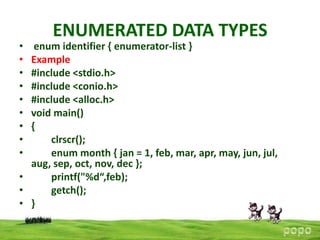
Enumerated types allow a set of named integer constants to be defined. An enumeration type declaration specifies the enumeration tag name and defines the enumerator constants. A variable of an enum type can only hold one of the defined enumerator constant values. Enumerations provide an alternative to #define with advantages like automatically generated values and normal scoping rules. Typedef allows custom type names to be defined as synonyms for existing types like int, float, and double without reserving new storage. Typedef names exist in the same namespace as other identifiers except for variably modified types which have block scope.