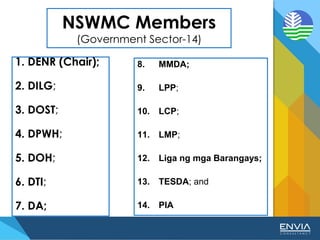
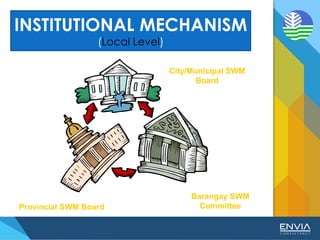
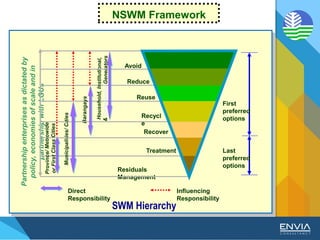
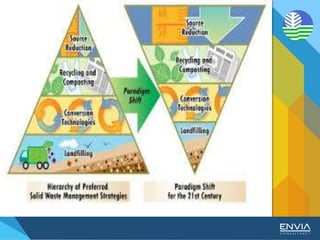
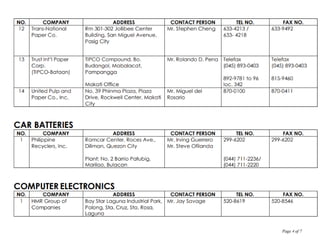
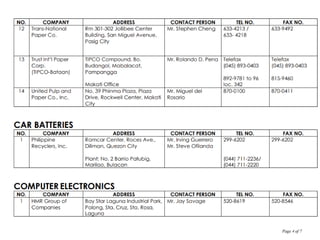
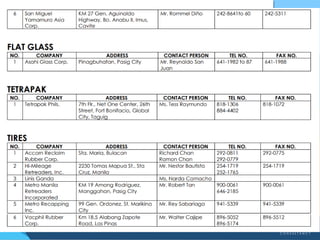
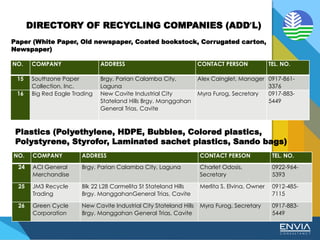
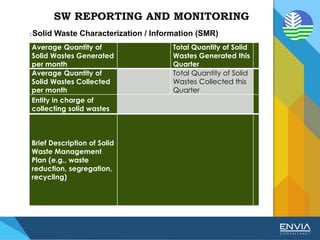
The document discusses Republic Act 9003 or the Ecological Solid Waste Management Act of 2000. It establishes the institutional framework for solid waste management in the Philippines from the national level down to local government units and barangays. Key points include the creation of the National Solid Waste Management Commission to oversee implementation, as well as mandatory waste diversion targets of 25% by 2006 that increase every 3 years. Proper solid waste management is important to avoid environmental and health impacts of improper disposal. Segregation, recycling, and other 3R practices are encouraged for the public.


















![DISPOSAL Controlled Dump Facilities
•Improvement only in the
operation such as provision
of [1] daily soil cover; [2]
drainage system; perimeter
fence; scheduled waste
picking, etc.
•Most are ill-sited.
•Deadline for Closure: Feb.
16, 2006
•Should be properly
rehabilitated.
All CDFs are also considered OD
SWM SITUATIONER](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-240405070057-1c499047/85/3-RA-9003-Ecological-Solid-Waste-Management-Act-pdf-21-320.jpg)