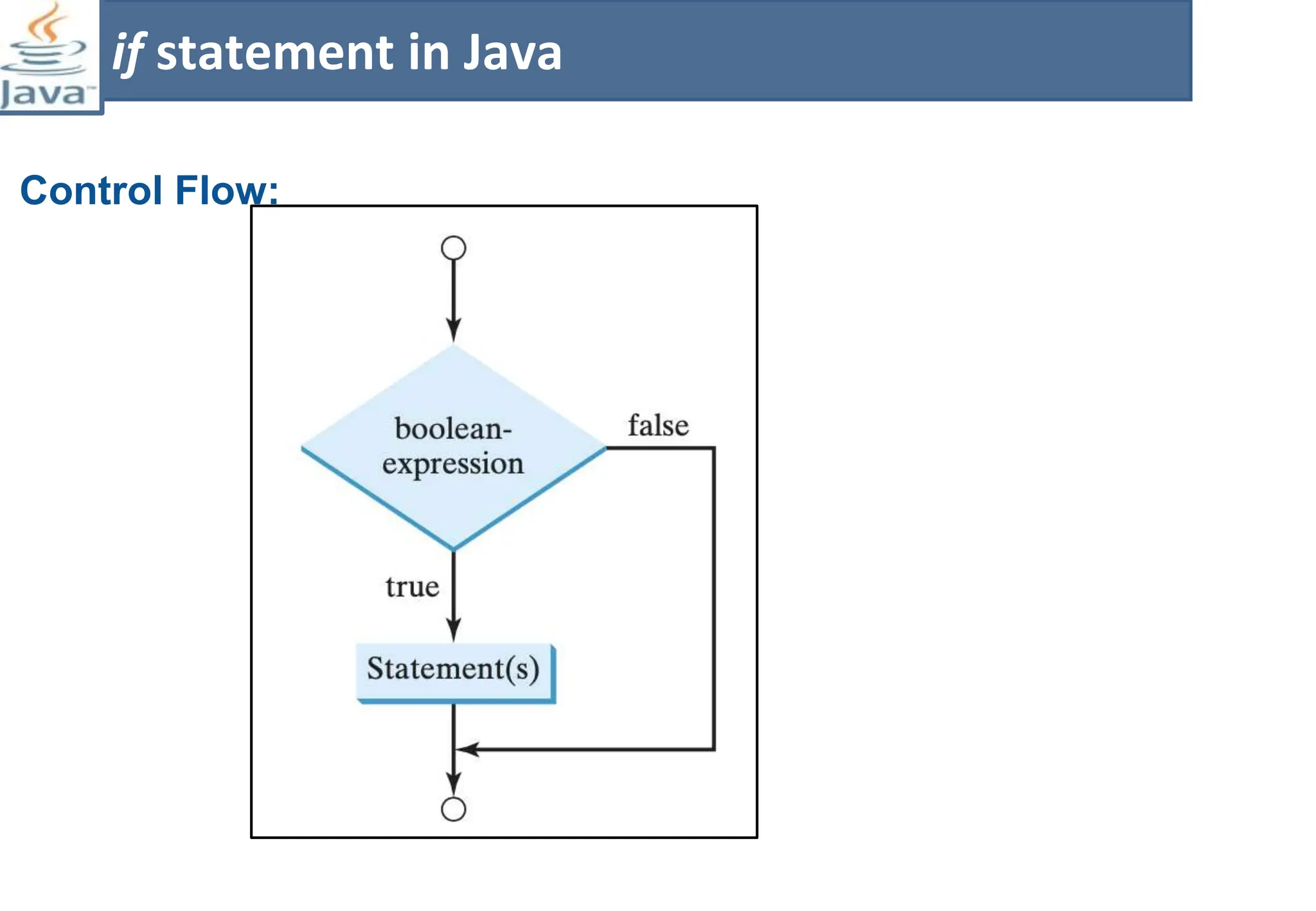
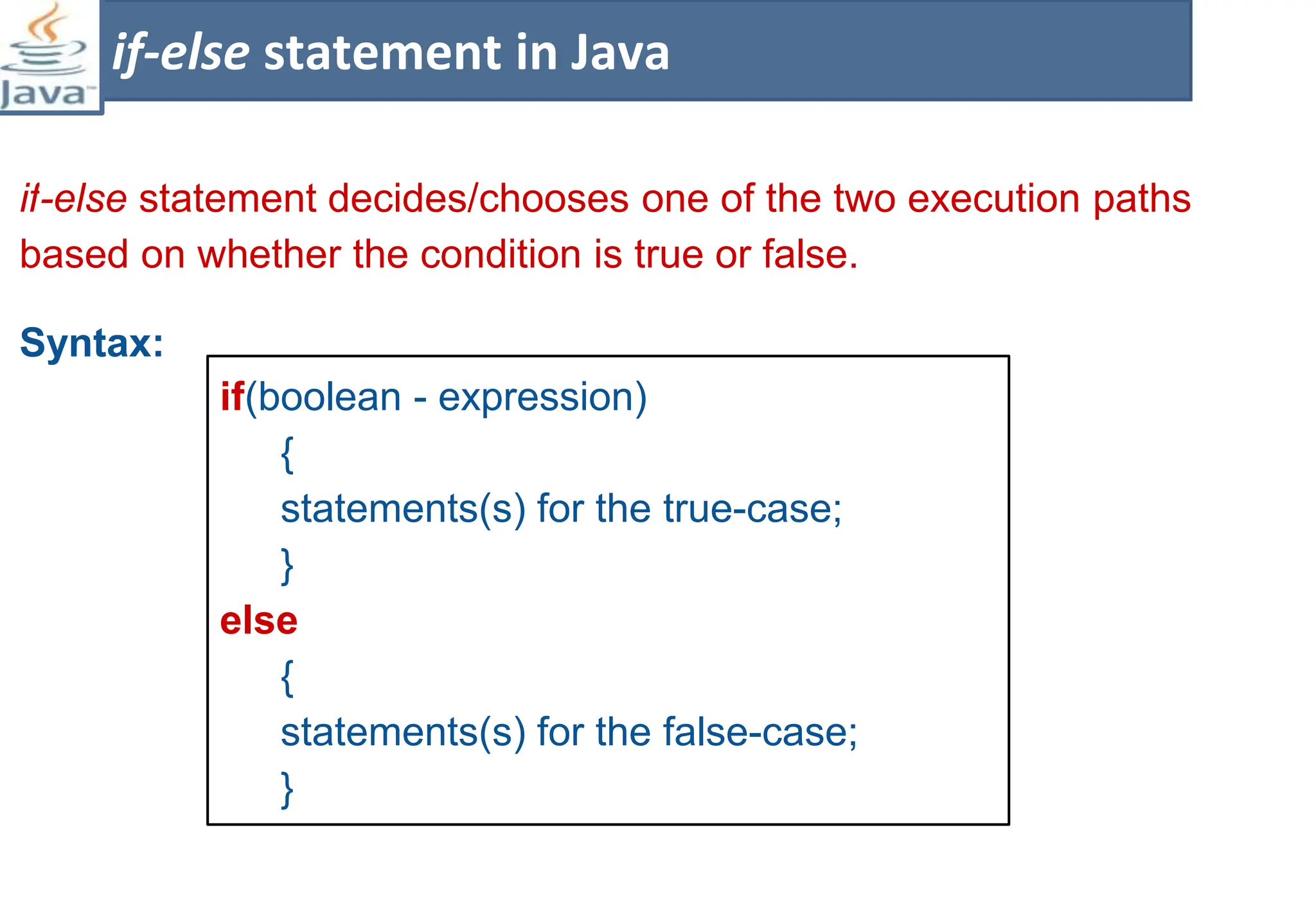
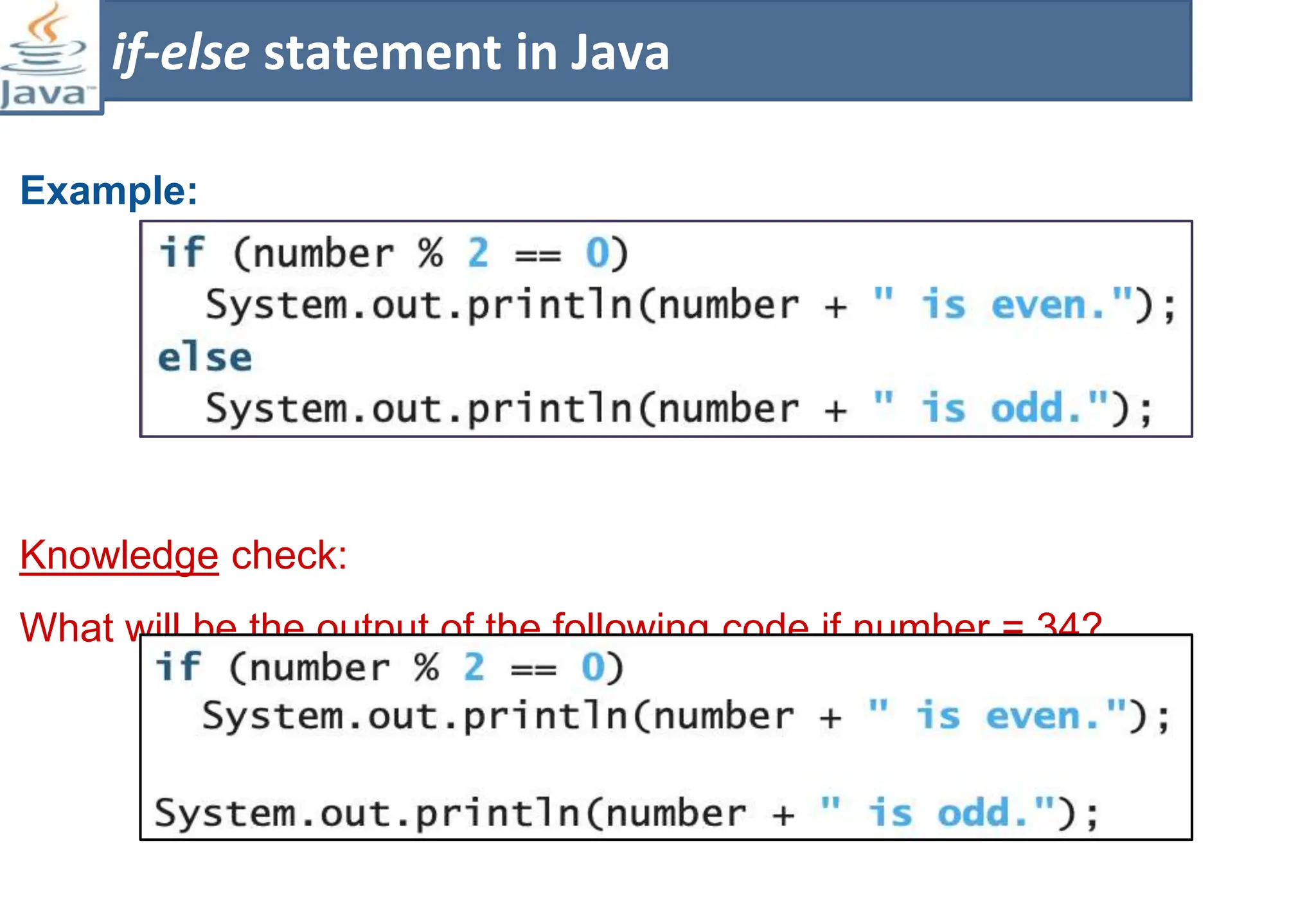
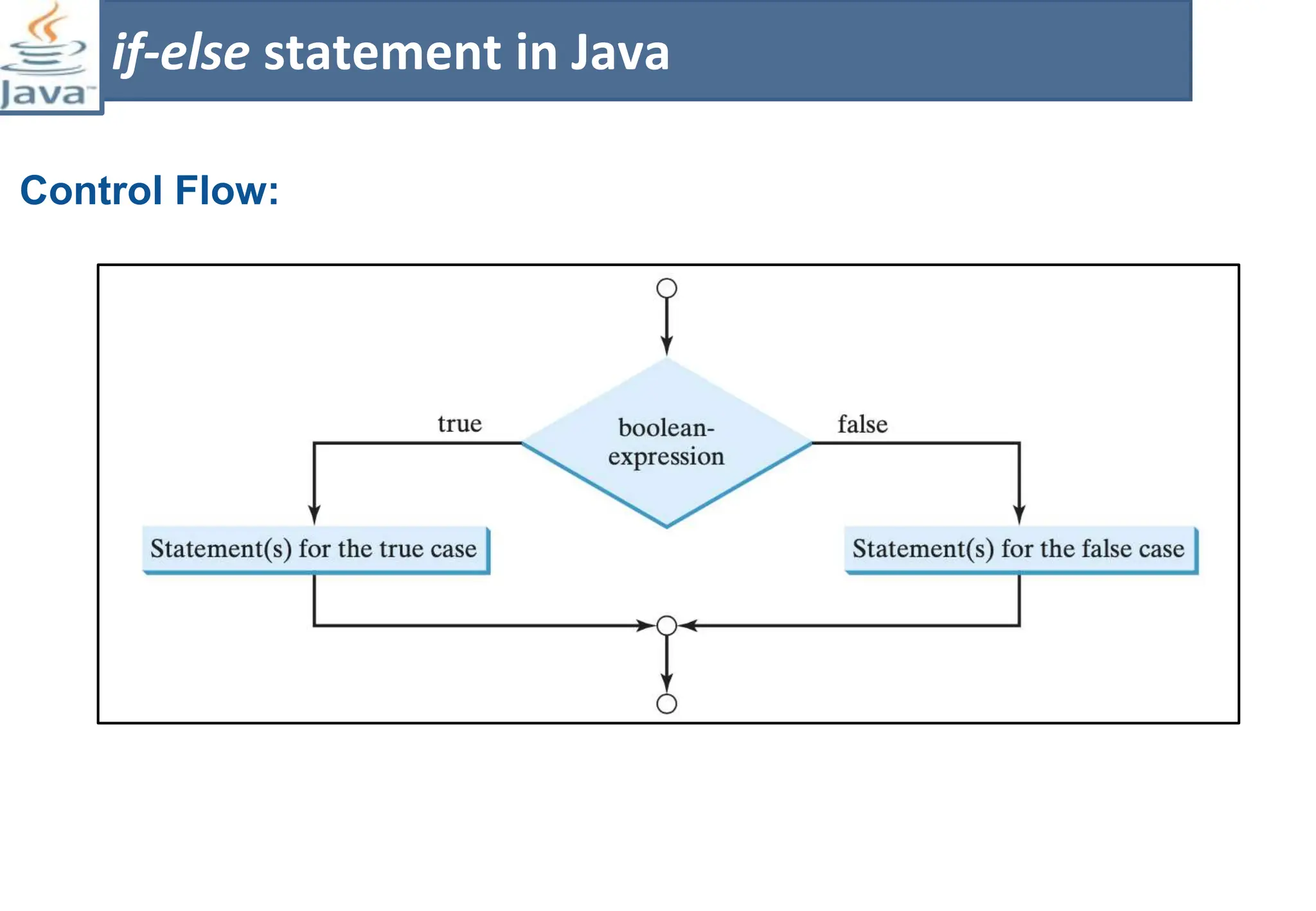
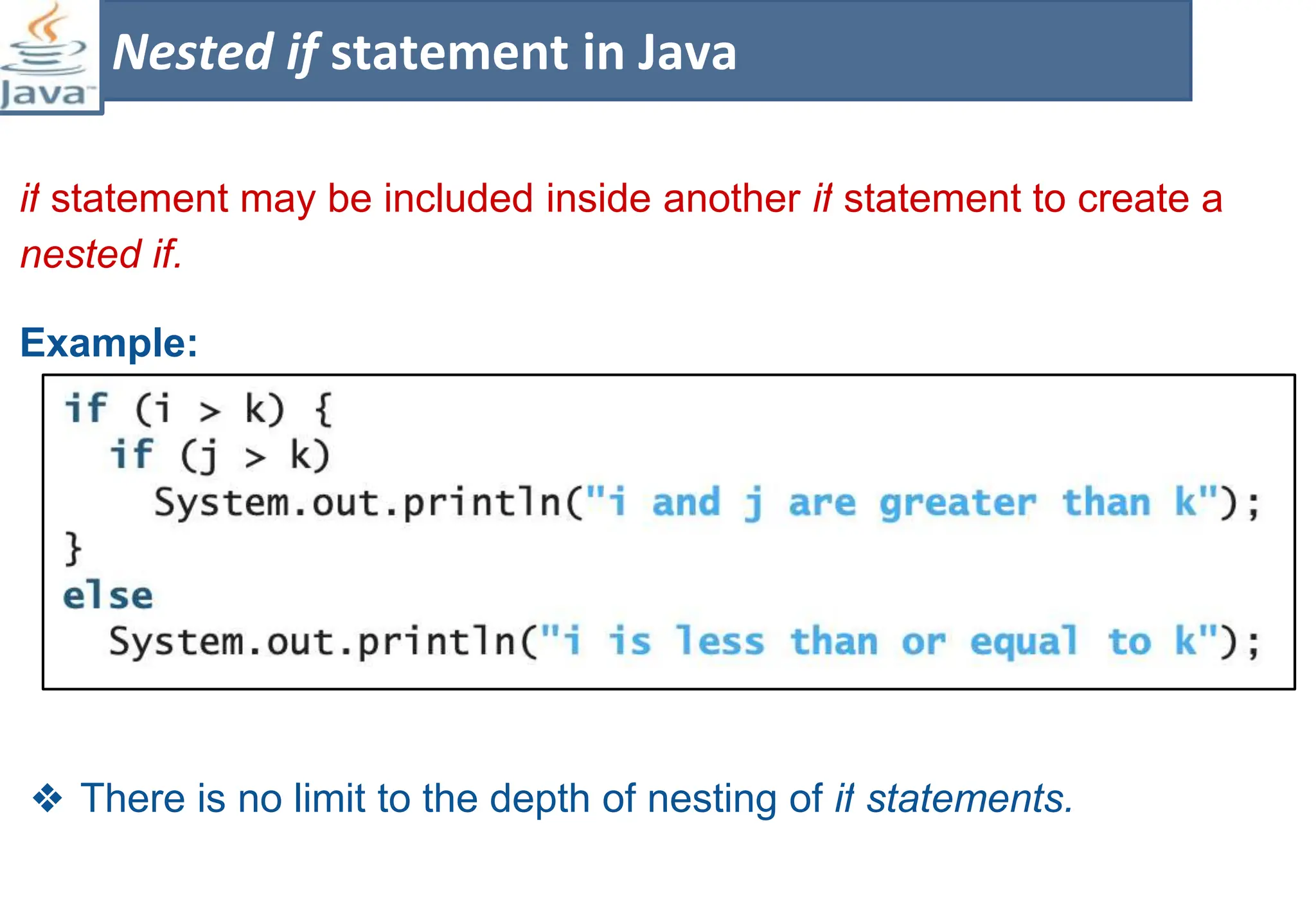
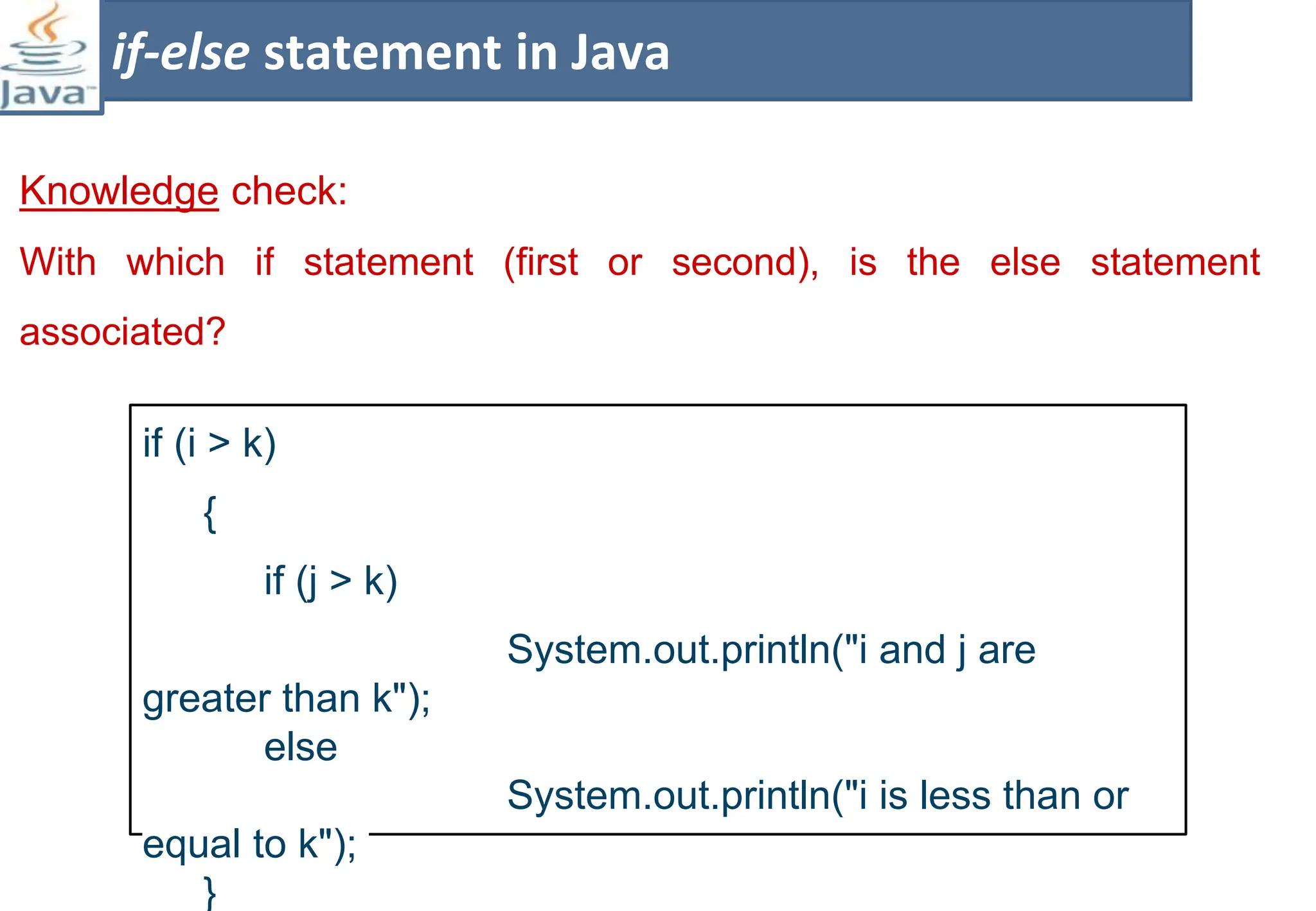
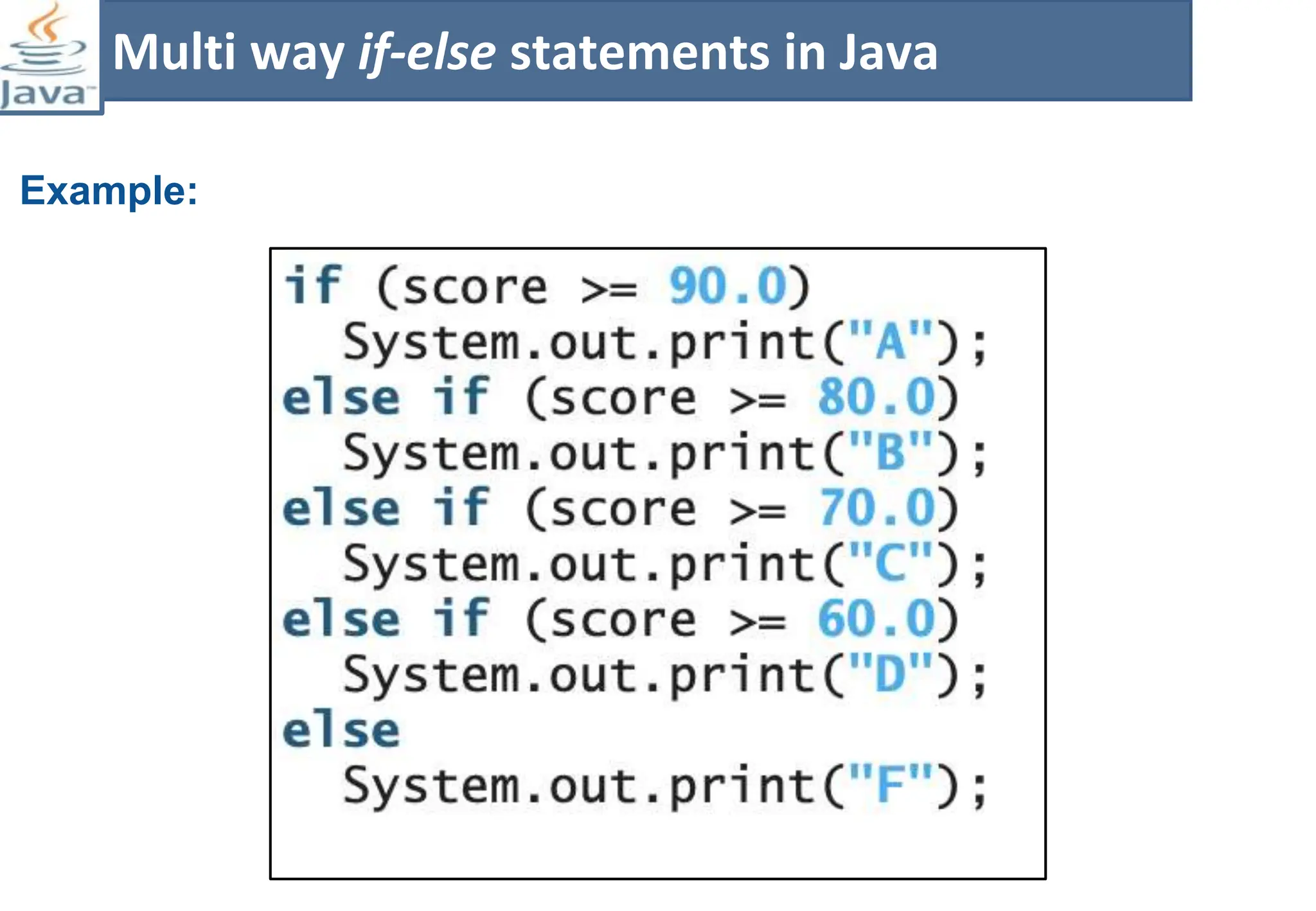
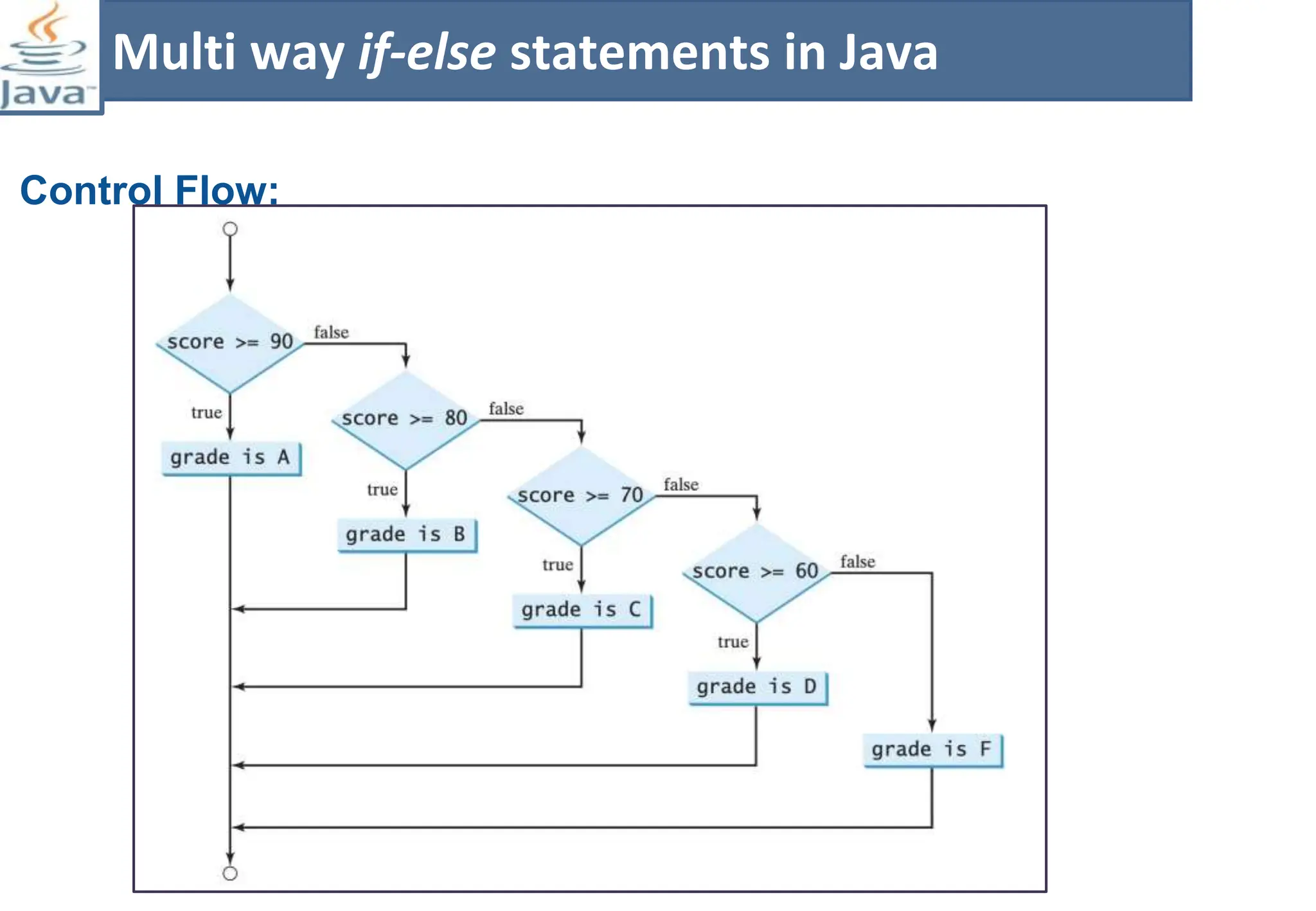
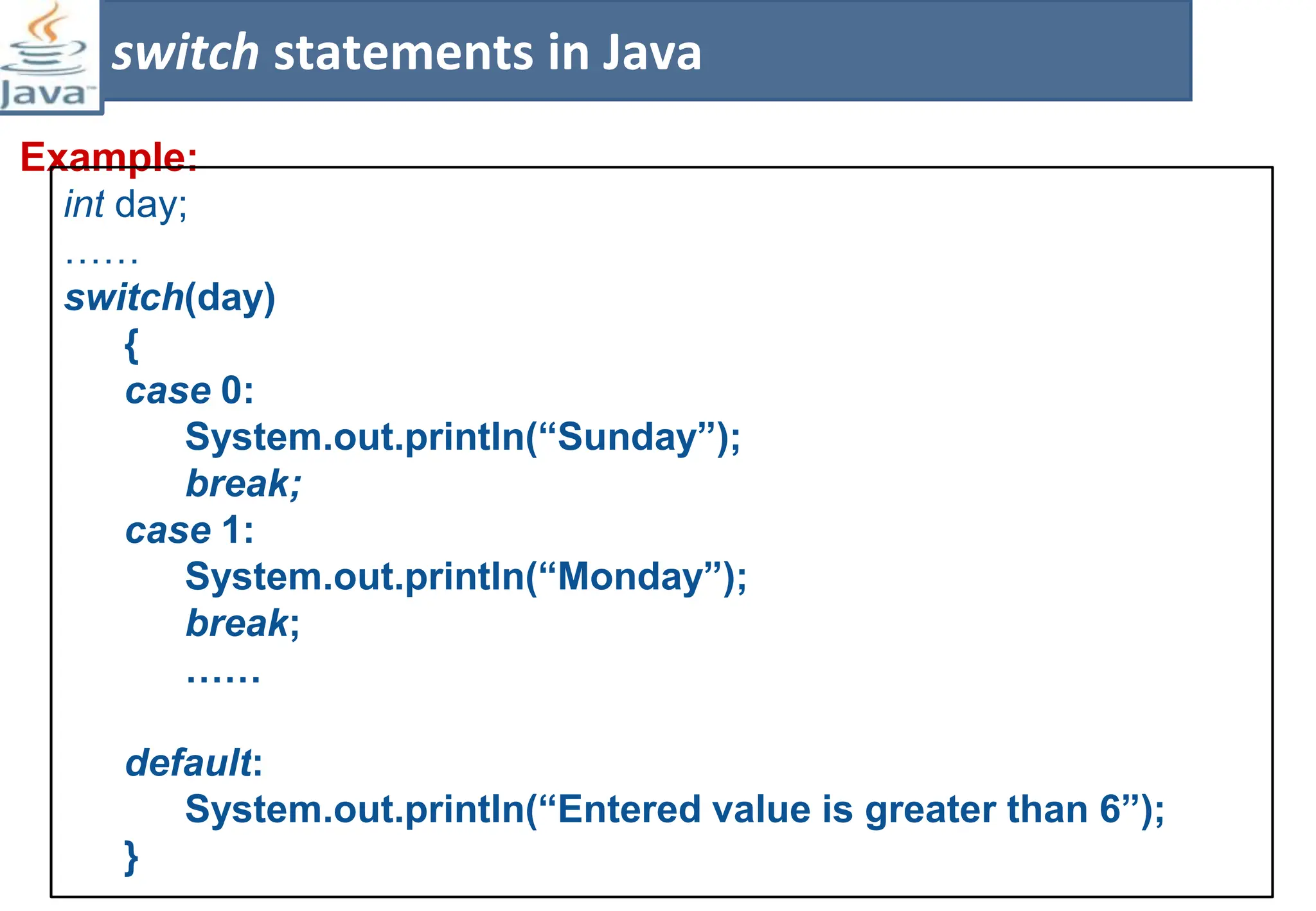
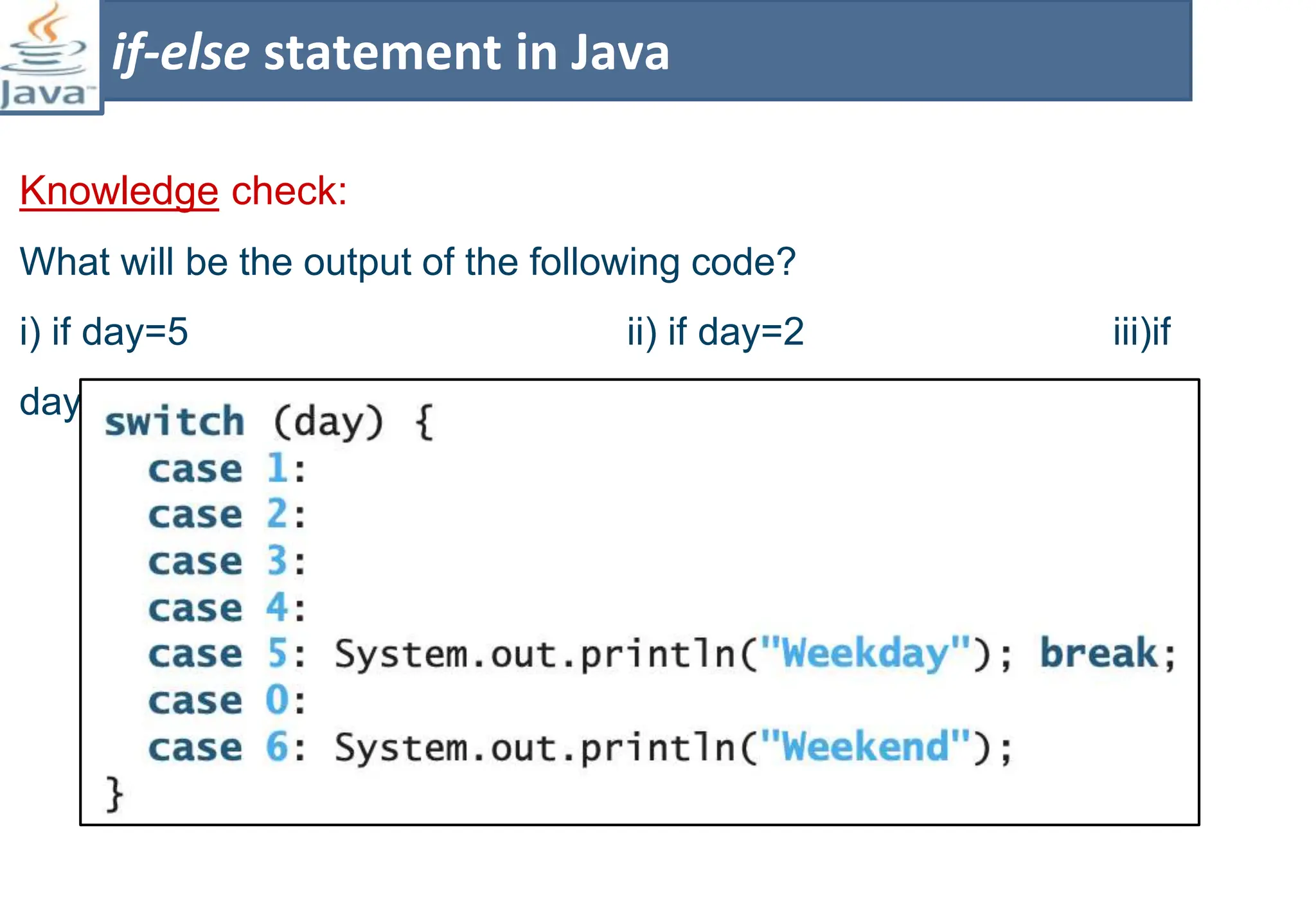
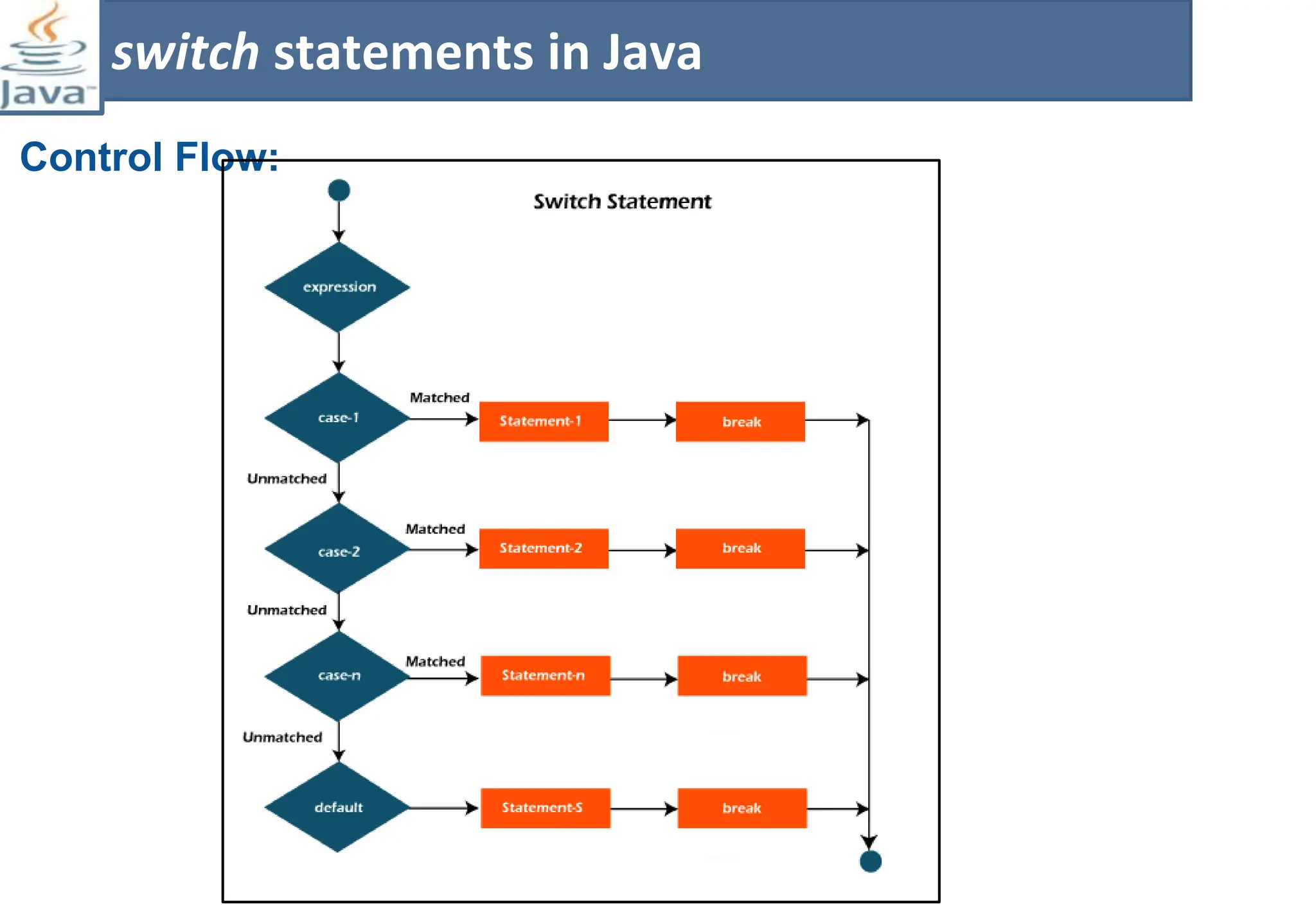
The document presents course material for Module 1 of Java Programming focusing on decision statements, including if statements, if-else branching, switch statements, and conditional operators. Key learning outcomes include understanding and applying various decision-making statements in Java for program logic. The content covers syntax and control flow for each statement type, along with examples and knowledge checks to reinforce learning.