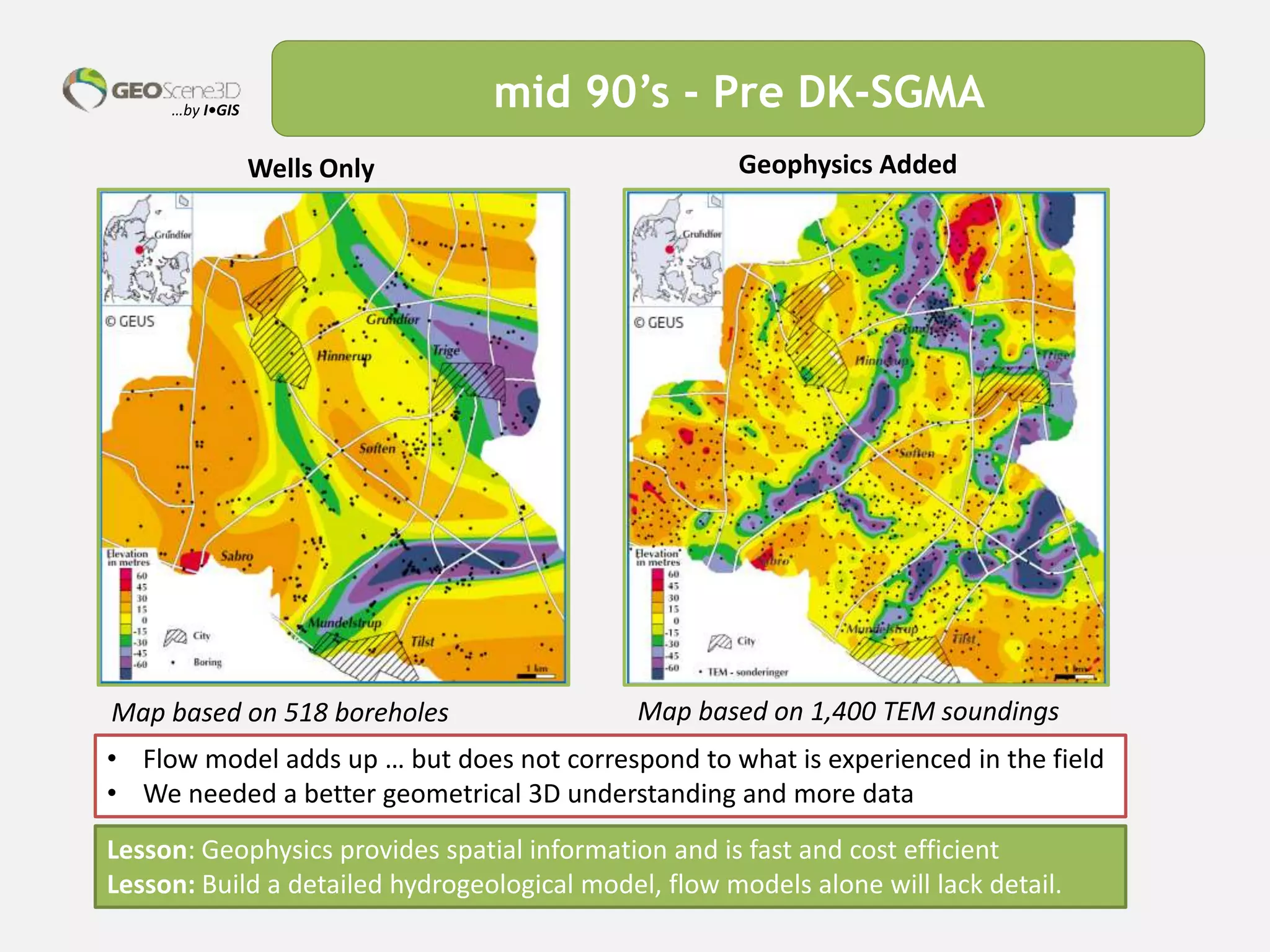
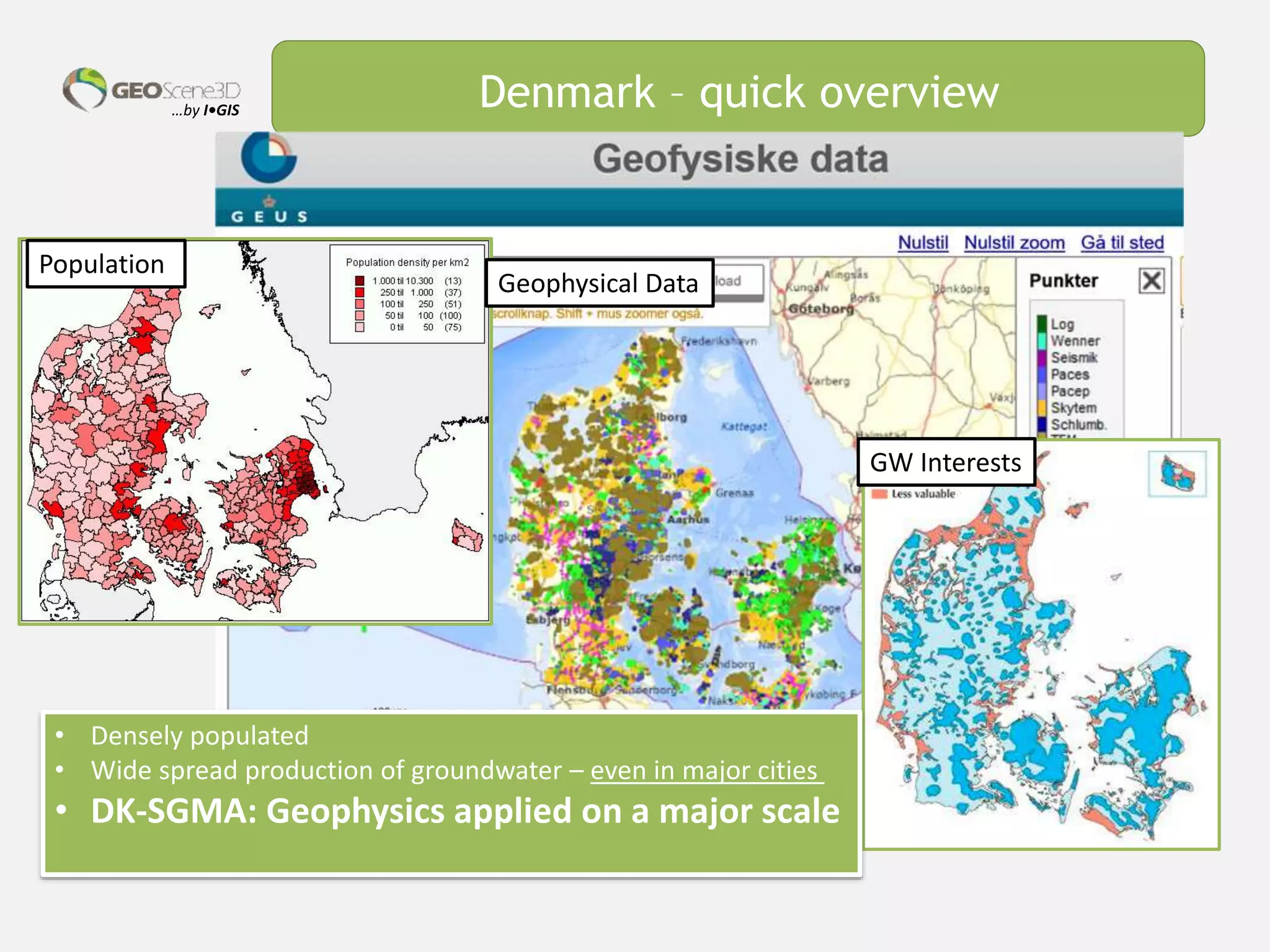
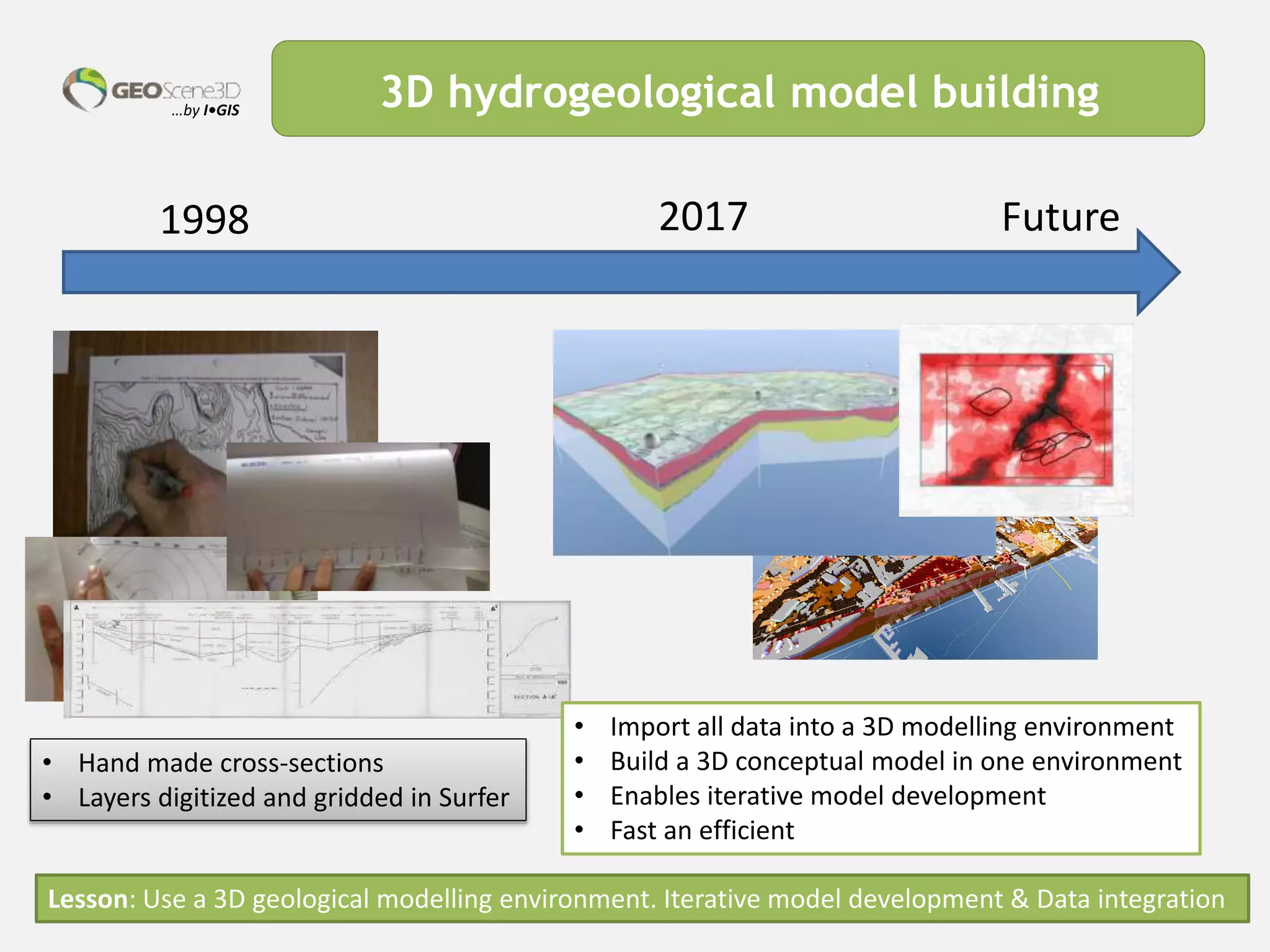
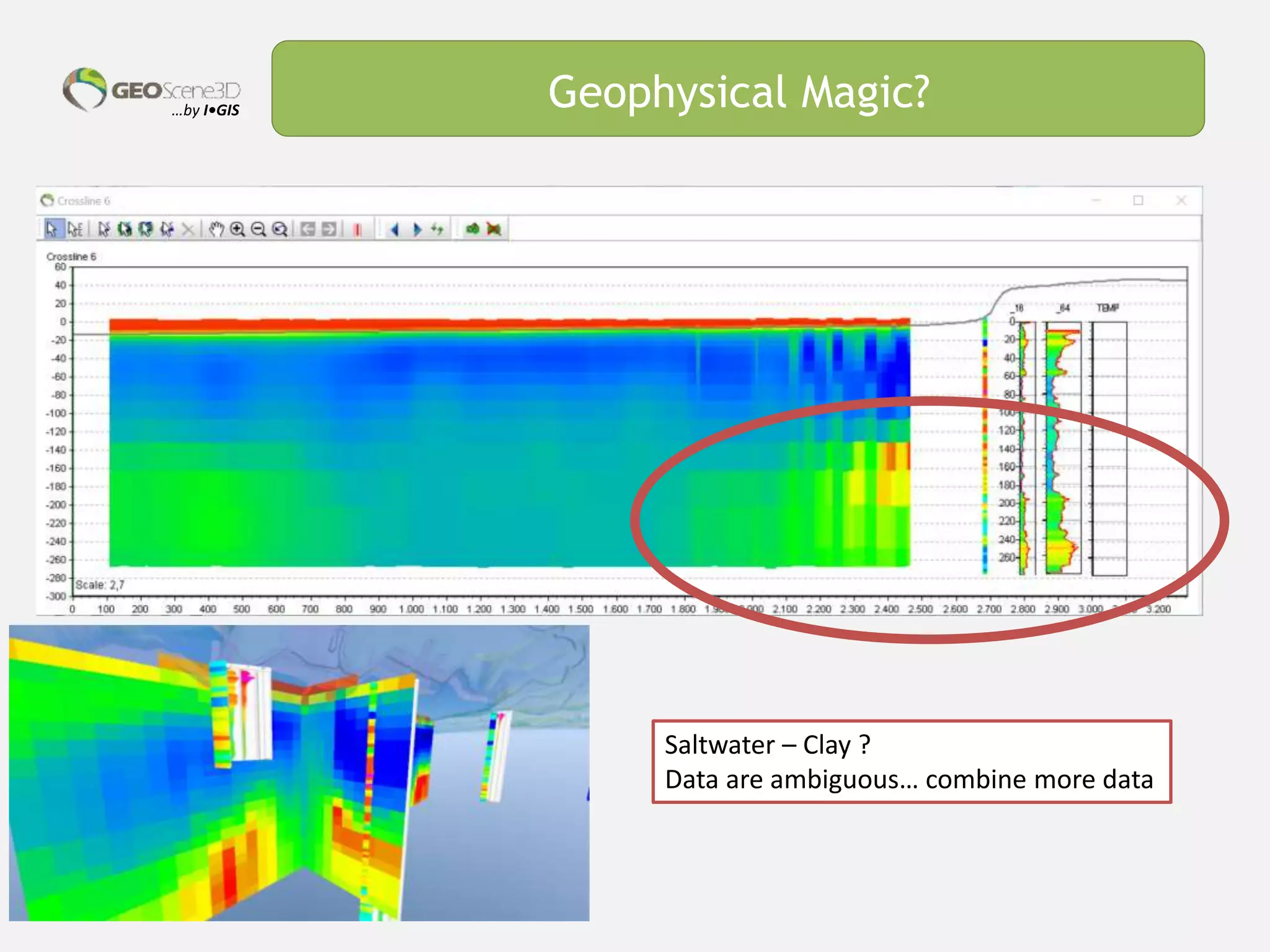
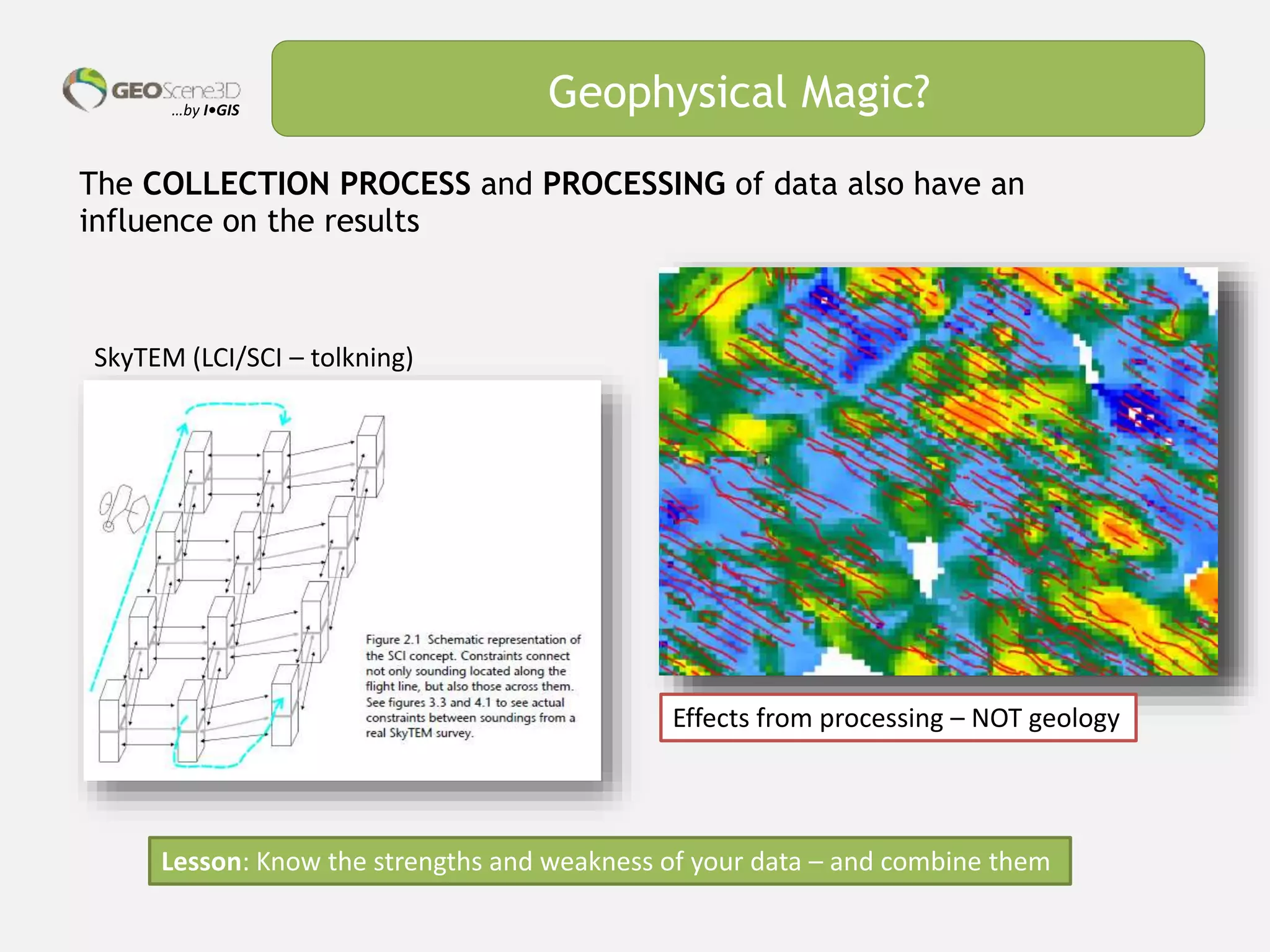
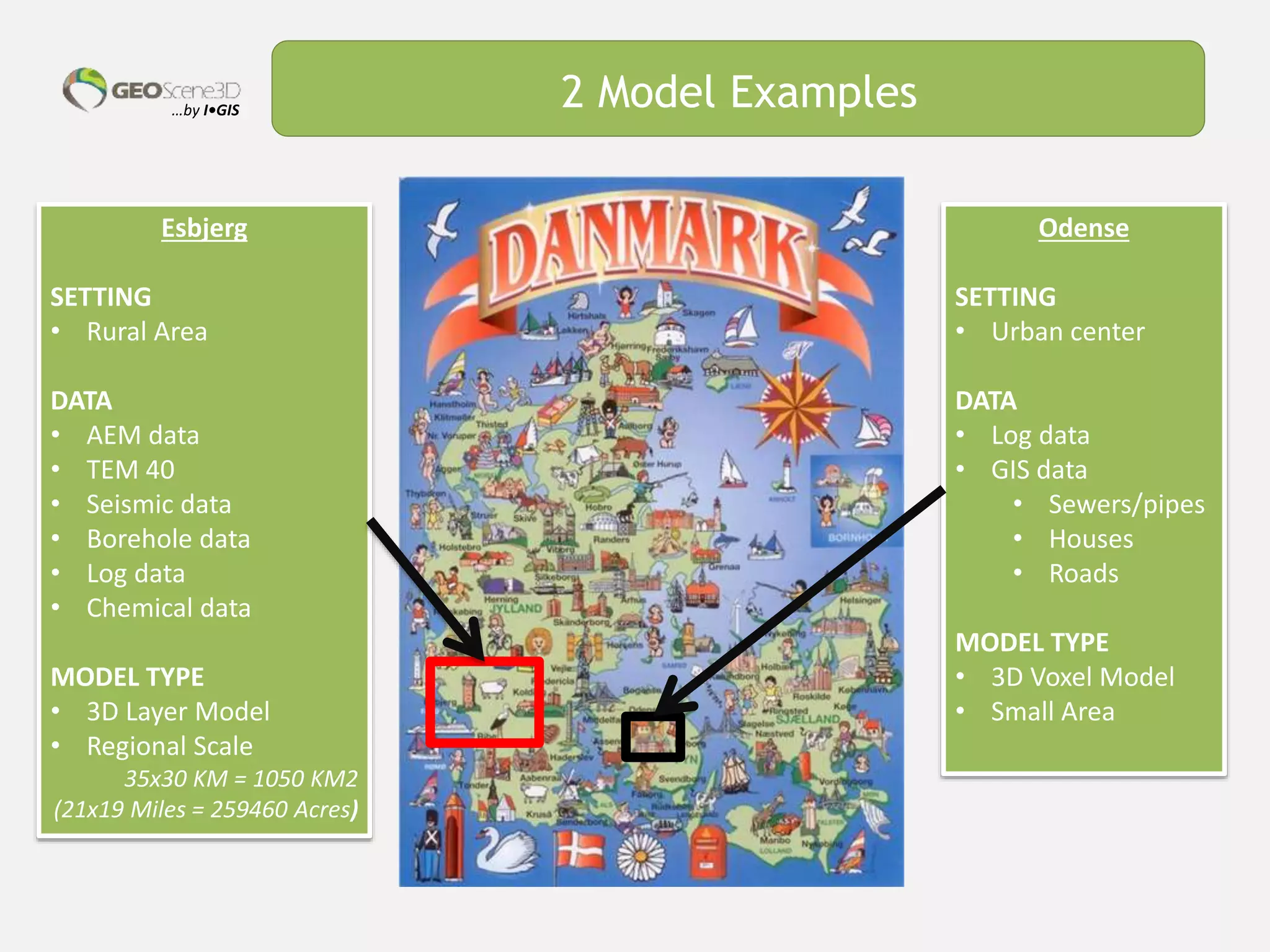
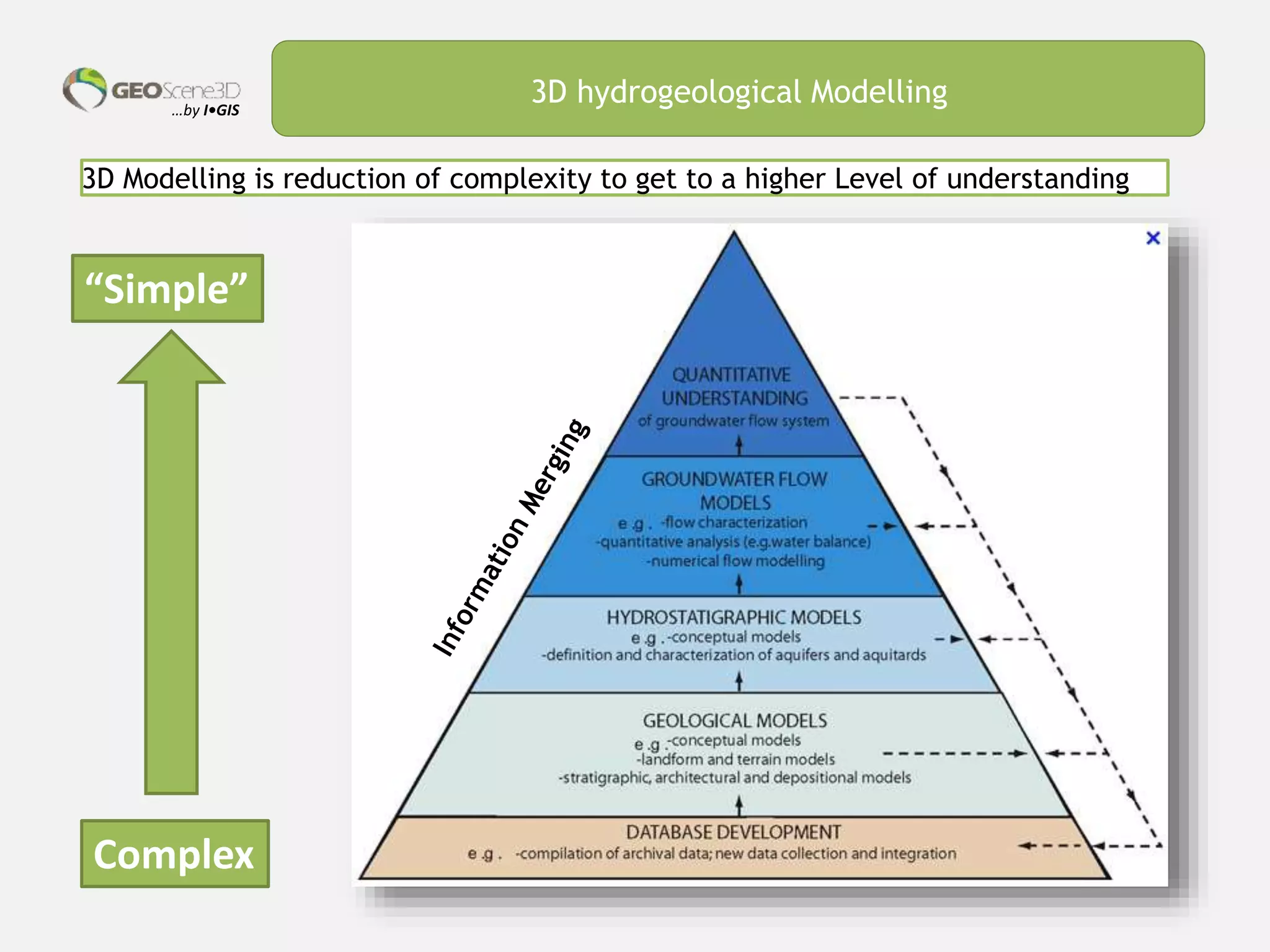
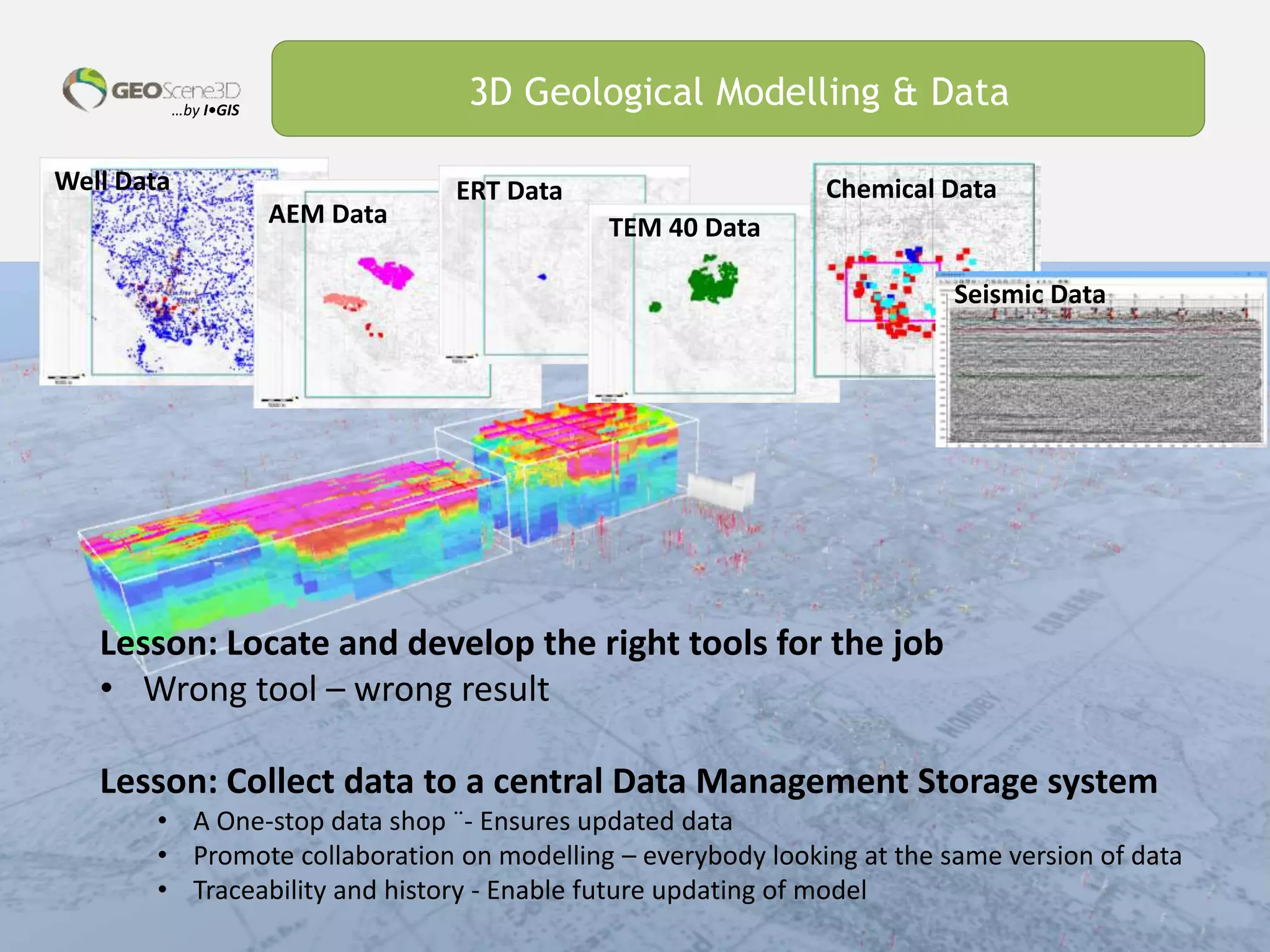
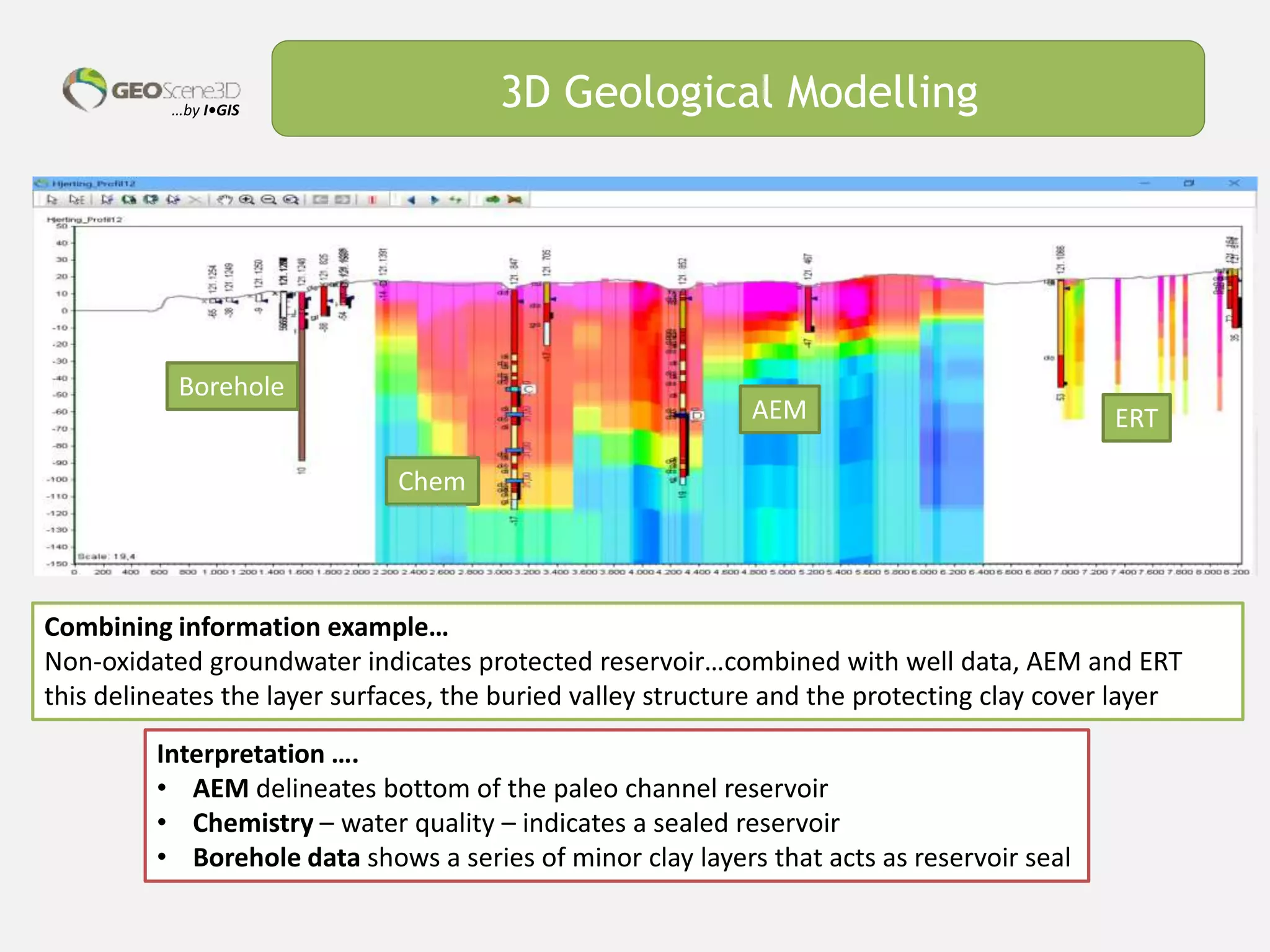
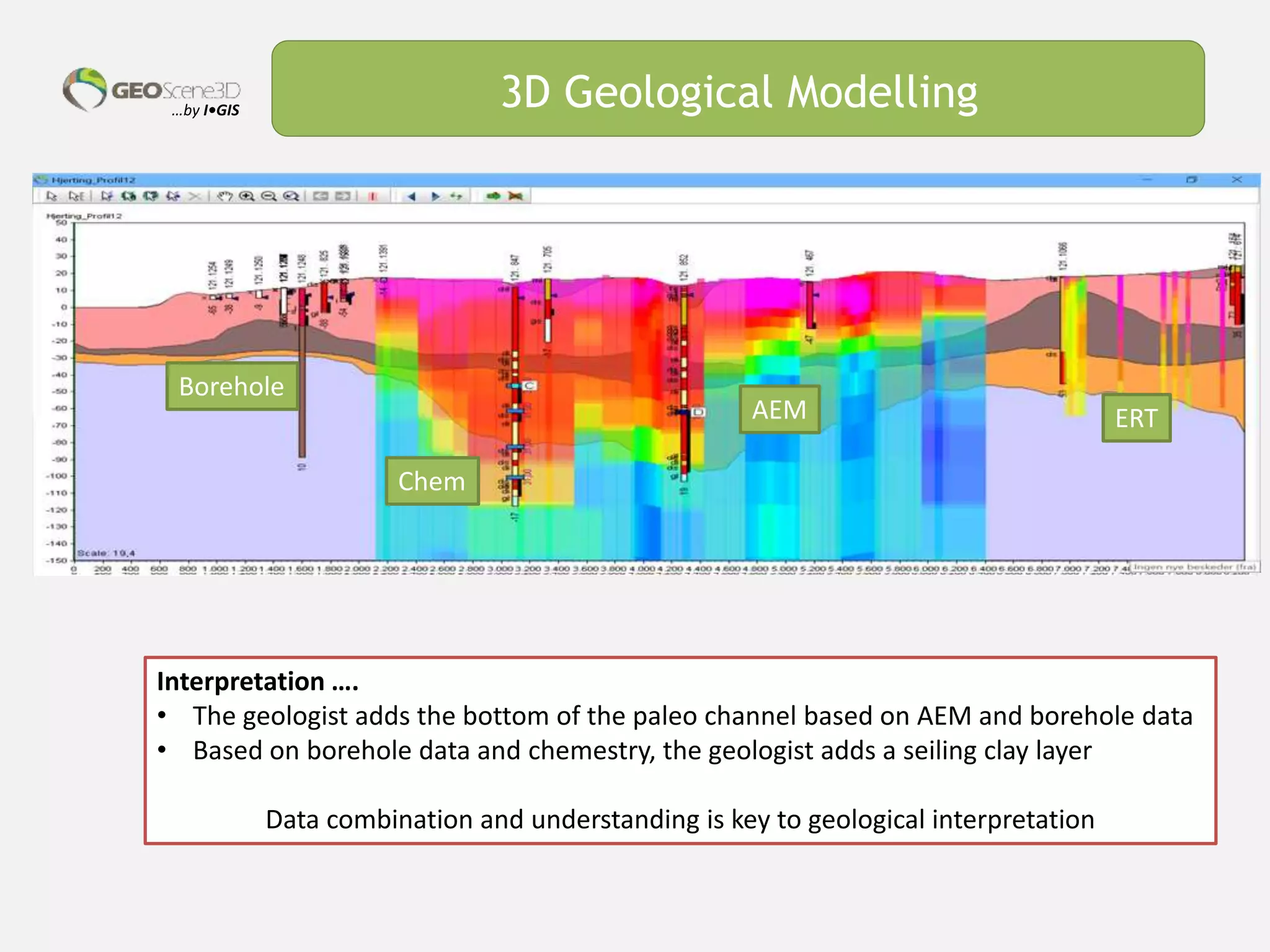
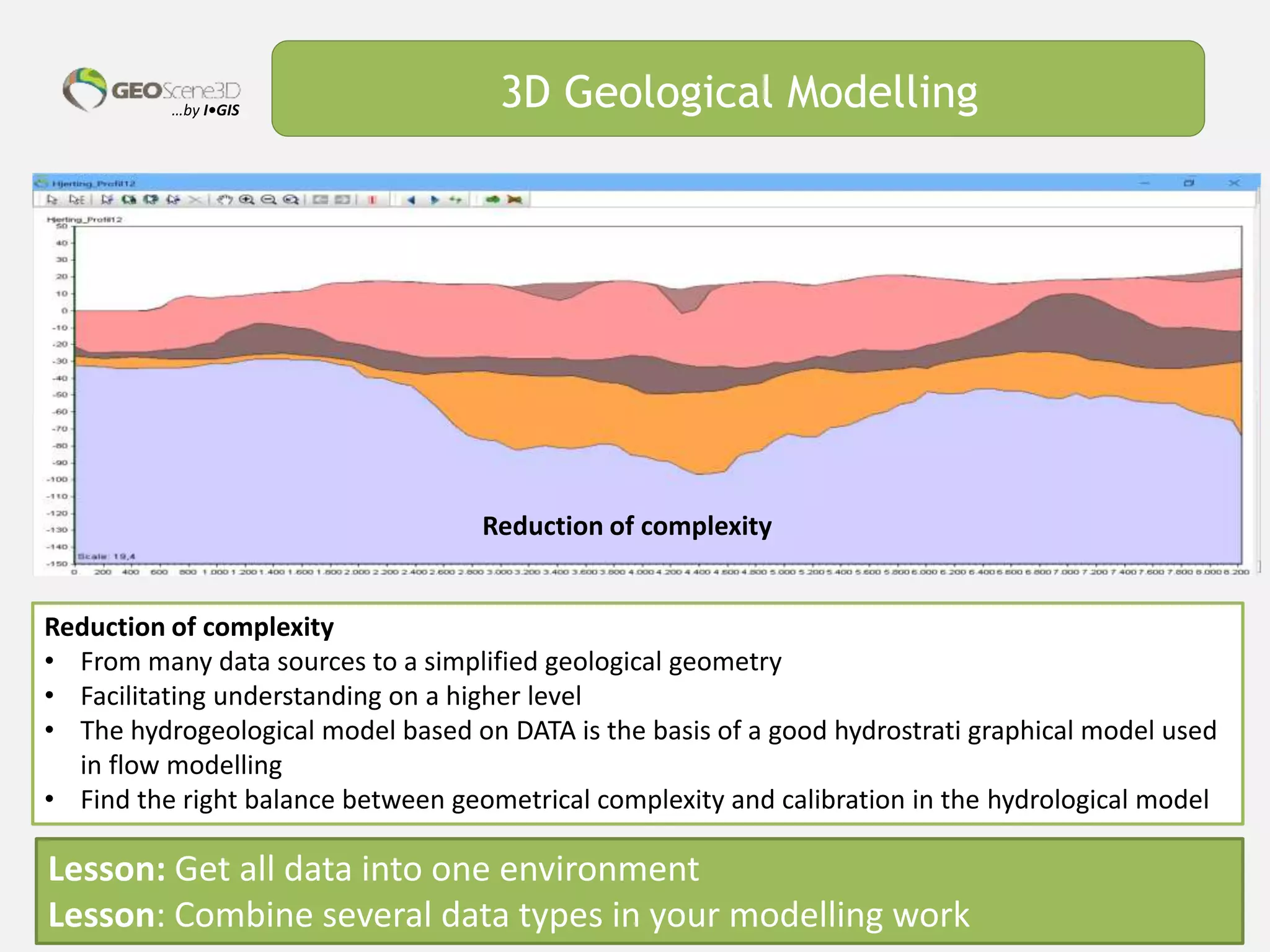
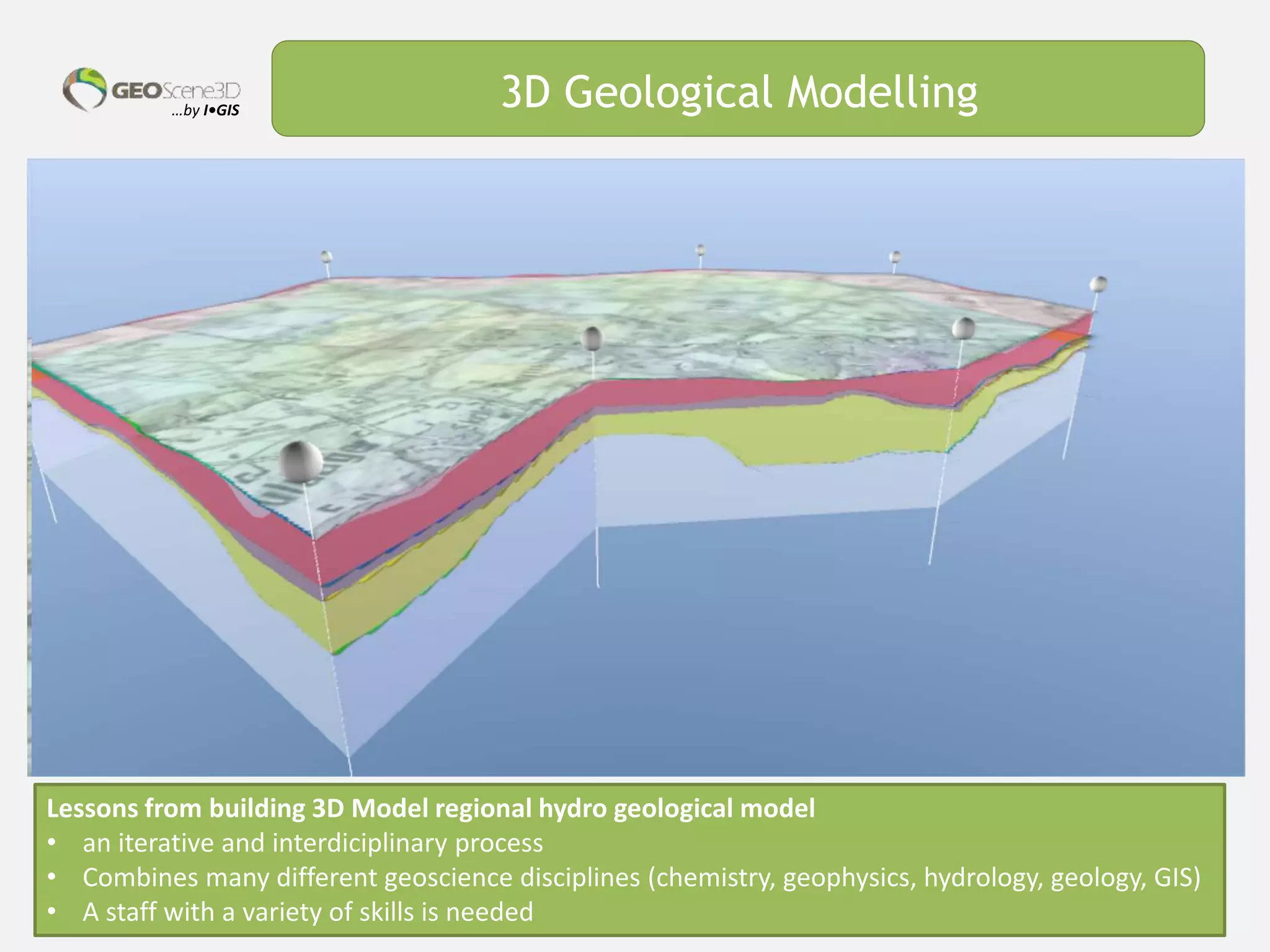
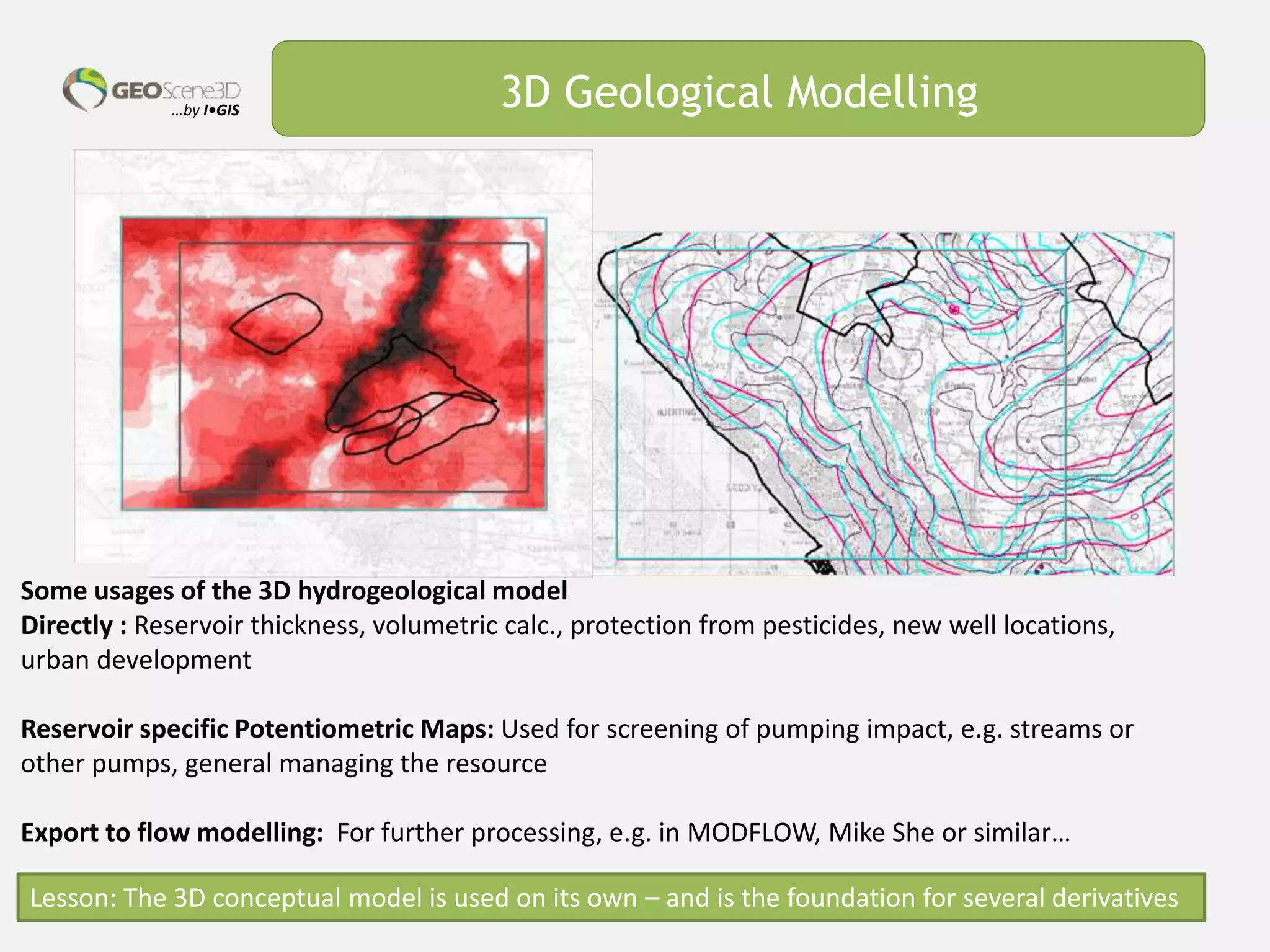
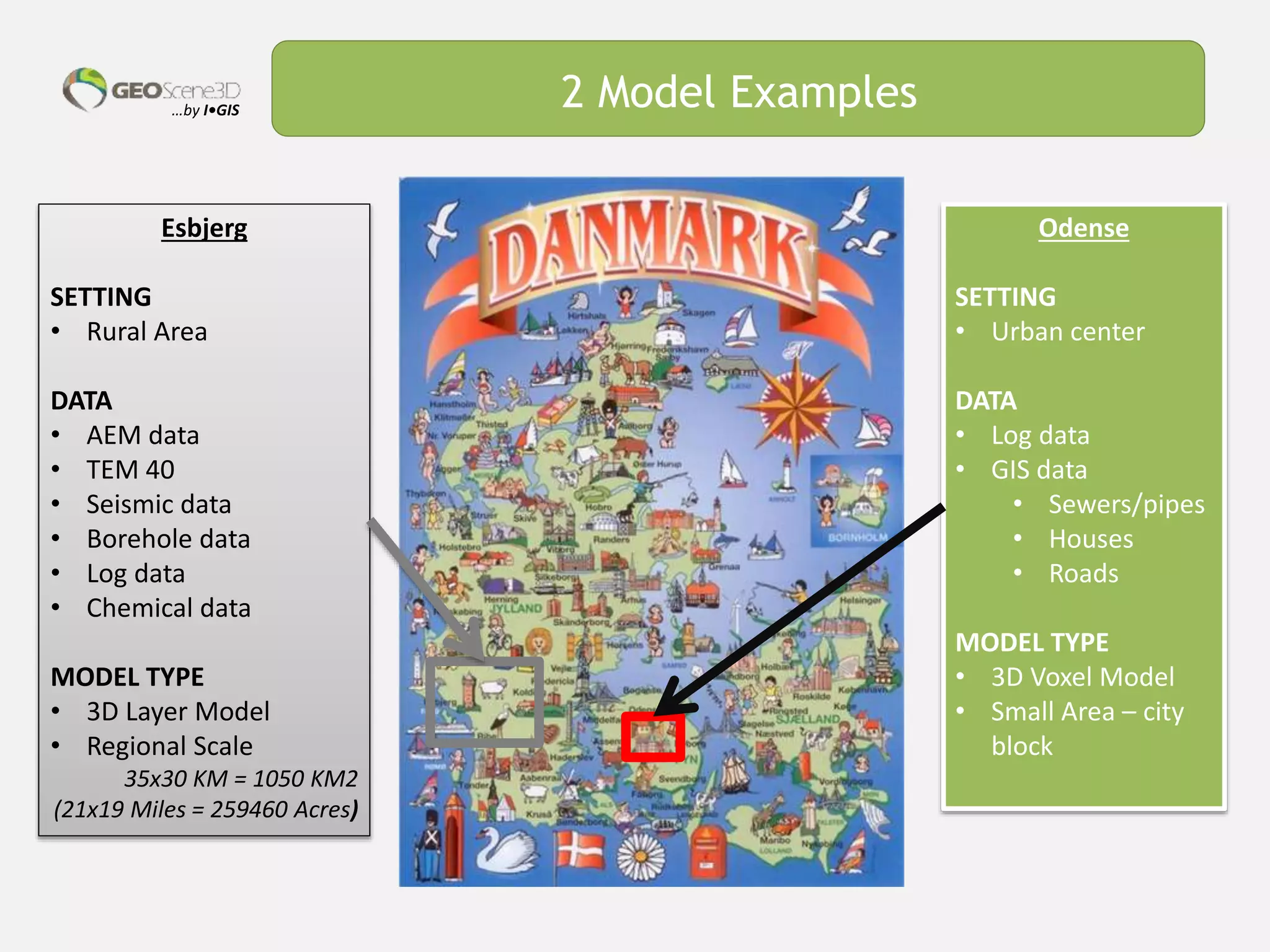
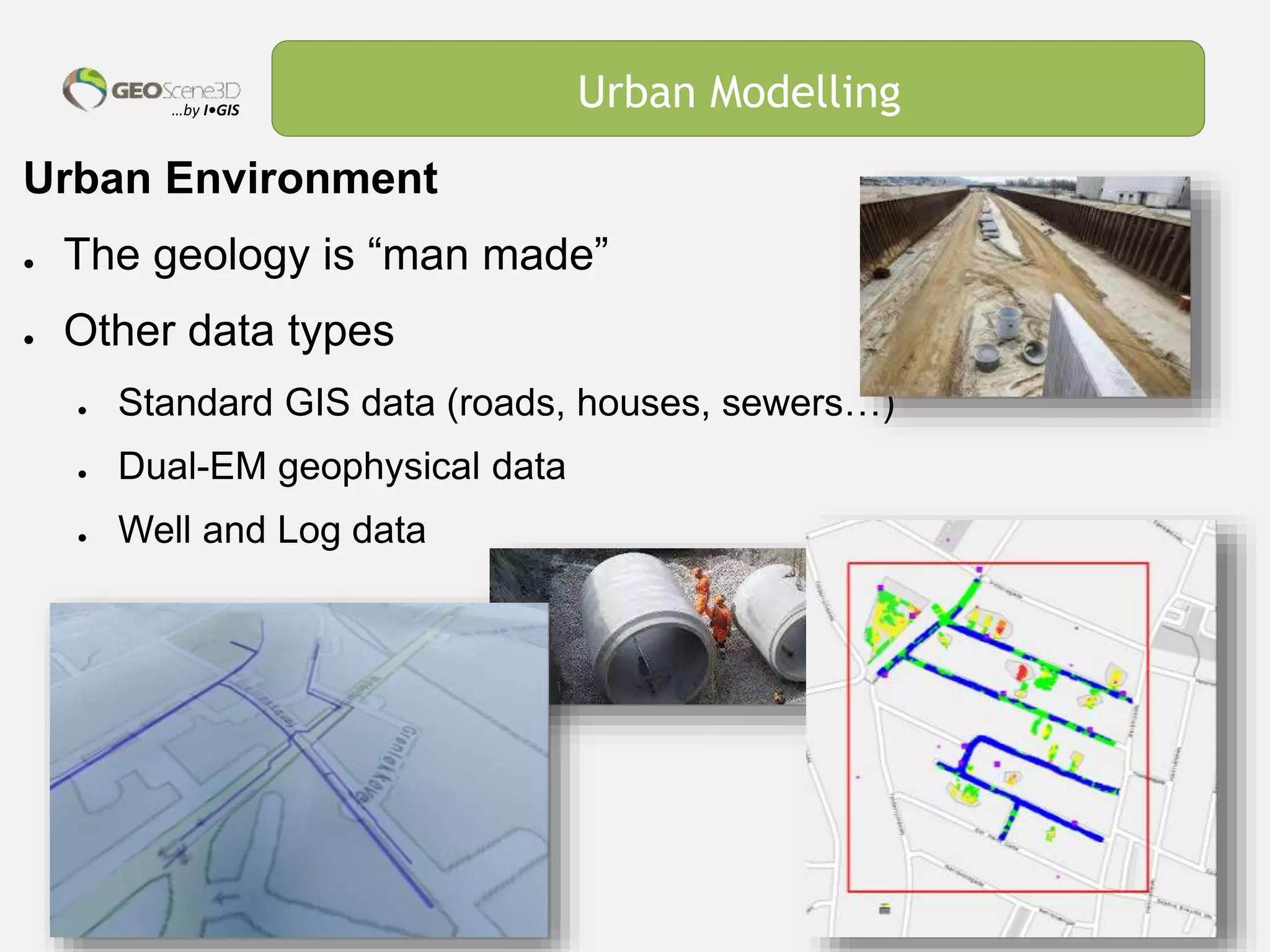
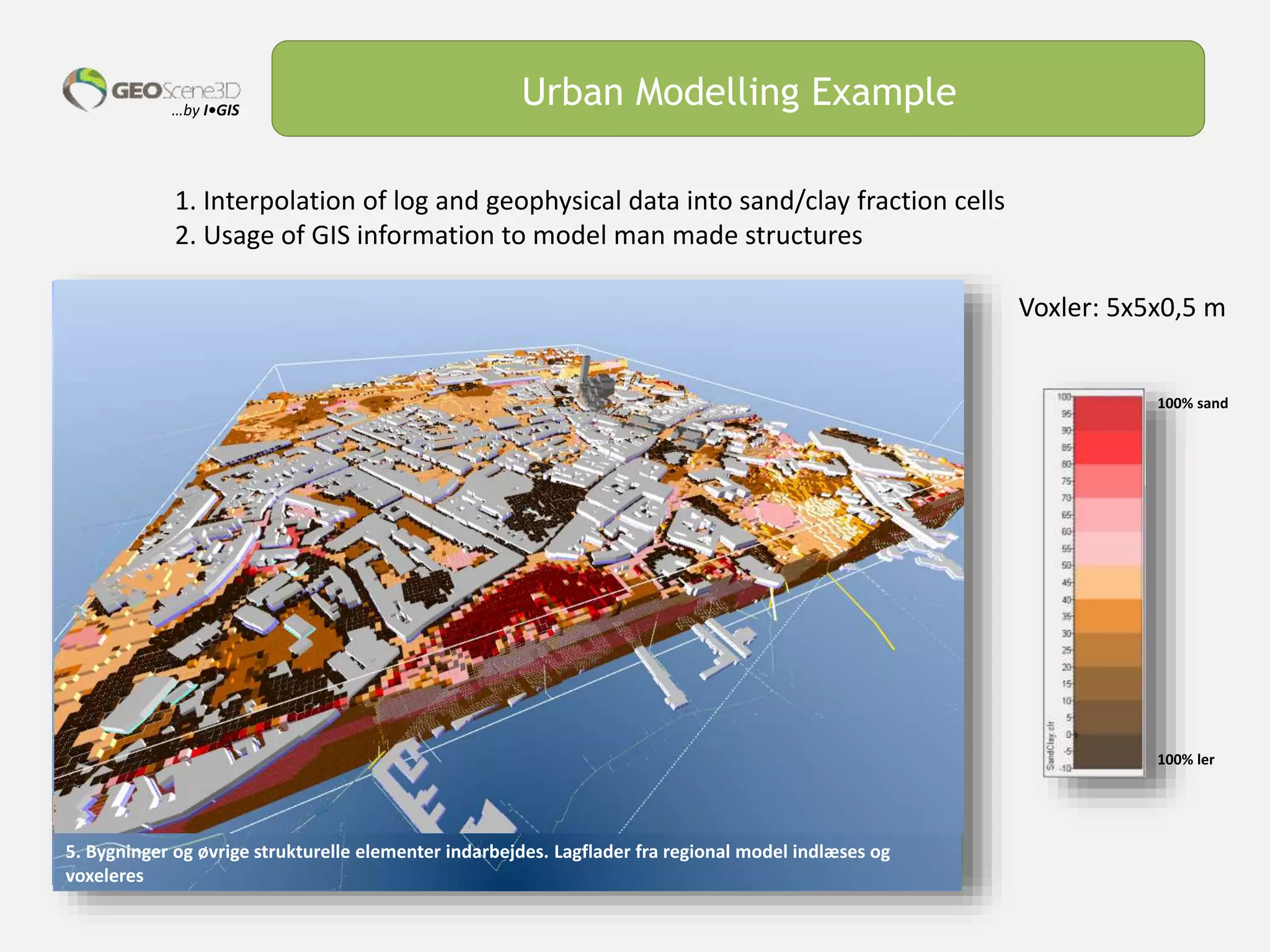
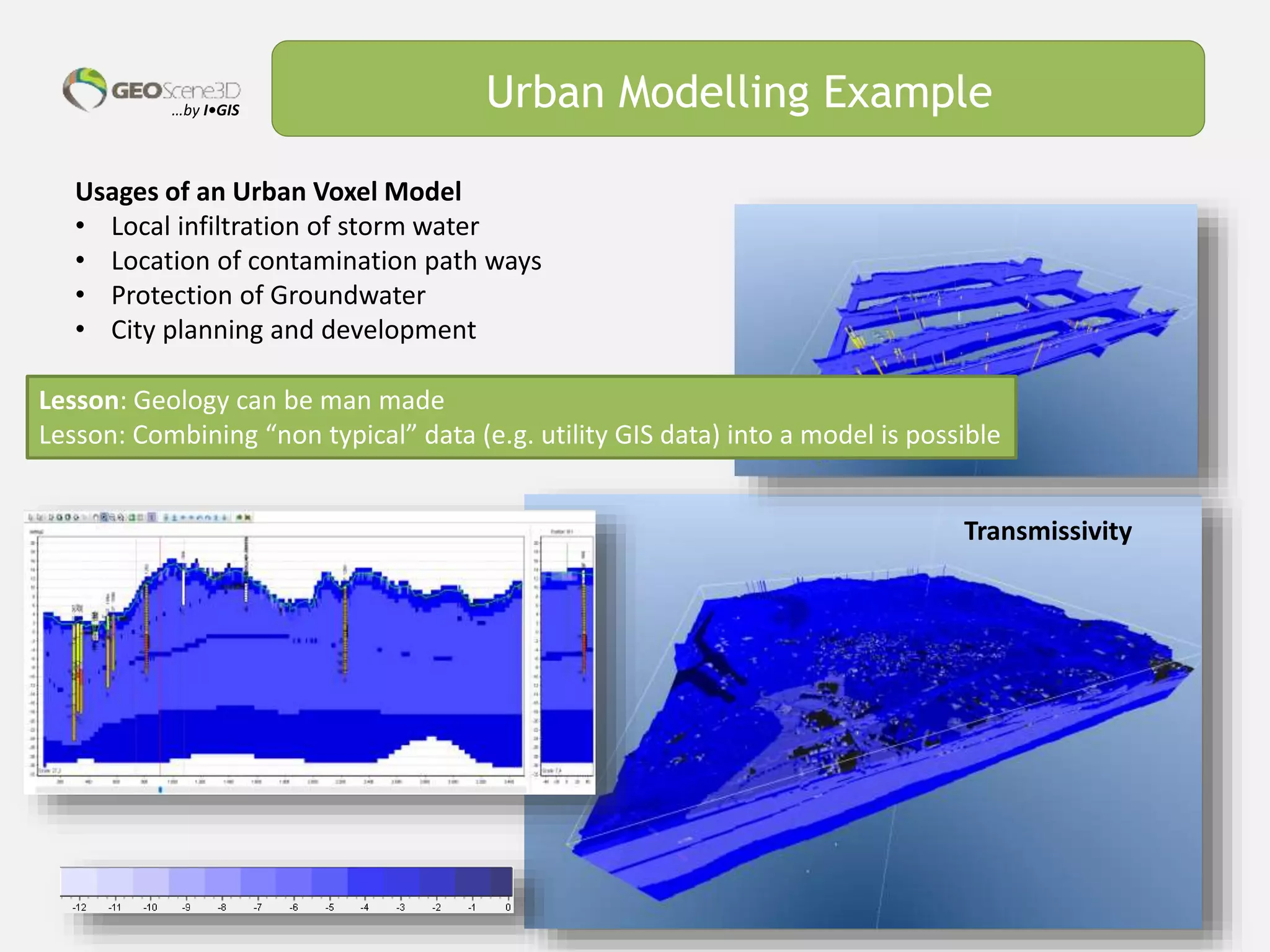
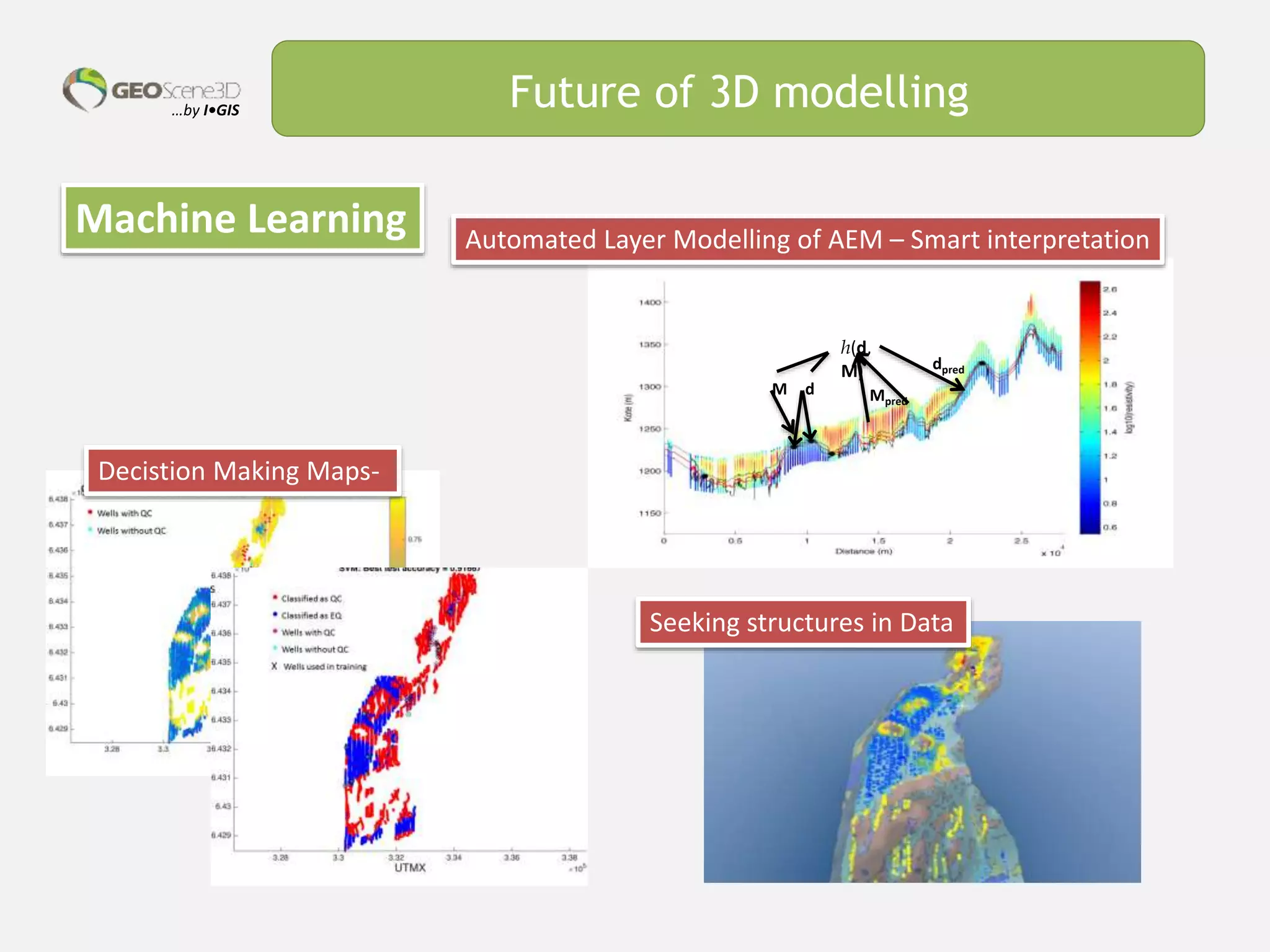
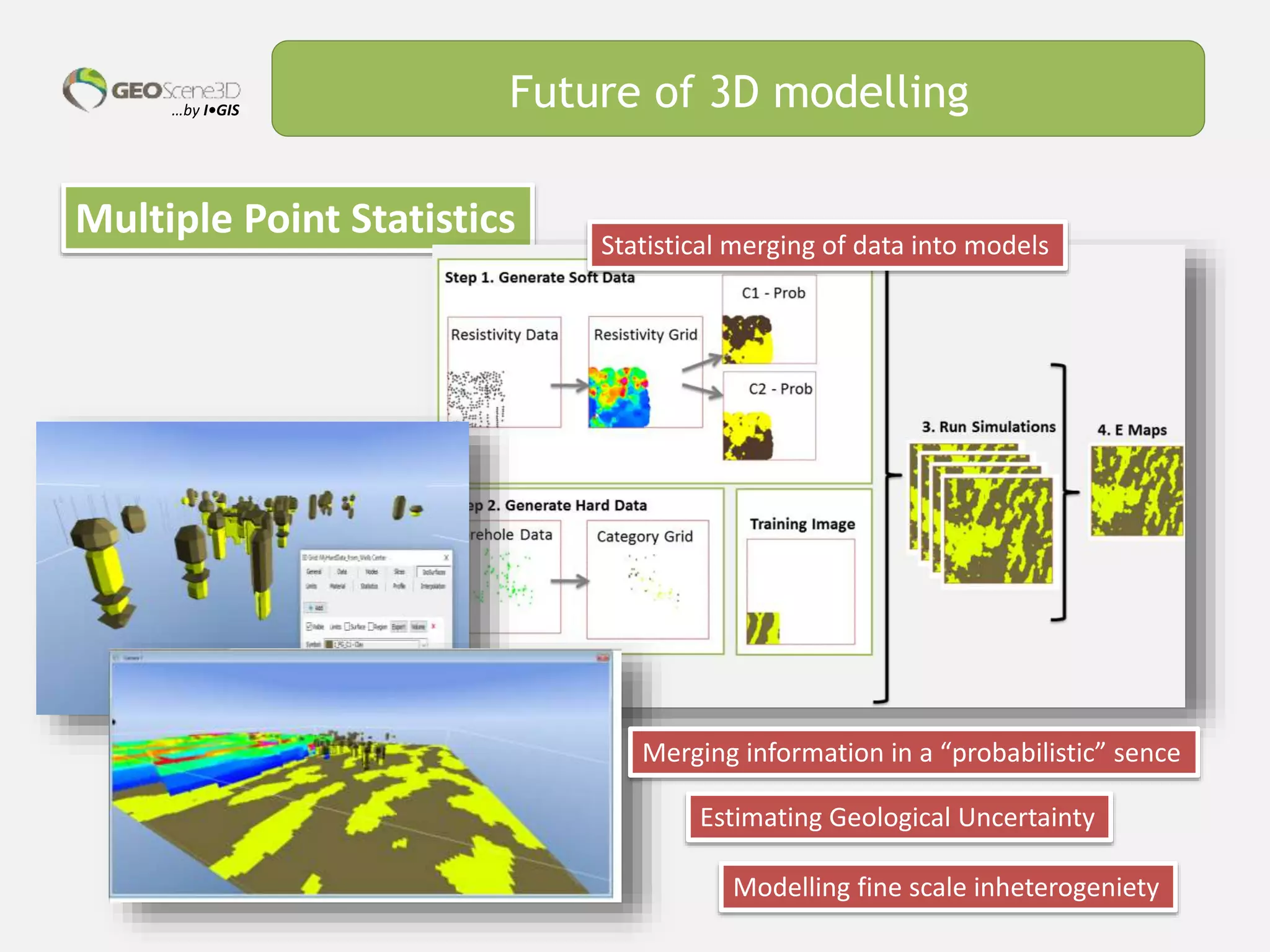
This document discusses lessons learned from building 3D hydrogeological conceptual models in Denmark, emphasizing the need for detailed models and the integration of various data types. It highlights the iterative and multidisciplinary process required for effective groundwater mapping, as well as the importance of data management and collaboration among geoscience professionals. The document concludes with a call to embrace change and adapt to new tools and methodologies for improved modeling.