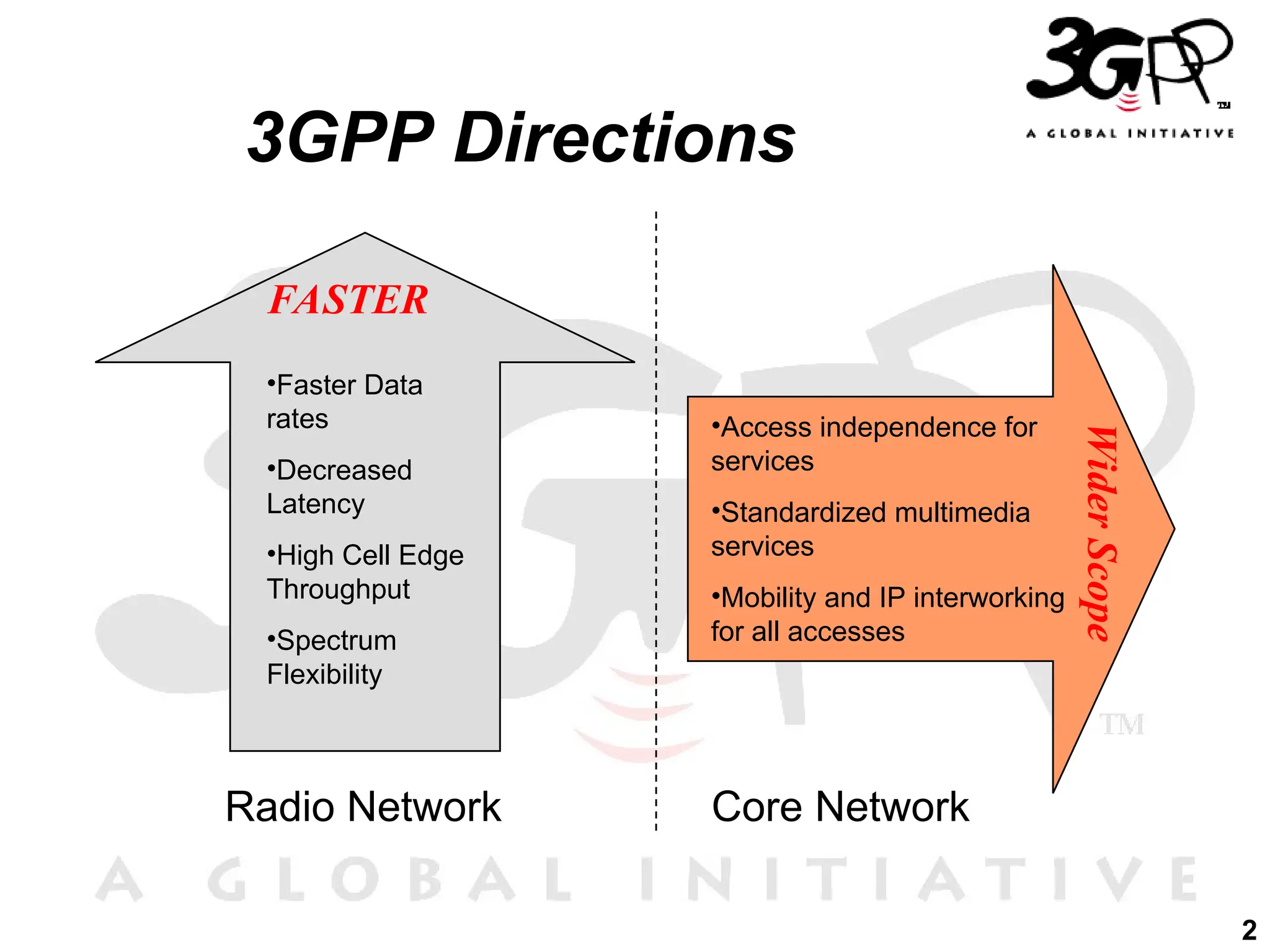
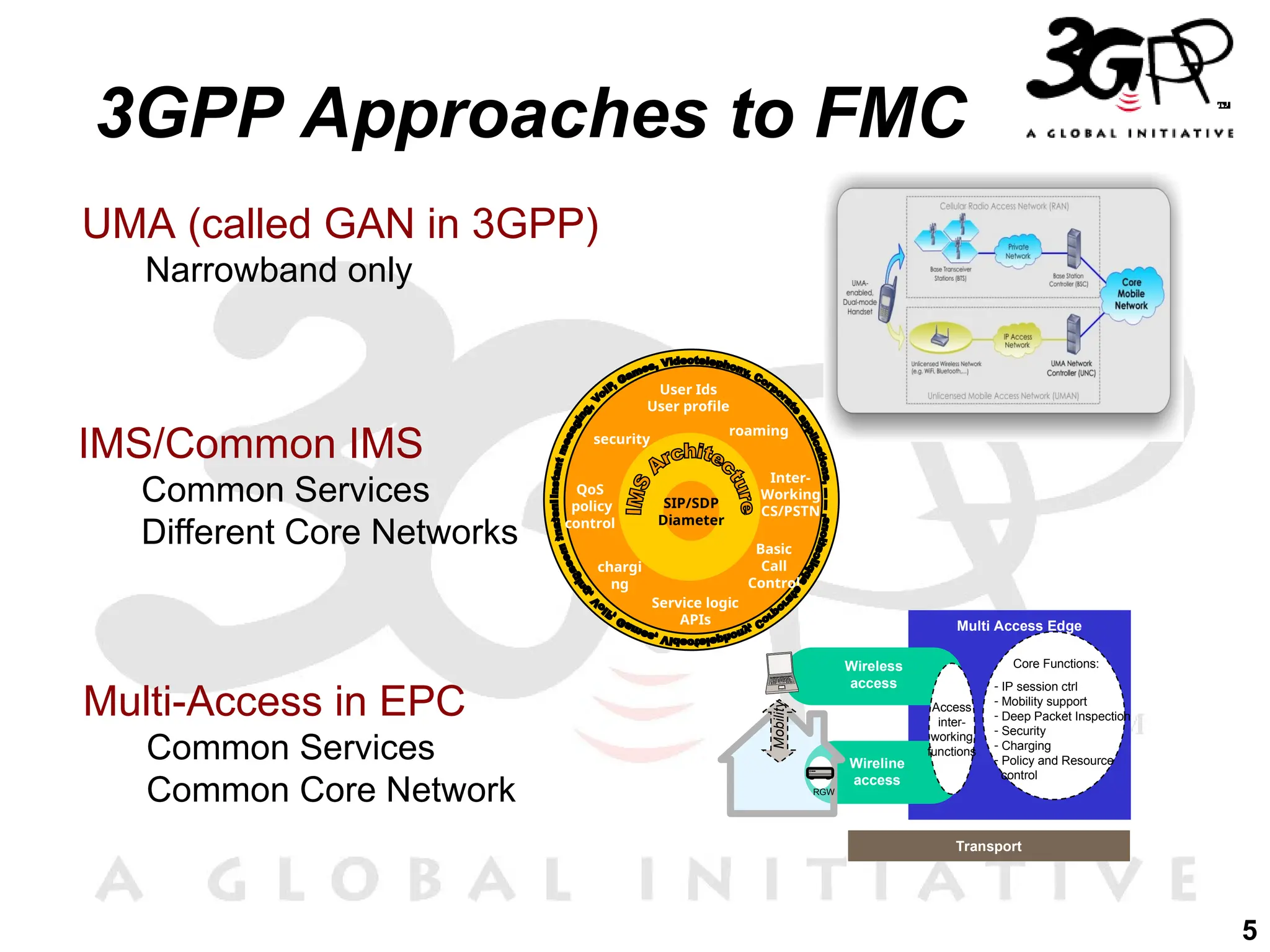
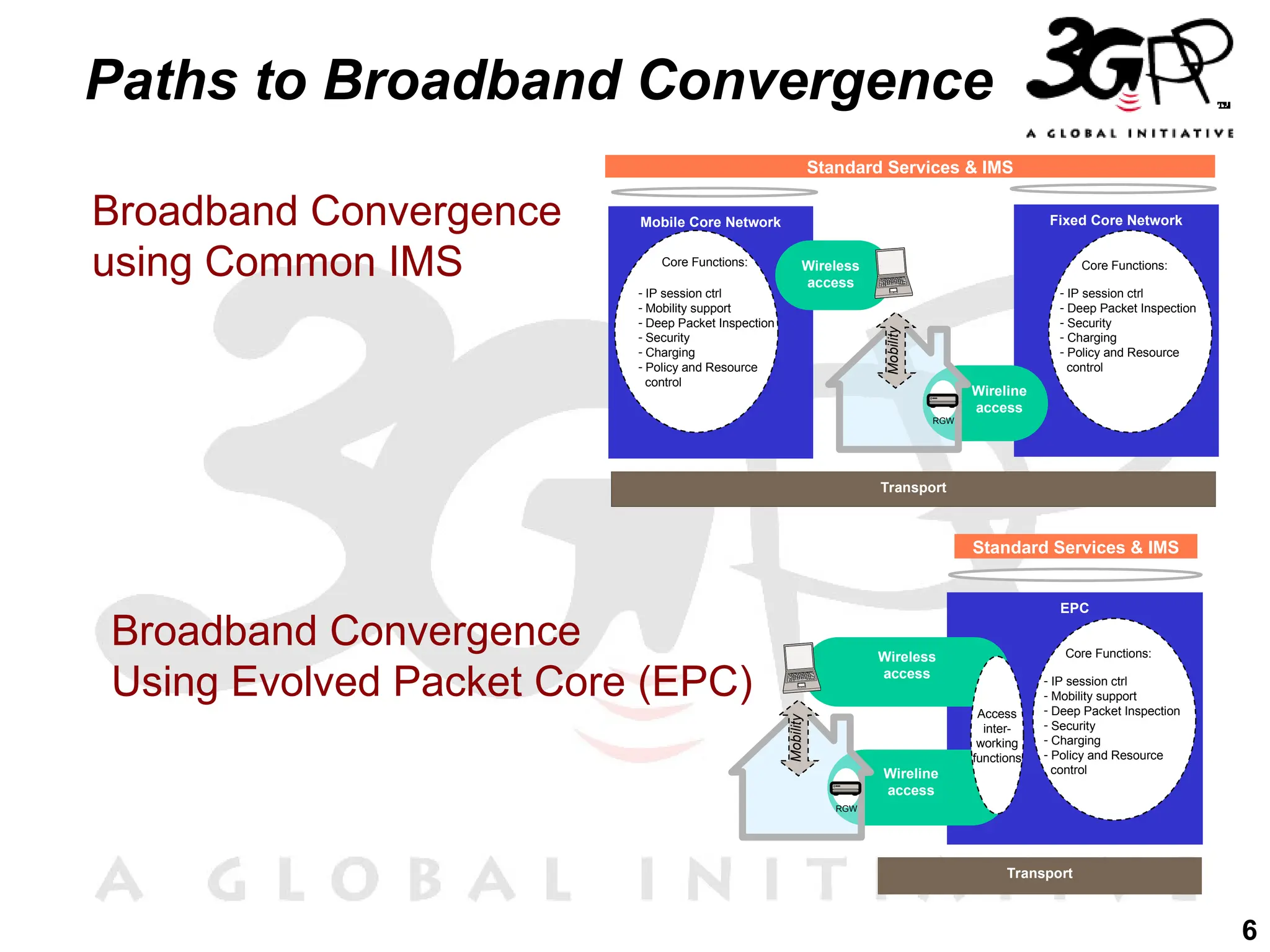
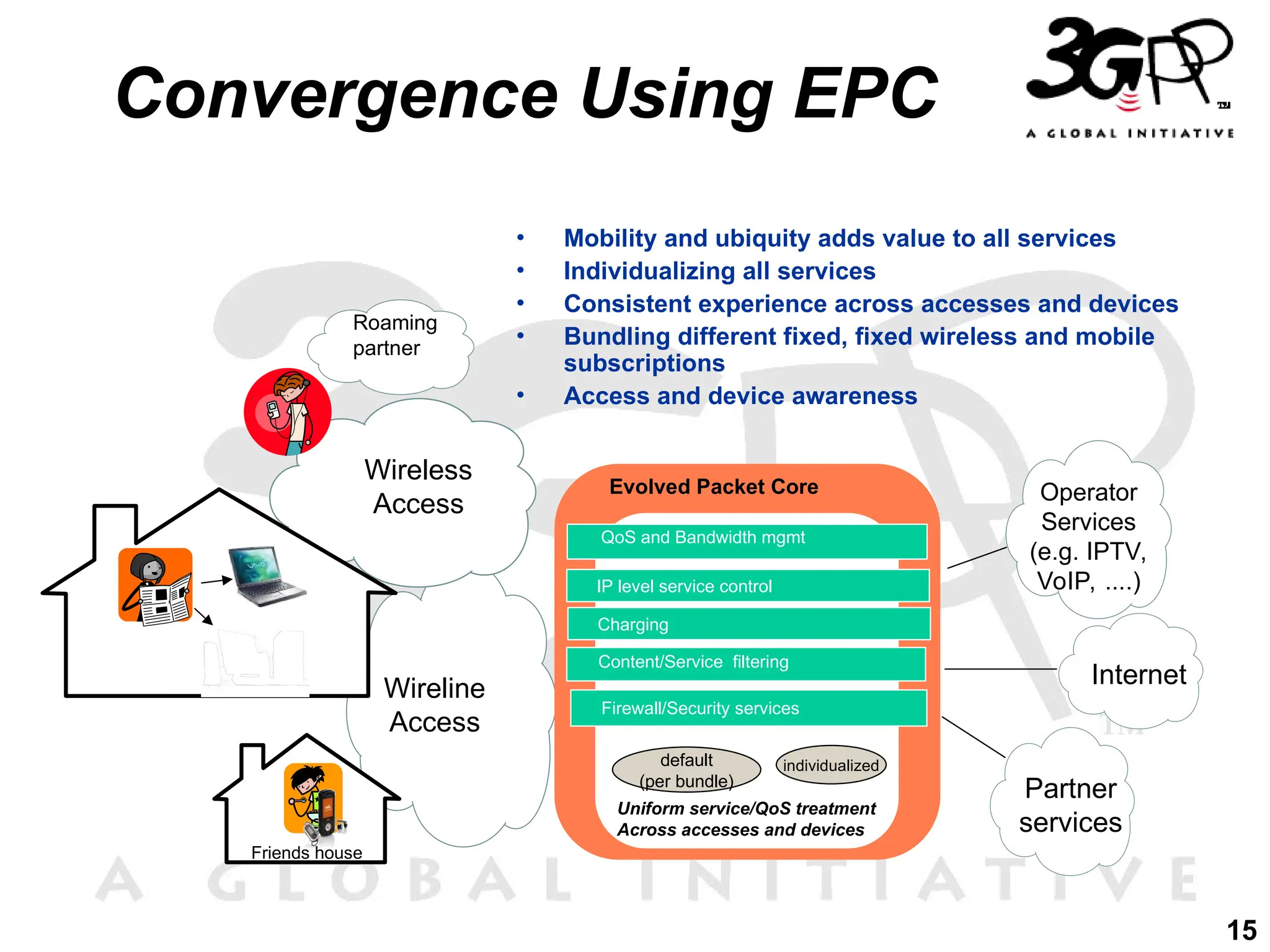
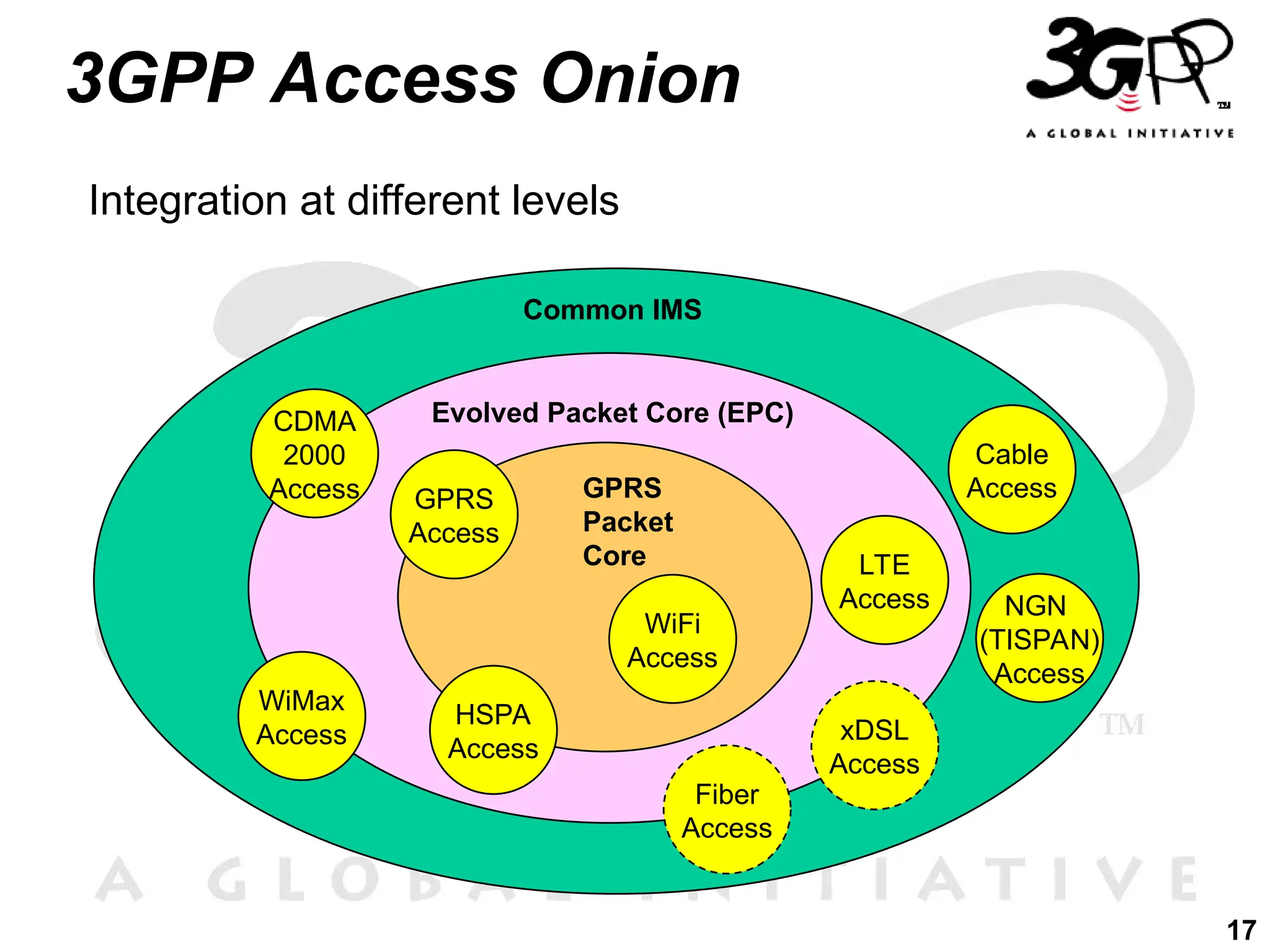
The document discusses 3GPP's direction towards broadband convergence and Fixed Mobile Convergence (FMC), focusing on high-speed data rates, low latency, and the integration of diverse access technologies. It outlines the roles of the IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) and the Evolved Packet Core (EPC) in facilitating multimedia services and mobility across fixed and mobile networks. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of common service platforms and the flexibility of access for users as key components of future network evolution.