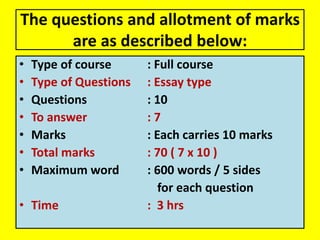
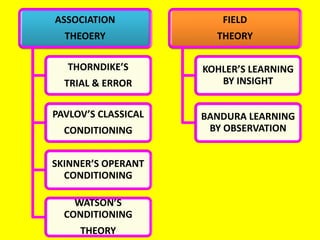
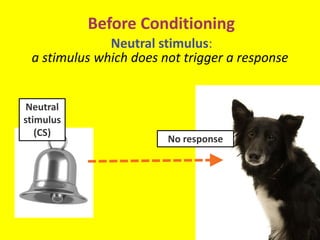
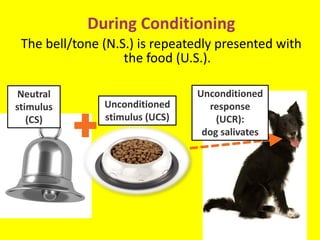
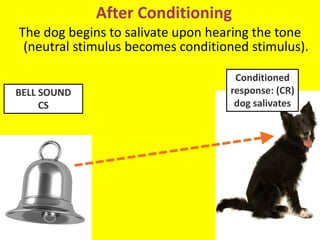
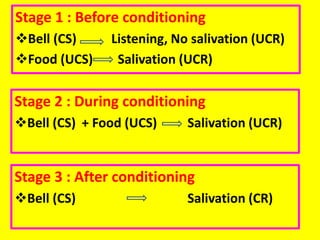
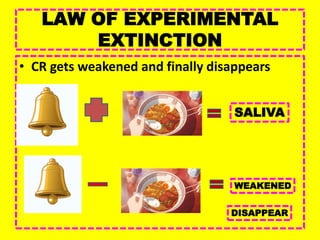
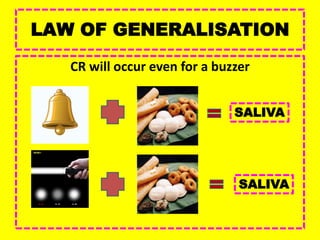
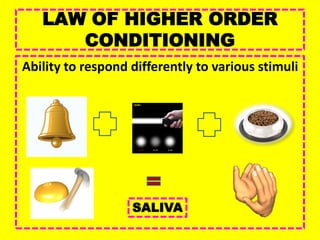
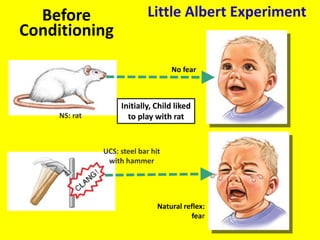
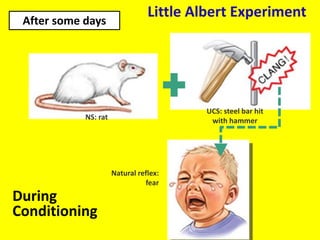
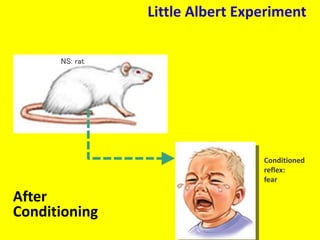
This document provides an overview of behavioral theories of learning, including classical and operant conditioning. It discusses Ivan Pavlov's classical conditioning experiments with dogs in which he found that dogs learned to associate neutral stimuli, like the sound of a bell, with the unconditioned stimulus of food, and would salivate in response to the neutral stimulus alone after conditioning. It also describes Watson's classical conditioning experiment with "Little Albert" in which a child was conditioned to fear a rat. The document outlines key concepts of behavioral theories like stimuli, responses, reinforcement, and punishment. It discusses theorists like Pavlov, Thorndike, Skinner, and their experiments that demonstrated principles of association, trial and error, and operant conditioning learning.