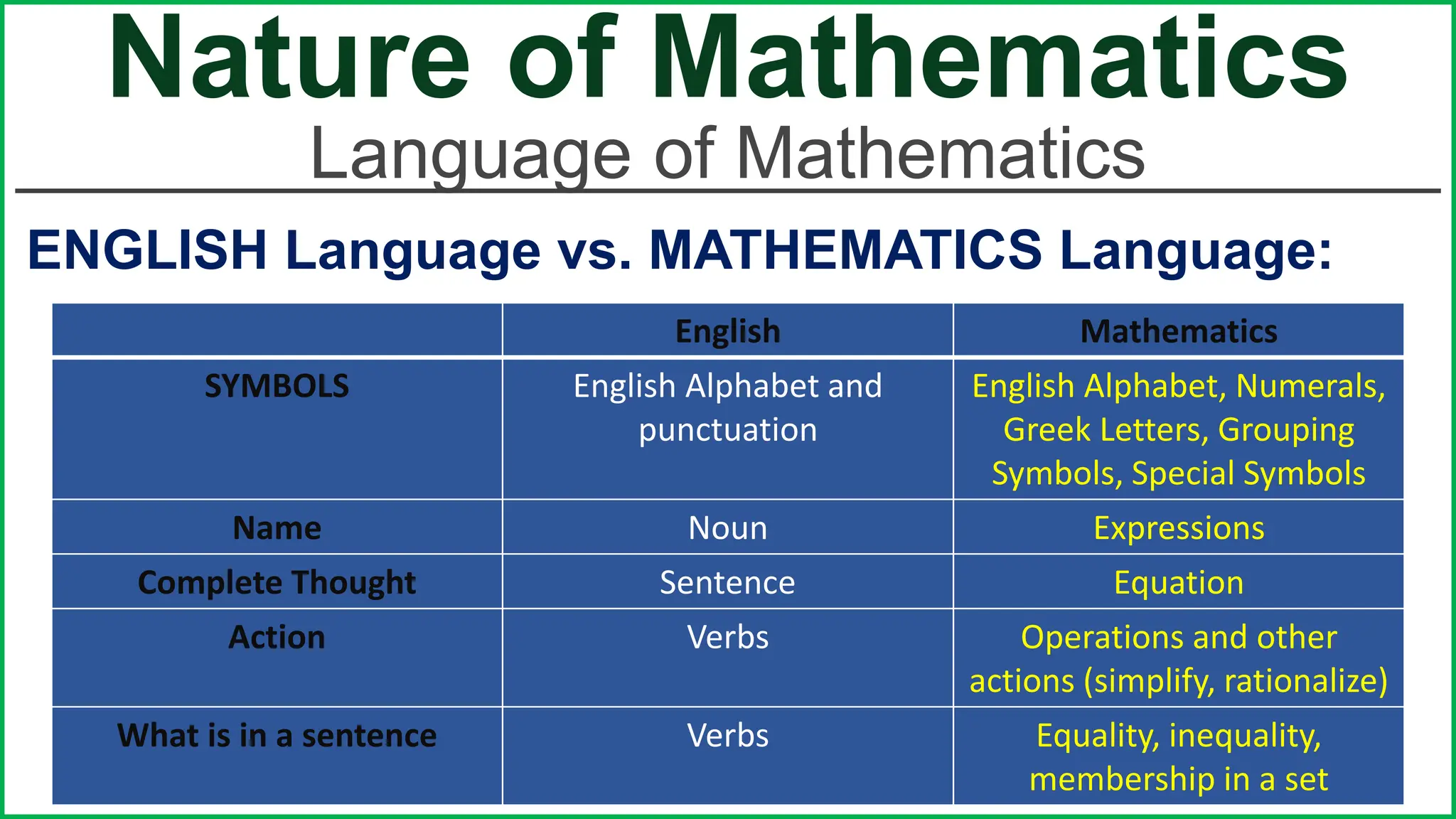
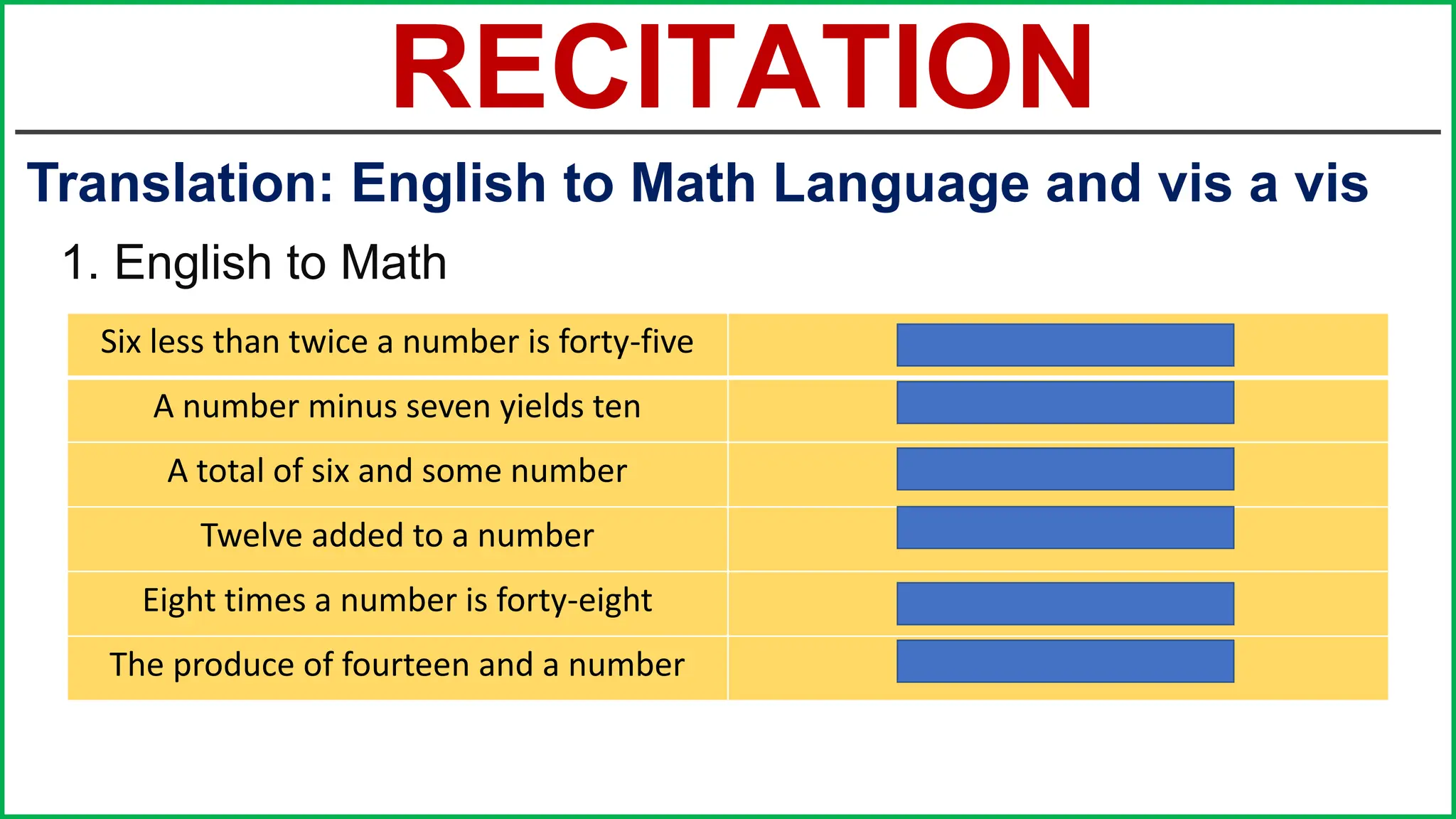
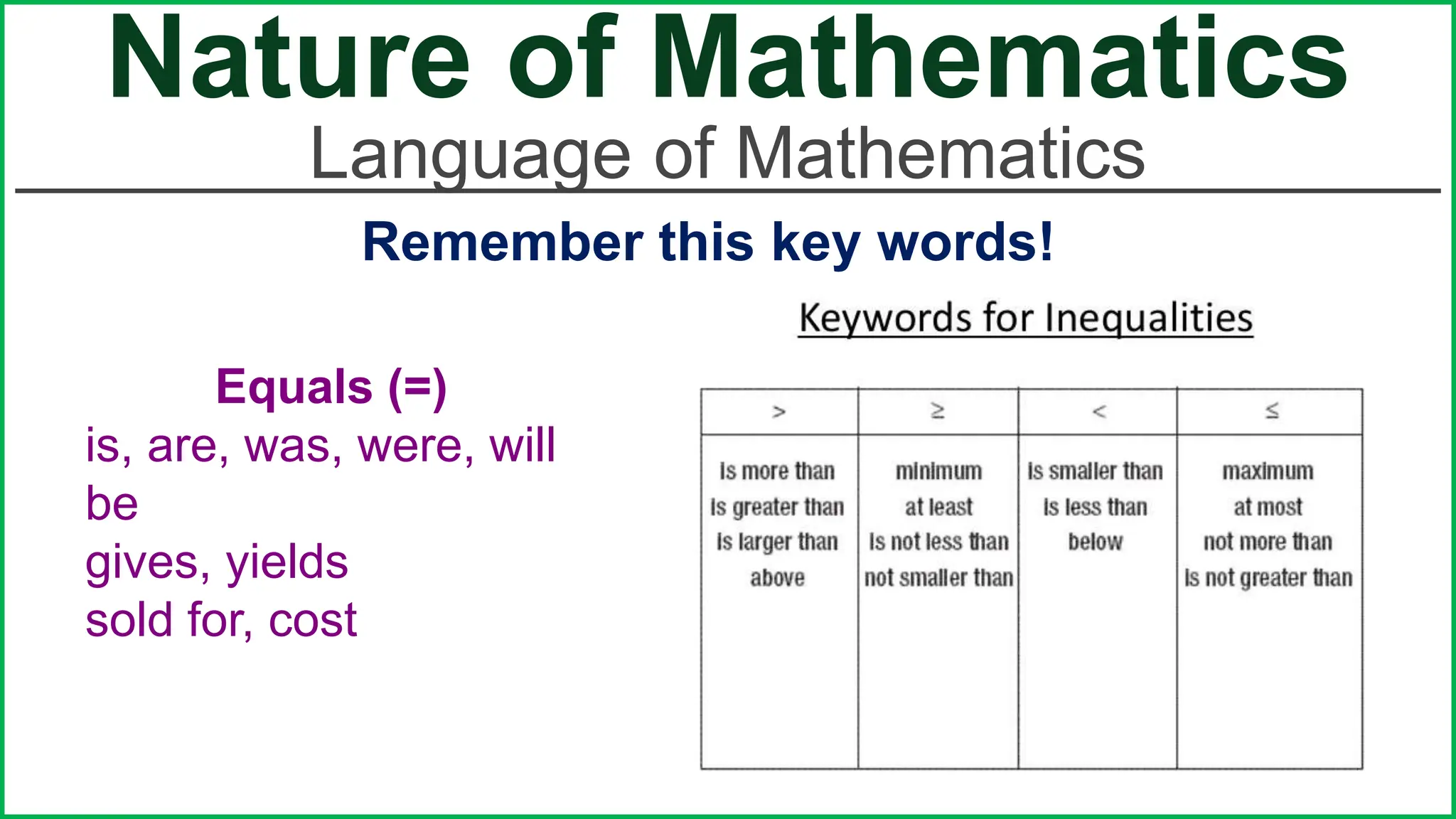
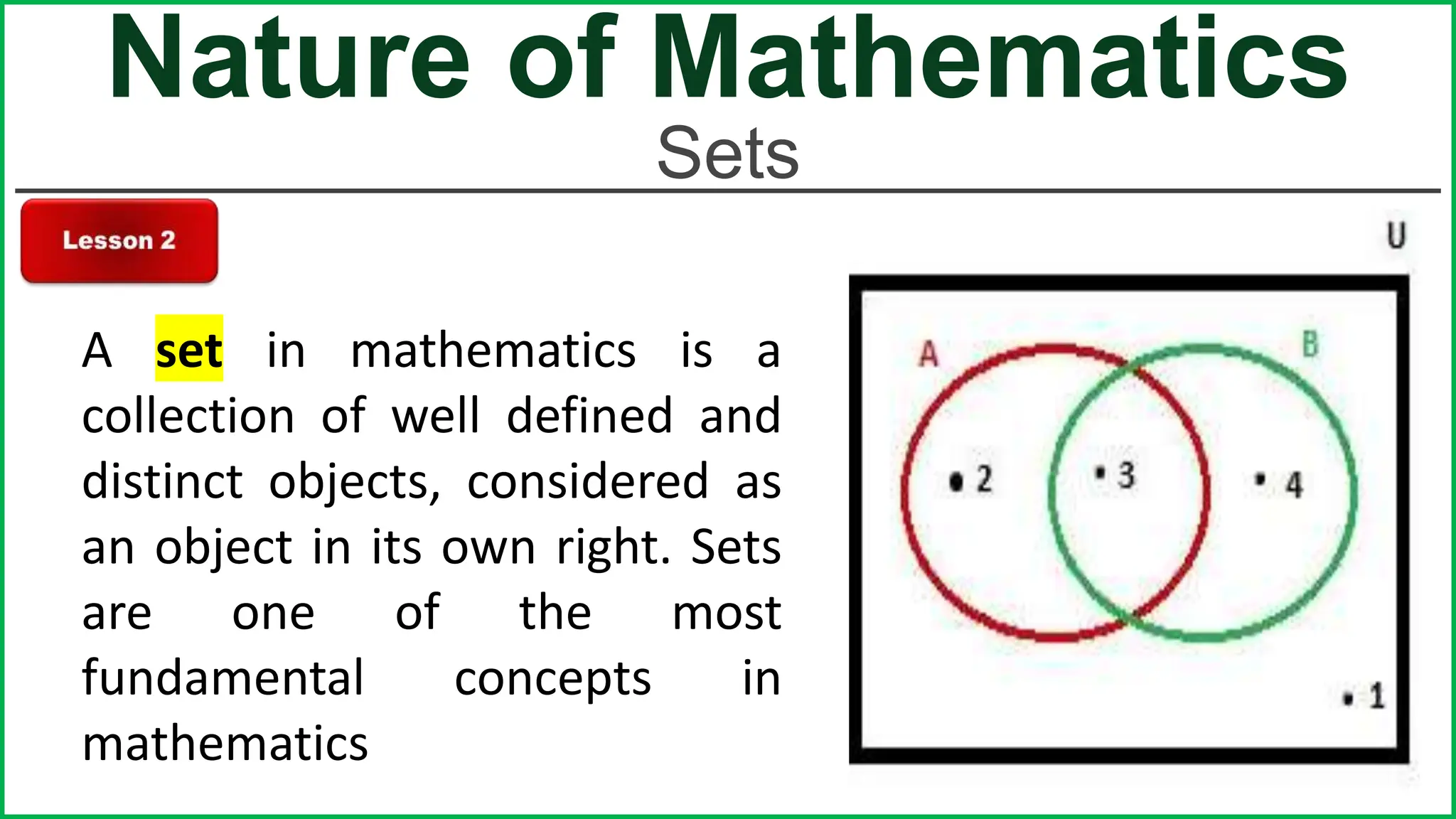
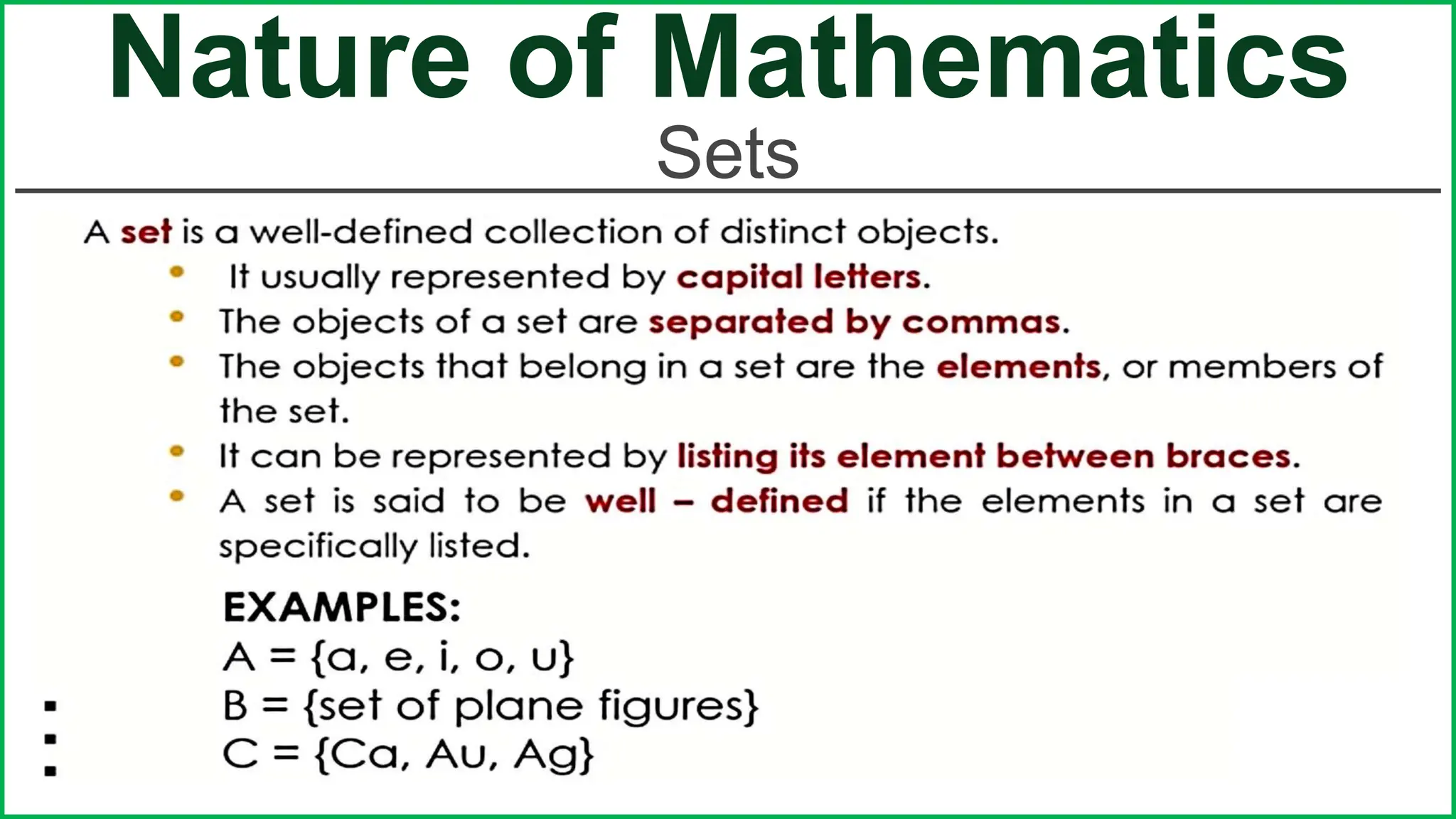
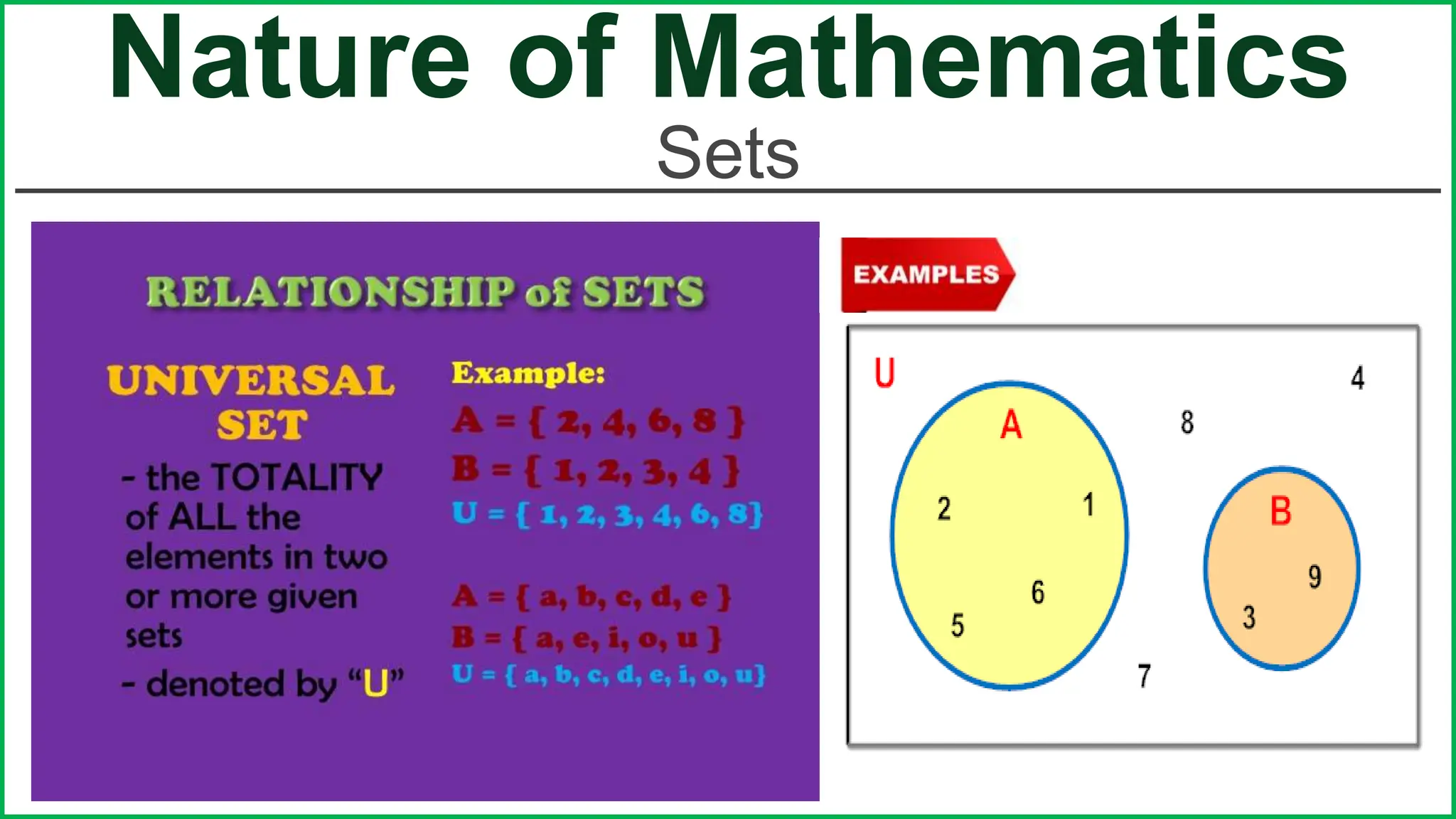
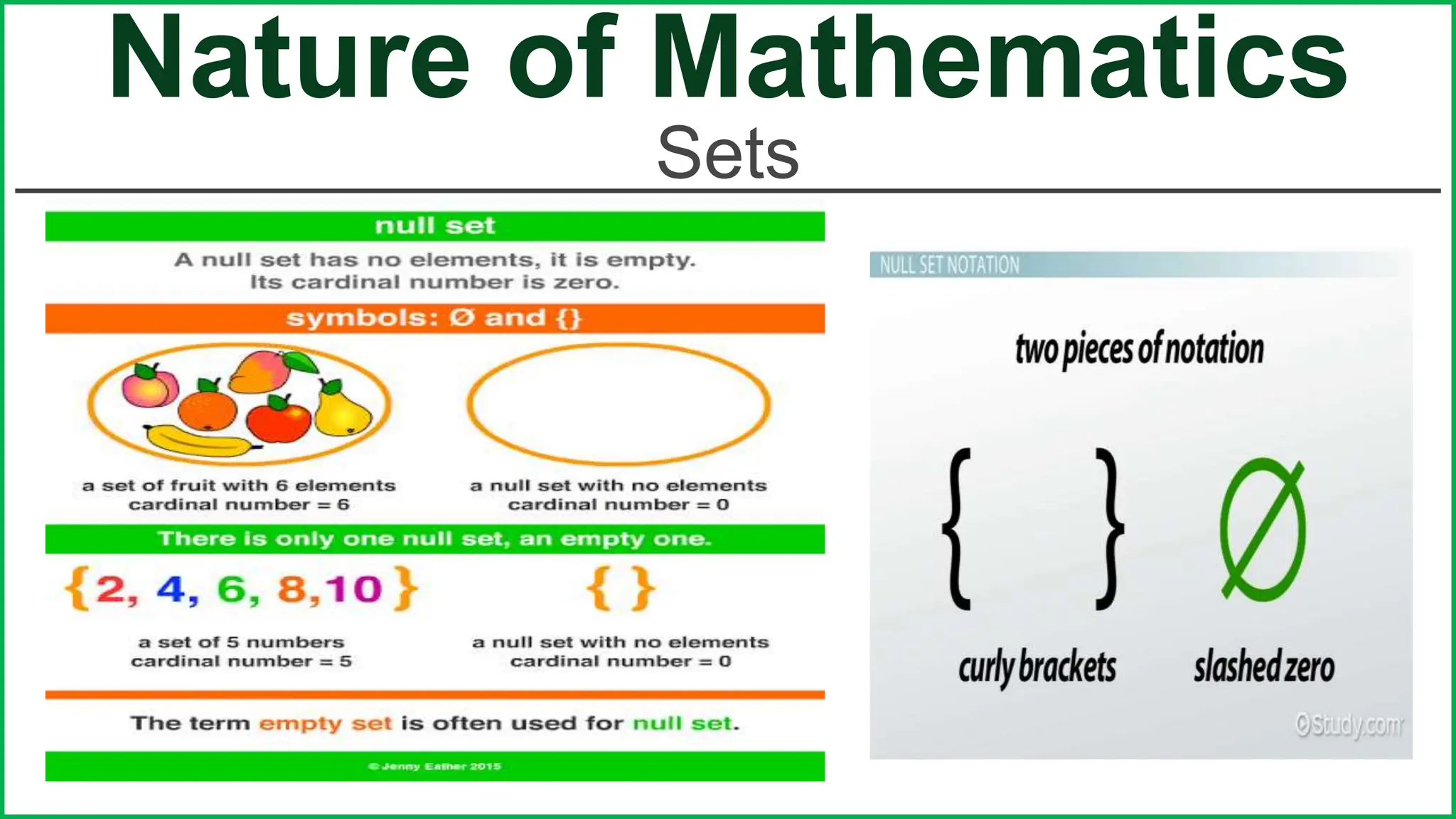
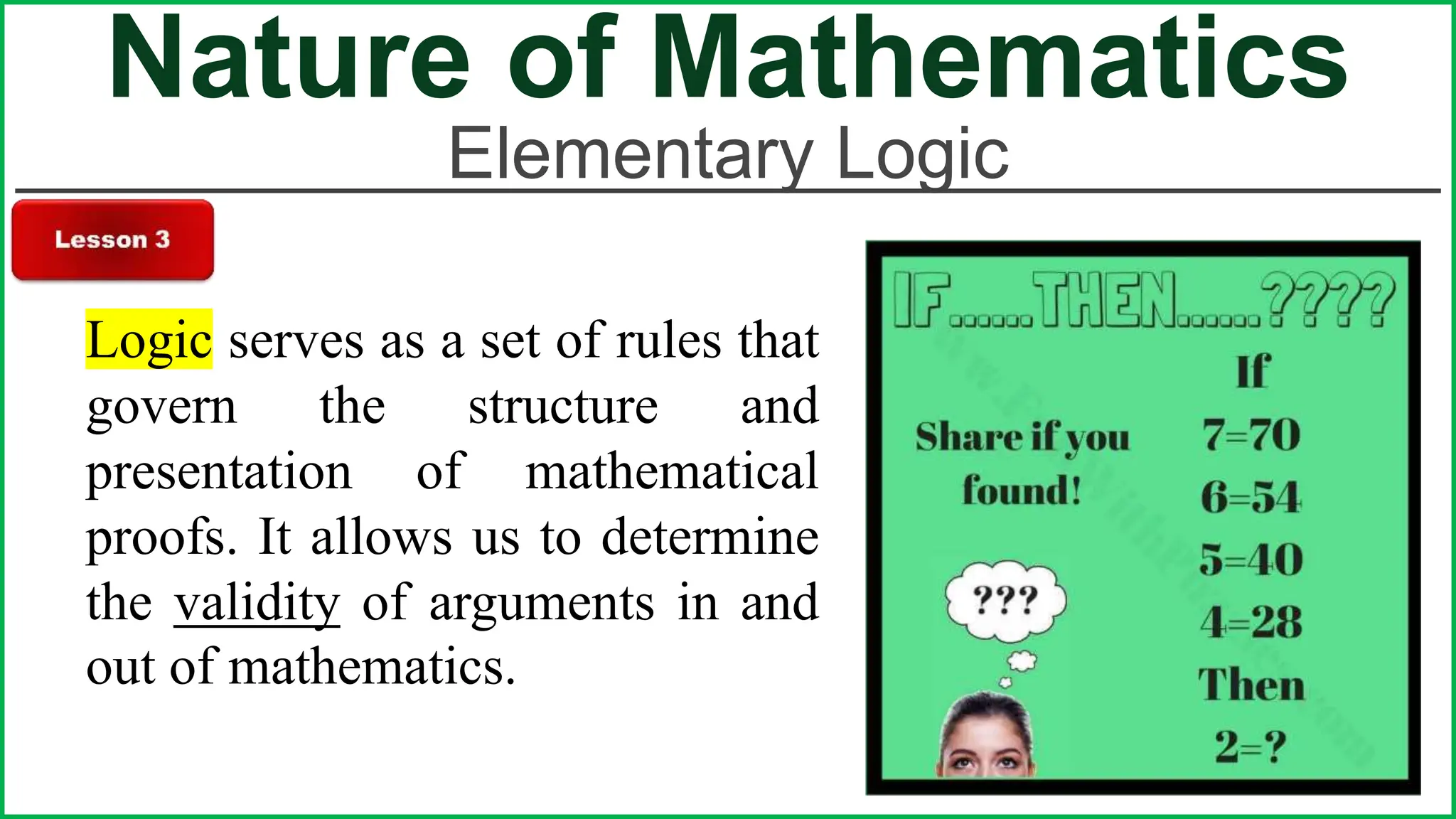
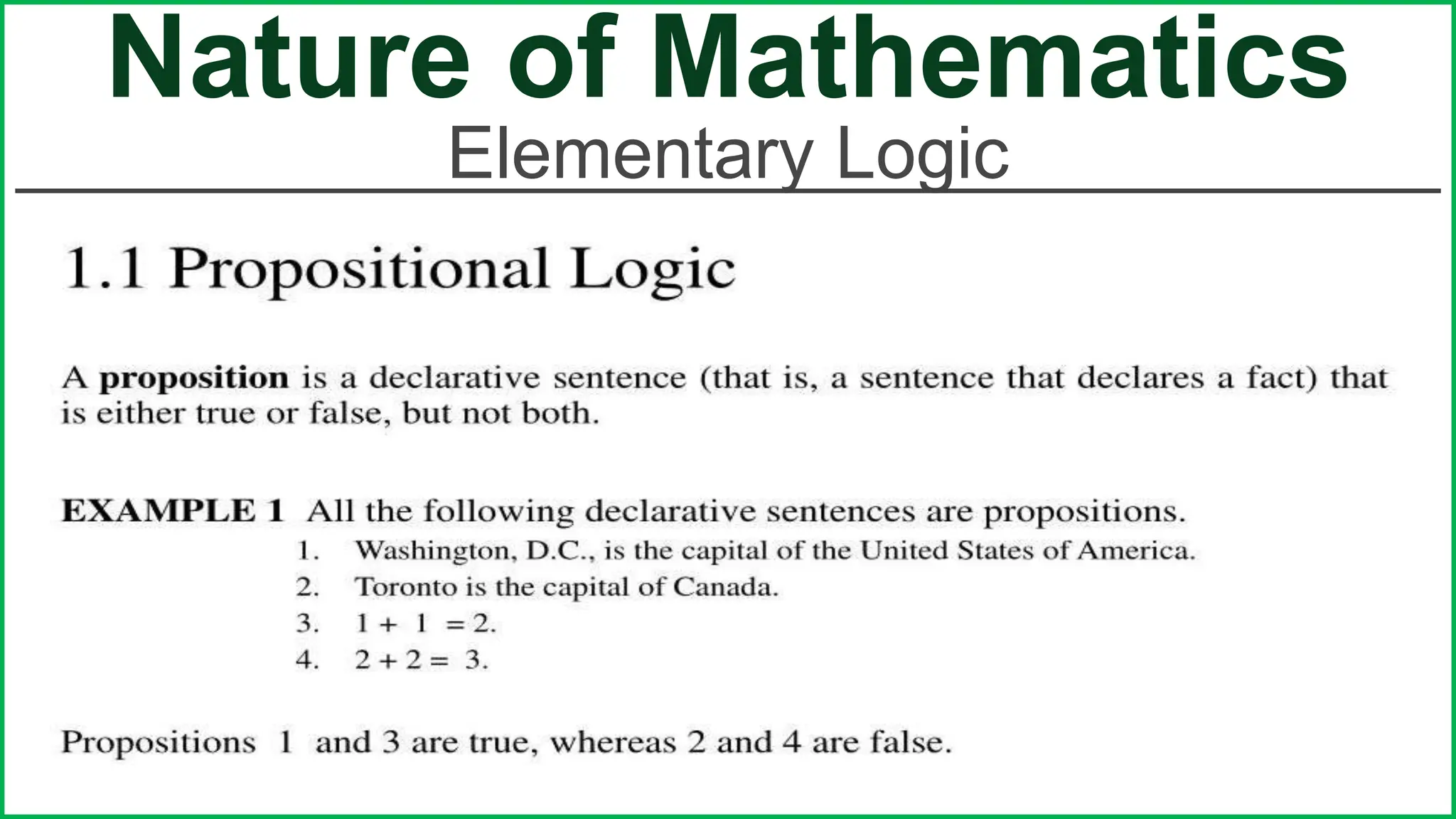
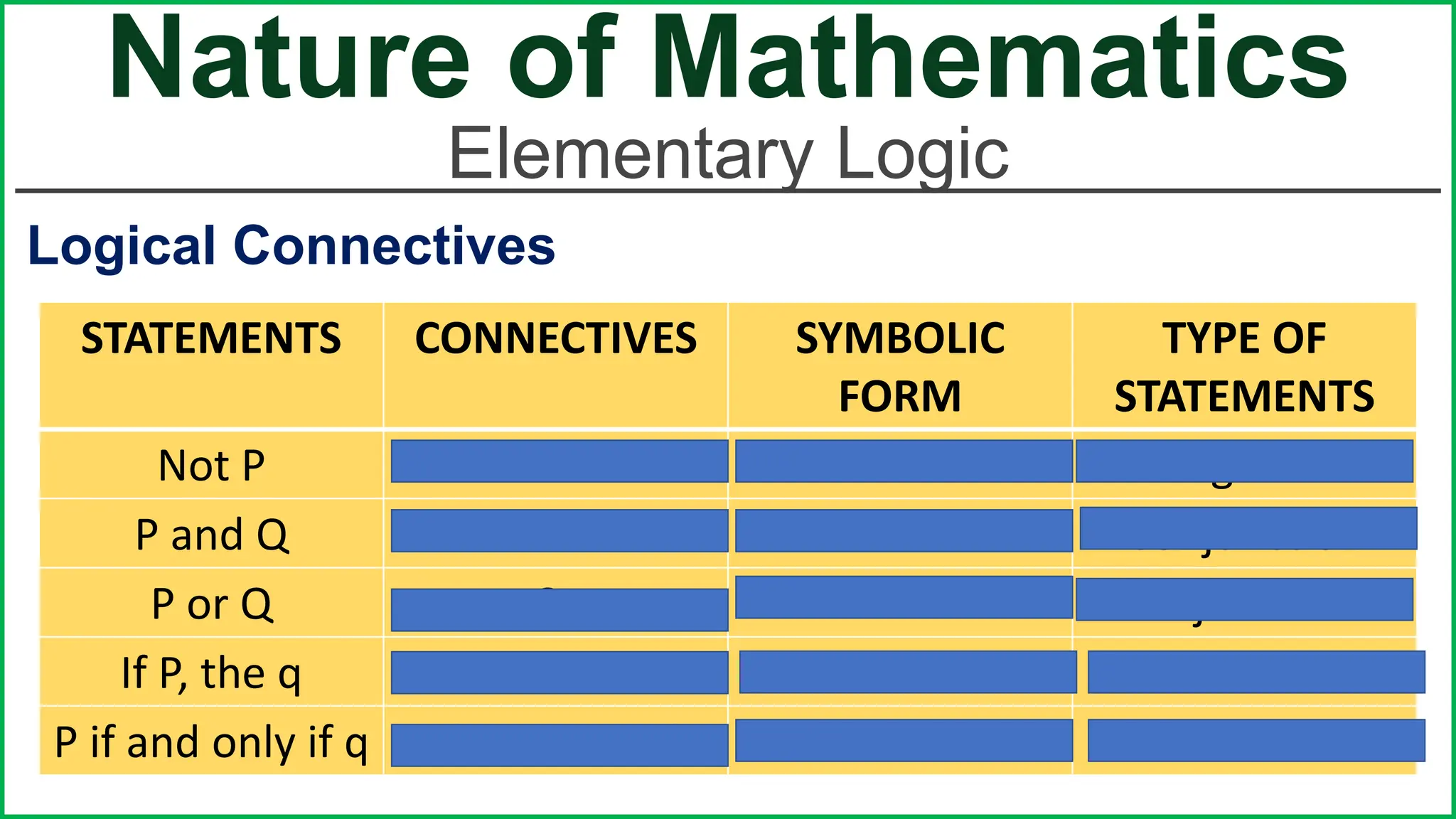
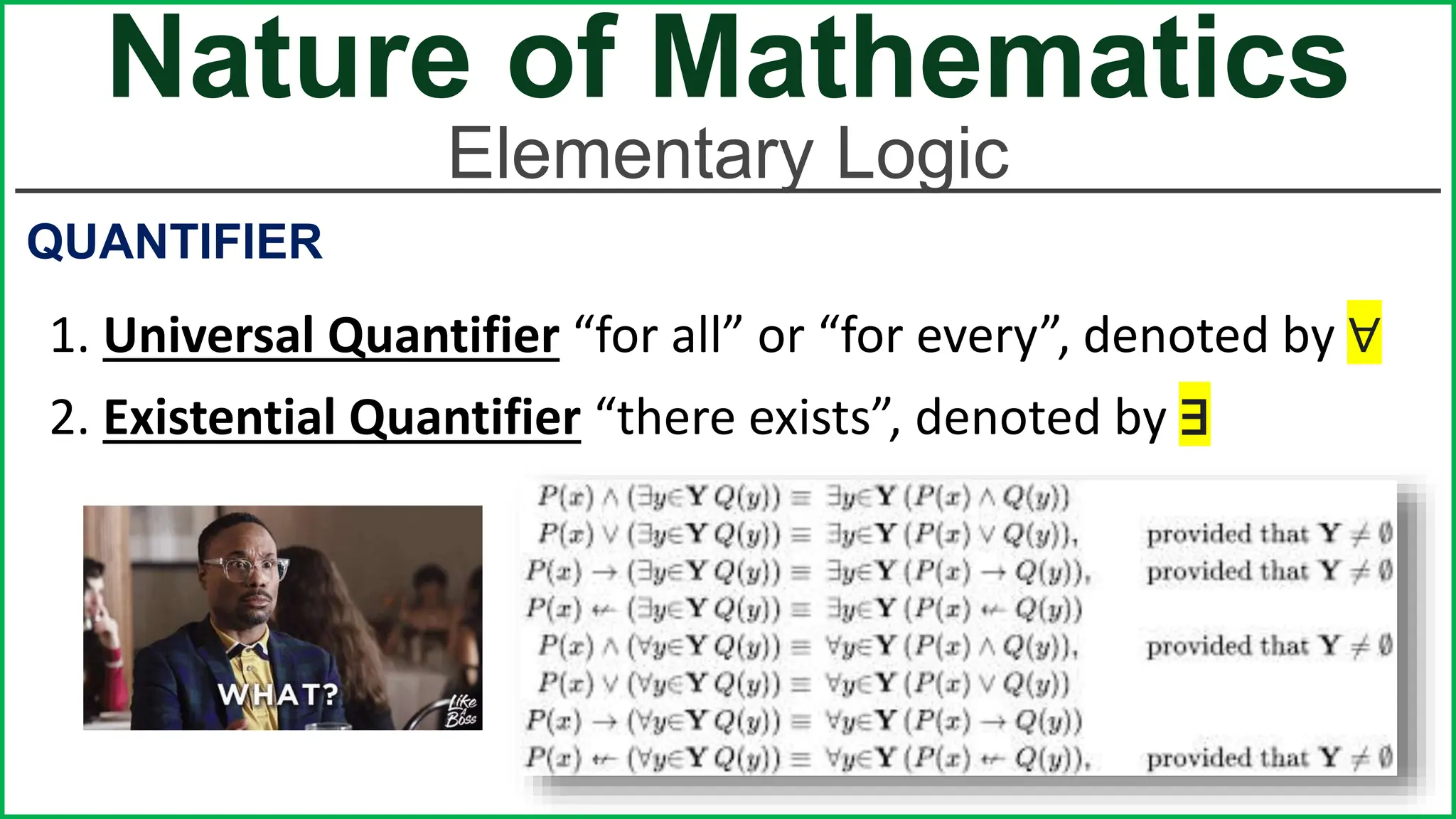
This document provides an outline for a lesson on the nature of mathematics, specifically focusing on mathematical language and symbols. It begins by defining key aspects of mathematical language, such as it being precise, concise, and powerful. It then compares the differences between English and mathematical language in terms of symbols used, naming conventions, complete thoughts/sentences, and synonyms. Examples are given to illustrate these differences. The document also discusses translating between English phrases and mathematical expressions. Finally, it introduces some basic concepts in sets and logic.