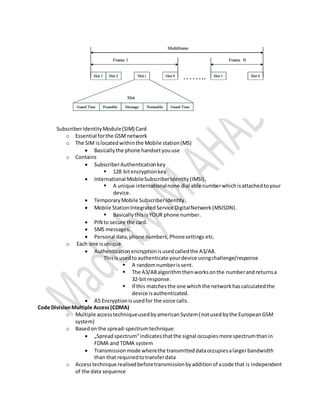
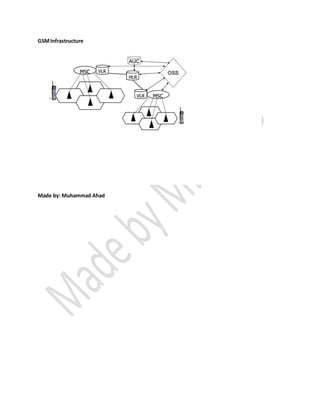
2nd generation mobile networks used digital technology to transmit voice calls and basic data via SMS. GSM was the first digital standard, using either TDMA or CDMA. GSM offered teleservices like calls and voicemail, bearer services for data transport, and supplementary services like call forwarding. It operated using TDMA, dividing frequencies into time slots for multiple access. Voice was digitized and encrypted for features like error correction. Subscriber identity was based on SIM cards containing keys and identifiers. CDMA used spread spectrum and unique codes to allow multiple devices on the same frequency band simultaneously. GSM consisted of the base station system for radio access, the network switching subsystem for call processing, and the operation and support system for