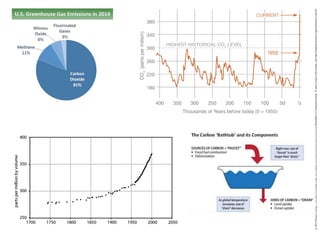
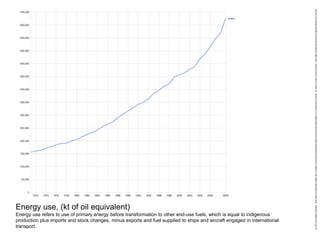
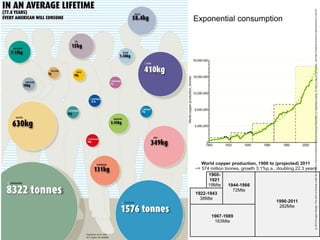
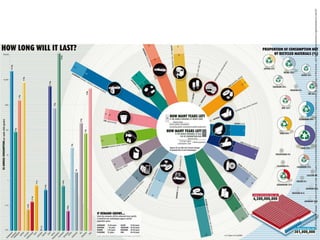
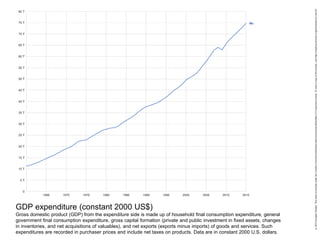
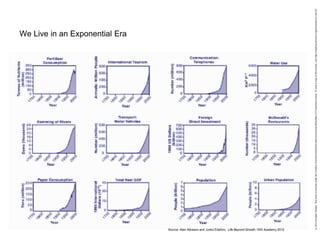
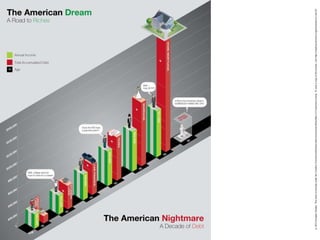
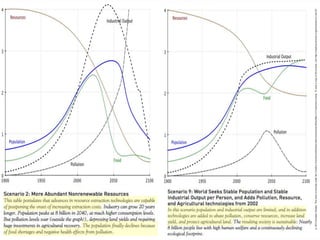
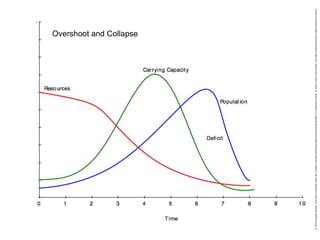
This document discusses three wicked problems - environmental degradation, India's climate change goals, and exponential consumption. It notes issues like pollution of rivers and forests disappearing. India aims to reduce emissions and create carbon sinks. Consumption and energy use are growing exponentially. The document also discusses the ideas in the 1972 book "Limits to Growth" which warned about exponential growth exceeding limits and potential collapse. It notes continued exponential growth in population and industry since then. Finally, it outlines perspectives on addressing these problems through long term planning, responsibility for others, and systems thinking education.