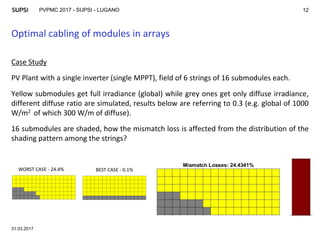
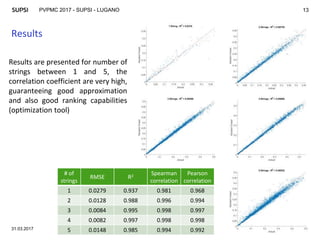
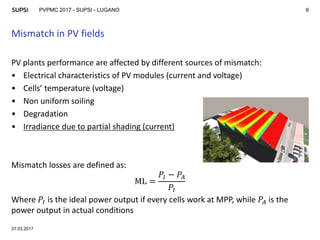
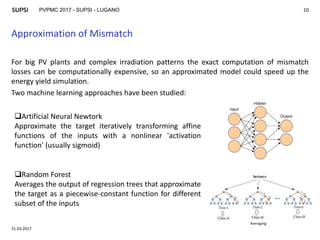
The document discusses modeling mismatch losses due to partial shading in PV plants. It presents a case study comparing different shading patterns across strings in a PV plant. Machine learning approaches like random forest and artificial neural networks were used to approximate mismatch losses, as exact computation can be computationally expensive. The random forest model provided accurate results, with correlation coefficients over 0.95, making it suitable for optimizing PV plant layout and minimizing mismatch losses. Future work involves generalizing and validating the approach for different module technologies and implementing an optimization tool.







![PVPMC 2017 - SUPSI - LUGANO
PV Field modelling
31.03.2017
11
To generalize the model to any number of submodules per string, the input of the ANN and
RF have been normalized to the length of the string (shading fraction), moreover the
diffuse fraction is considered as input. The test case is a Poly-Si module.
Machine Learning
s1
s2
…
sN
kD
Mismatch
Losses
Example
s = [7/16 6/16 3/16 0 0 0]
kD = 0.3
ML = 0.244
Both machine learning approaches
need to be trained with a large dataset
of examples, to minimize the size of
the training dataset some equivalence
classes are considered:
• the shading fraction is sorted
• Position of modules inside its string
is not considered
The computation of the prediction is
extremely fast in both cases.
si ∈ [0, 1] kD ∈ 0.1, 1 ML ∈ [0.1, 1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/26corbellinirandomforestformismatch-170404212001/85/26-corbellini-random-forest-for-mismatch-11-320.jpg)