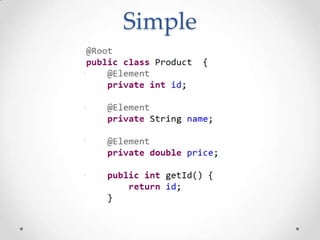
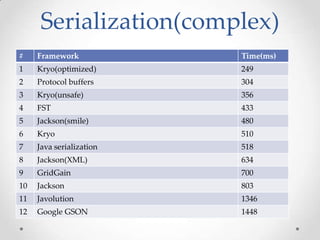
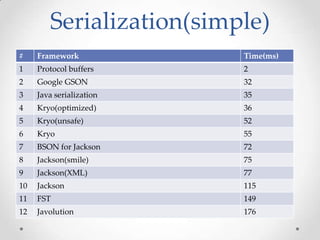
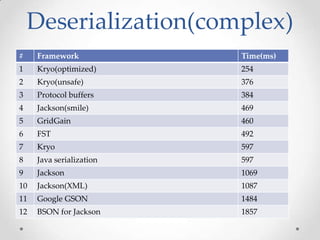
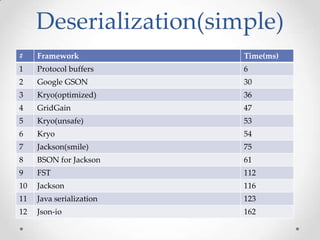
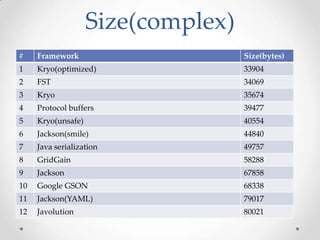
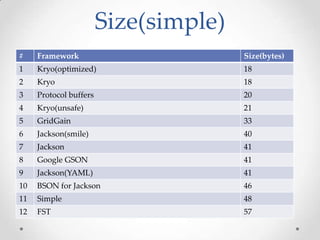
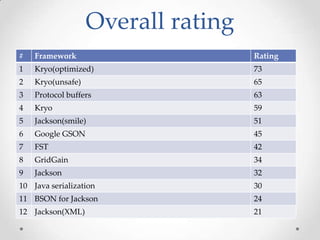
The document discusses serialization frameworks in Java and compares their performance. It provides an overview of popular serialization frameworks like Java serialization, Kryo, Protocol Buffers, Jackson, Google GSON, and others. Benchmark tests were conducted to compare the frameworks' speed of serialization and deserialization, as well as the size of serialized objects. Kryo with optimizations was generally the fastest, while Protocol Buffers was very fast for simple objects. The document concludes with recommendations on when to use different frameworks.













![Avro
{
"namespace": "org.test.domain",
"type": "record",
"name": "User",
"fields":
[
{"name": "login", "type": "string"},
]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/serializationandperformance-131125101329-phpapp01/85/Serialization-and-performance-by-Sergey-Morenets-14-320.jpg)