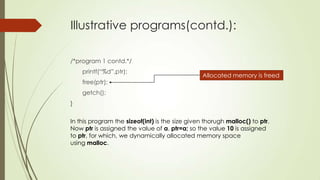
malloc() and calloc() are functions in C that allocate memory dynamically from the heap. malloc() allocates a block of memory of a specified size, while calloc() allocates memory and initializes it to zero. Two sample programs are provided to illustrate the use of malloc() and calloc(): one program allocates memory for an integer using malloc() and assigns a value to it, while the other allocates an array of integers using calloc() and prints the values. Both programs free the allocated memory after use.





![Ilustrative programs(contd.):
/*Program 2: Illustration of calloc()*/
#include<stdio.h>
calloc() comes under it
#include<conio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
void main()
{
int *ptr,a[6]={1,2,3,4,5,6};
int i;
ptr=(int*)calloc(a[6]*sizeof(int),2);
Allocating memory for ptr](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mallocandcallocinc-140206191045-phpapp02/85/Malloc-and-calloc-in-c-7-320.jpg)
![Illustrative programs(contd.):
/*program 2 contd.*/
for(i=0;i<7;i++)
{
printf(“n%d”,*ptr+a[i]);
}
free(ptr);
getch();
}
Allocated memory is freed](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mallocandcallocinc-140206191045-phpapp02/85/Malloc-and-calloc-in-c-8-320.jpg)
![Illustrative programs(contd.):
In program 2 6 blocks of memory is allocated using calloc() with each block
having 2 bytes of space. Now variable i is used in for to cycle the loop 6
times on incremental mode. On each cycle the data in allocated memory
in ptr is printed using *ptr+a[i].
Output of program 2:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mallocandcallocinc-140206191045-phpapp02/85/Malloc-and-calloc-in-c-9-320.jpg)