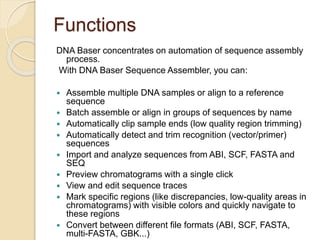
The document discusses two bioinformatics software tools: DNA Baser and Darwin. DNA Baser is a tool for manual and automatic DNA sequence assembly, analysis, editing, and more. It allows for automation of sequence assembly through functions like end trimming, vector removal, and batch assembly of thousands of sequences. Darwin is an interpreted computer language for research in bioscience that provides libraries and functions for tasks like sequence comparison, alignment, phylogenetics, and more.