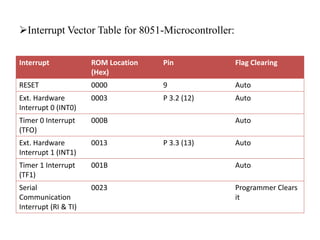
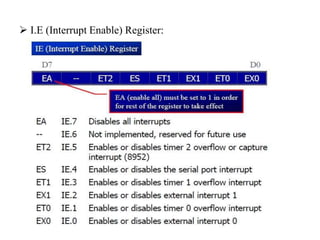
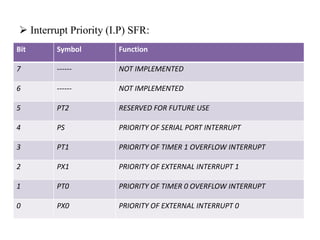
This document discusses interrupts in the 8051 microcontroller. It explains that interrupts allow a microcontroller to serve multiple devices by interrupting its main program flow to service higher priority requests, unlike polling which wastes time monitoring inactive devices. When an interrupt occurs, the microcontroller saves context and jumps to an interrupt service routine (ISR) located via an interrupt vector table. The 8051 has interrupts for timers, serial communication, and external pins which are enabled via the interrupt enable register and prioritized using the interrupt priority register.