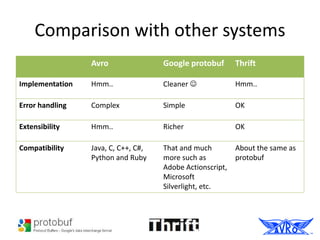
Apache Avro is a data serialization system and RPC framework that provides rich data structures and compact, fast binary data formats. It uses JSON for schemas and relies on schemas stored with data to allow serialization without per-value overhead. Avro supports Java, C, C++, C#, Python and Ruby and is commonly used in Hadoop for data persistence and communication between nodes. It compares similarly to Protobuf and Thrift but with some differences in implementation, error handling and extensibility.







![Specification, example protocol
{
"namespace": "com.acme",
"protocol": "HelloWorld",
"doc": "Protocol Greetings",
"types": [
{"name": "Greeting", "type": "record", "fields": [
{"name": "message", "type": "string"}]},
{"name": "Curse", "type": "error", "fields": [
{"name": "message", "type": "string"}]}
],
"messages": {
"hello": {
"doc": "Say hello.",
"request": [{"name": "greeting", "type": "Greeting" }],
"response": "Greeting",
"errors": ["Curse"]
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-apache-avro-120318172900-phpapp02/85/3-apache-avro-11-320.jpg)



