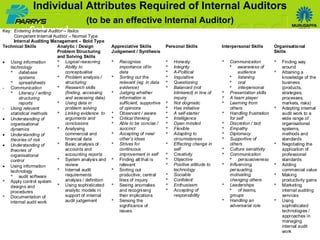
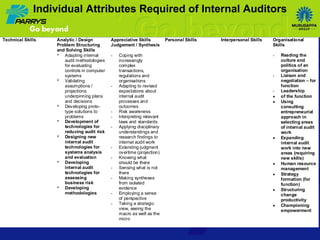
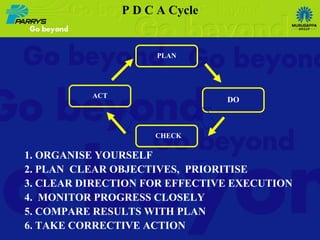
The document discusses the evolving role of internal auditors, emphasizing how their perception can shift from being seen as a 'bane' to a 'boon' through value addition. It highlights the transition from traditional auditing practices to a more integrated and consultative approach, where auditors not only assure compliance but also add strategic value to organizations. Key attributes for success involve building competencies, effective communication, and aligning with organizational objectives to enhance overall governance and risk management.