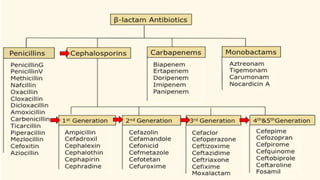
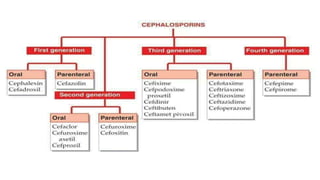
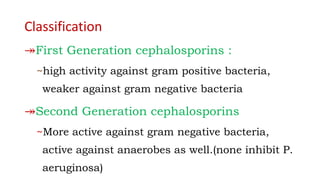
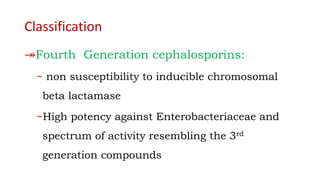
Cephalosporins are a class of beta-lactam antibiotics derived from the fungus Cephalosporium. They work by inhibiting cell wall synthesis in bacteria and are primarily bactericidal. Cephalosporins are grouped into generations based on their antimicrobial spectra, with later generations having activity against more drug-resistant gram-negative bacteria. They are used to treat a variety of bacterial infections and have similar mechanisms and side effects as penicillin, including potential allergic reactions. Nurses play an important role in monitoring patients taking cephalosporins for signs of adverse effects or drug interactions.