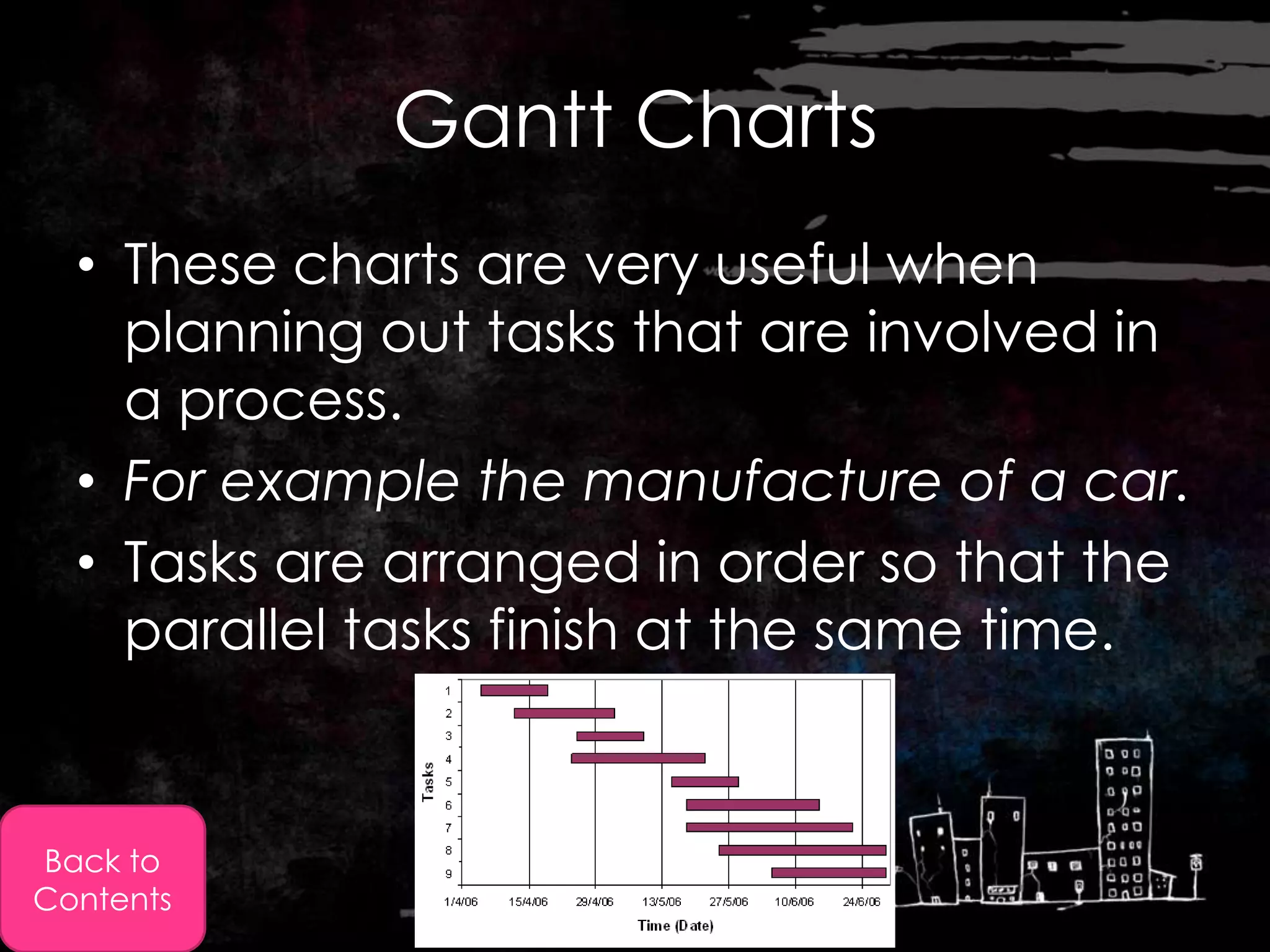
This document discusses time management approaches that organizations can take, including hiring a full-time employee to manage time, identifying targets, prioritizing tasks, planning, making decisions, and using information and communication technologies like software packages. It provides examples of how project management software allows scheduling meetings and workload, and creating calendars, timelines, and Gantt charts to plan sequential and parallel tasks for research projects.