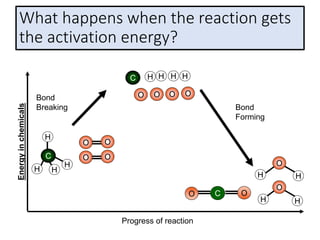
The document discusses energy changes that occur during chemical reactions. It provides information on:
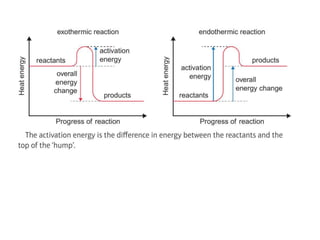
1) Exothermic reactions release energy when bonds form, while endothermic reactions absorb energy to break bonds.
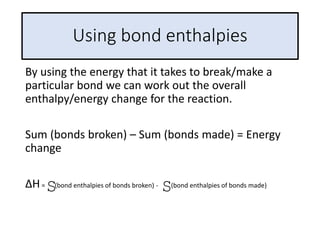
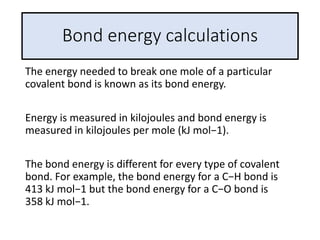
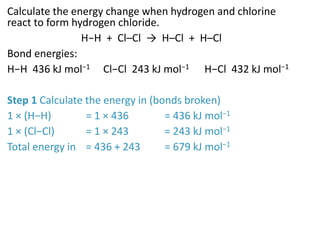
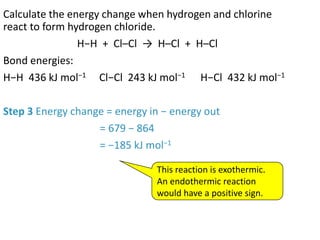
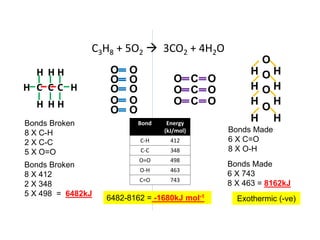
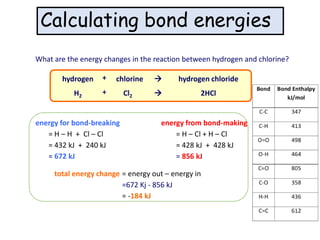
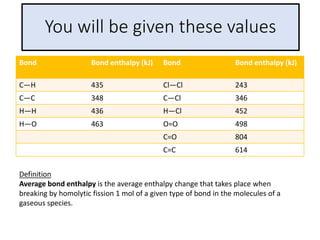
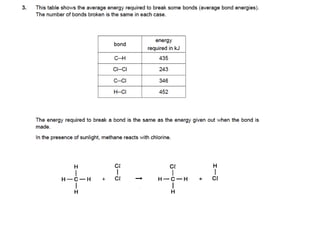
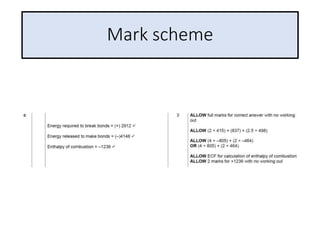
2) The energy change of a reaction can be calculated by adding the bond energies of bonds broken and subtracting the bond energies of bonds formed.
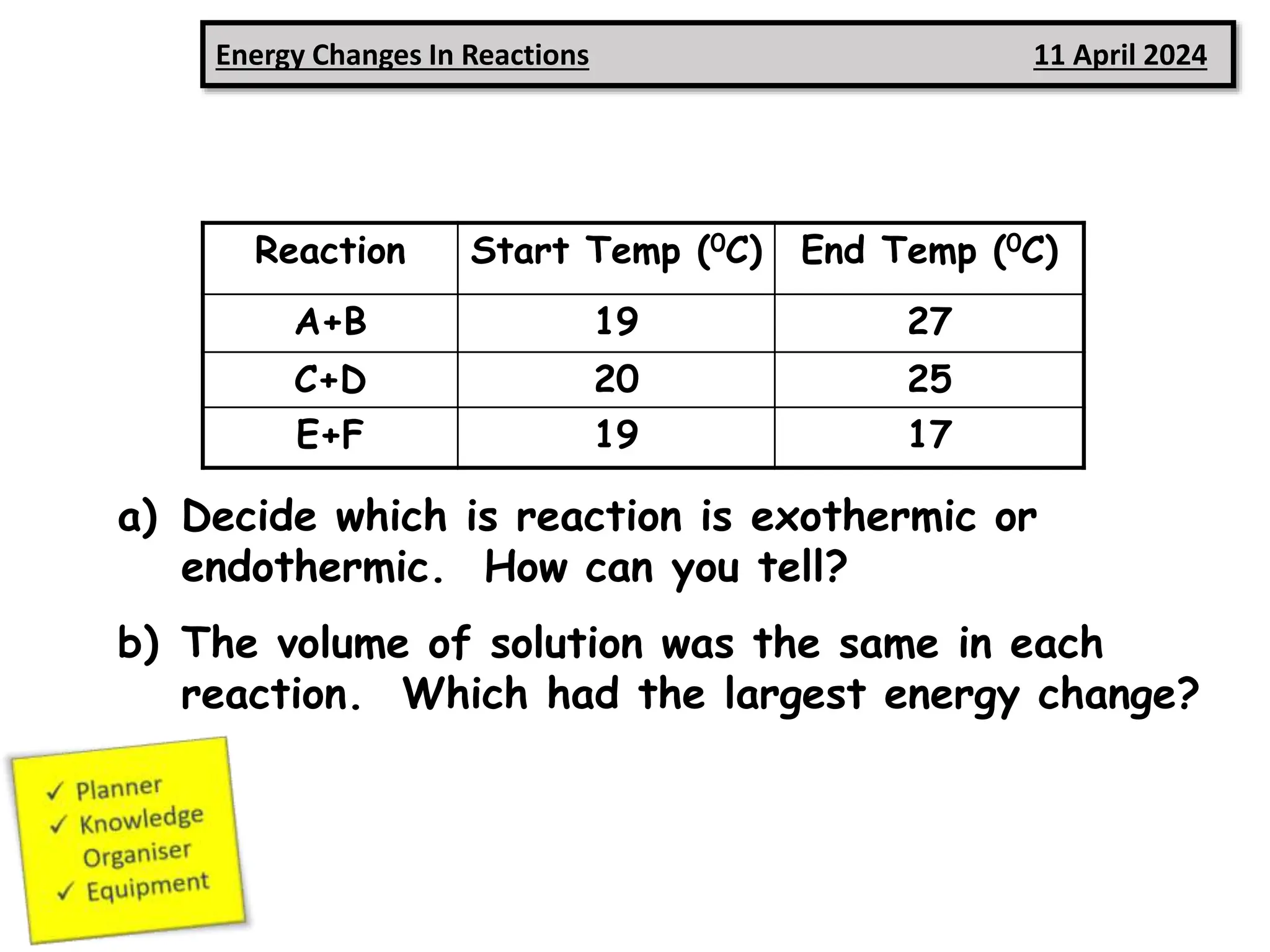
3) Reaction A+B increased in temperature, indicating it was exothermic since more energy was released in bond formation than absorbed in bond breaking.