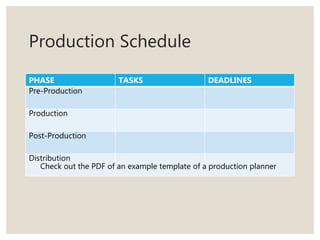
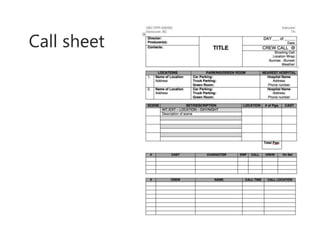
The document provides guidance on conducting interviews for documentaries. It recommends preparing questions in advance, making interview subjects feel comfortable, asking open-ended questions, avoiding yes or no questions, and considering location and visual elements. The workflow of documentary production is also outlined, including pre-production research, casting, shooting, and post-production editing, sound design, and distribution. Crew roles like the director, cinematographer, sound person, and editor are defined.