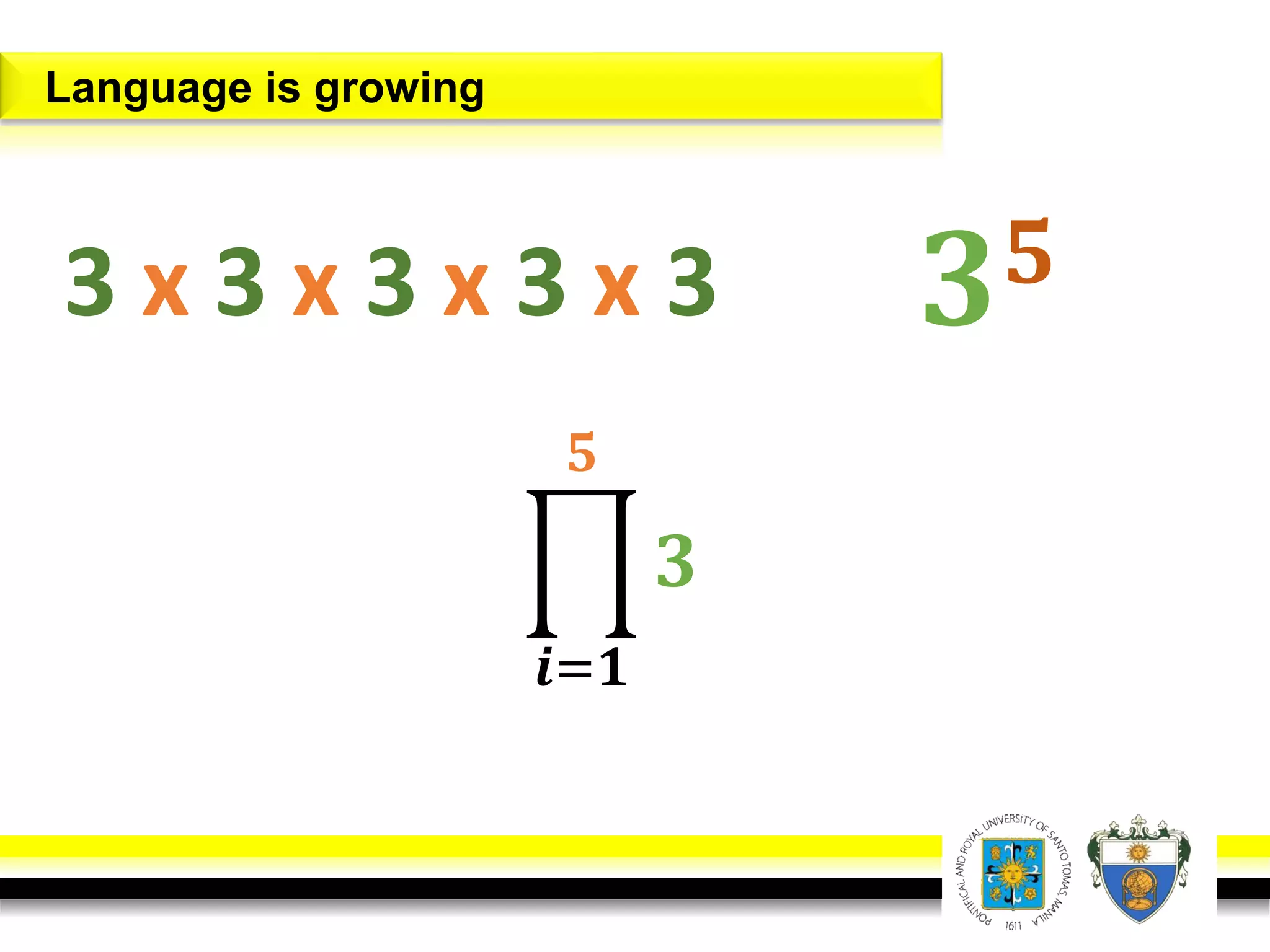
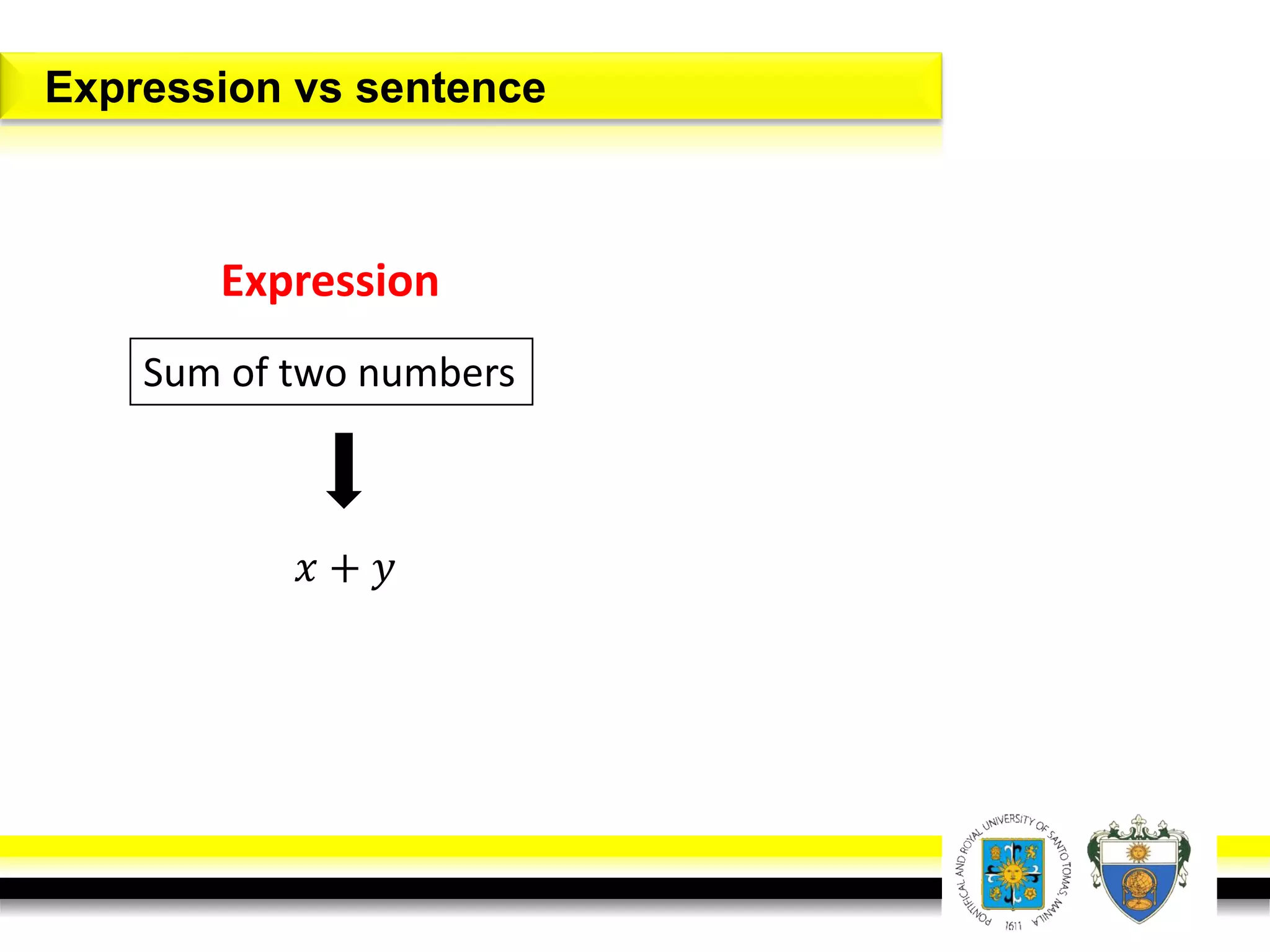
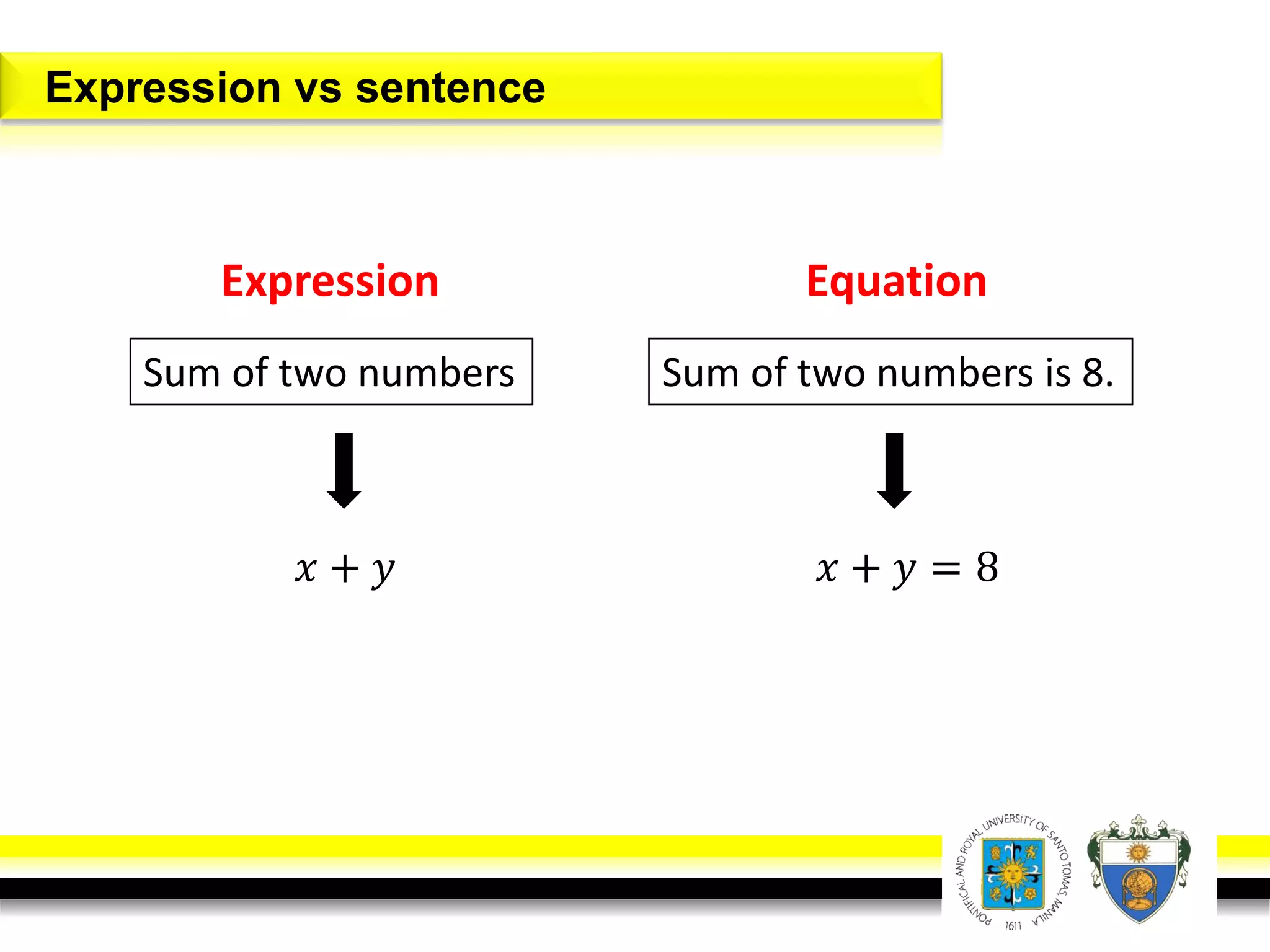
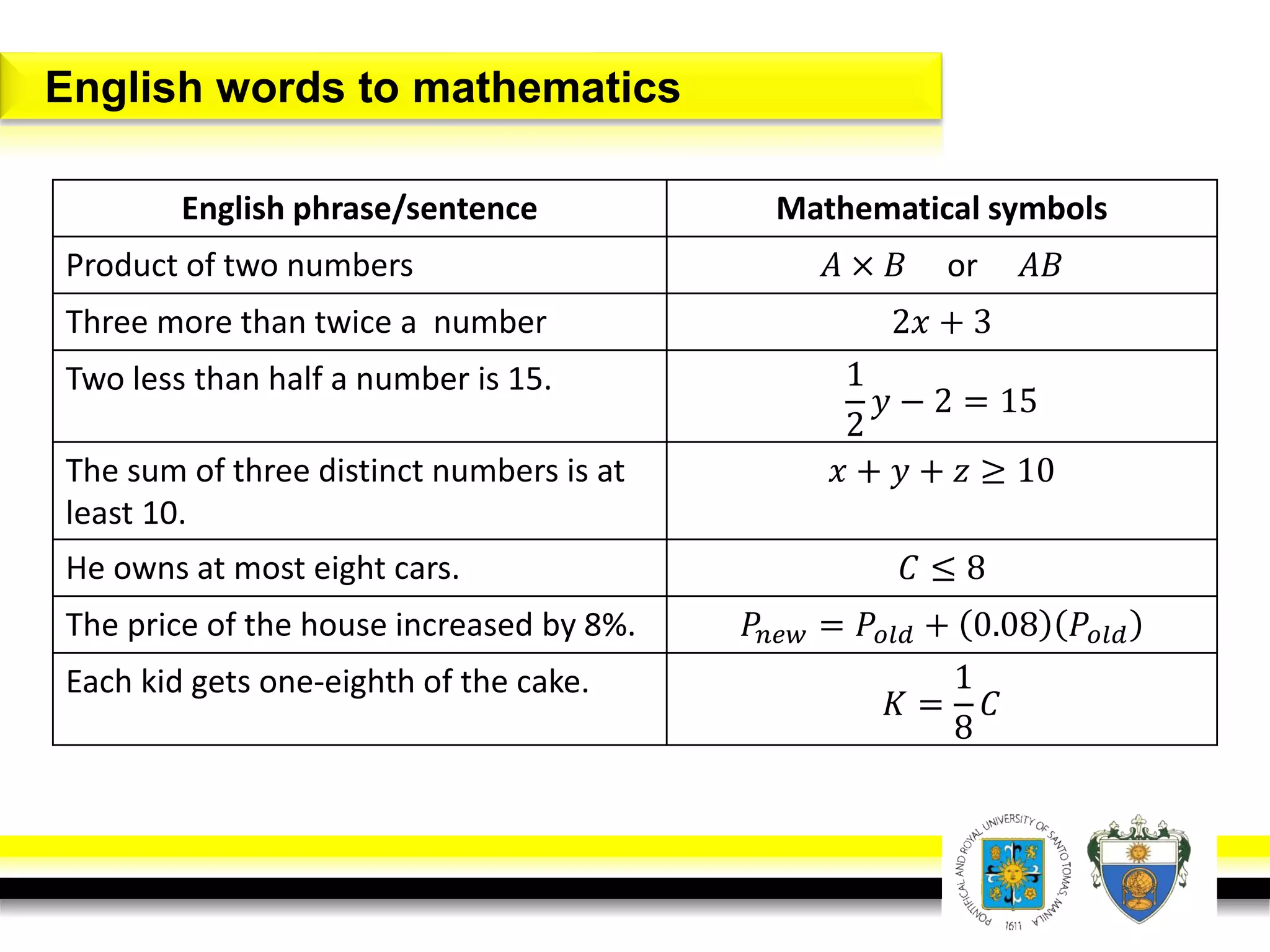
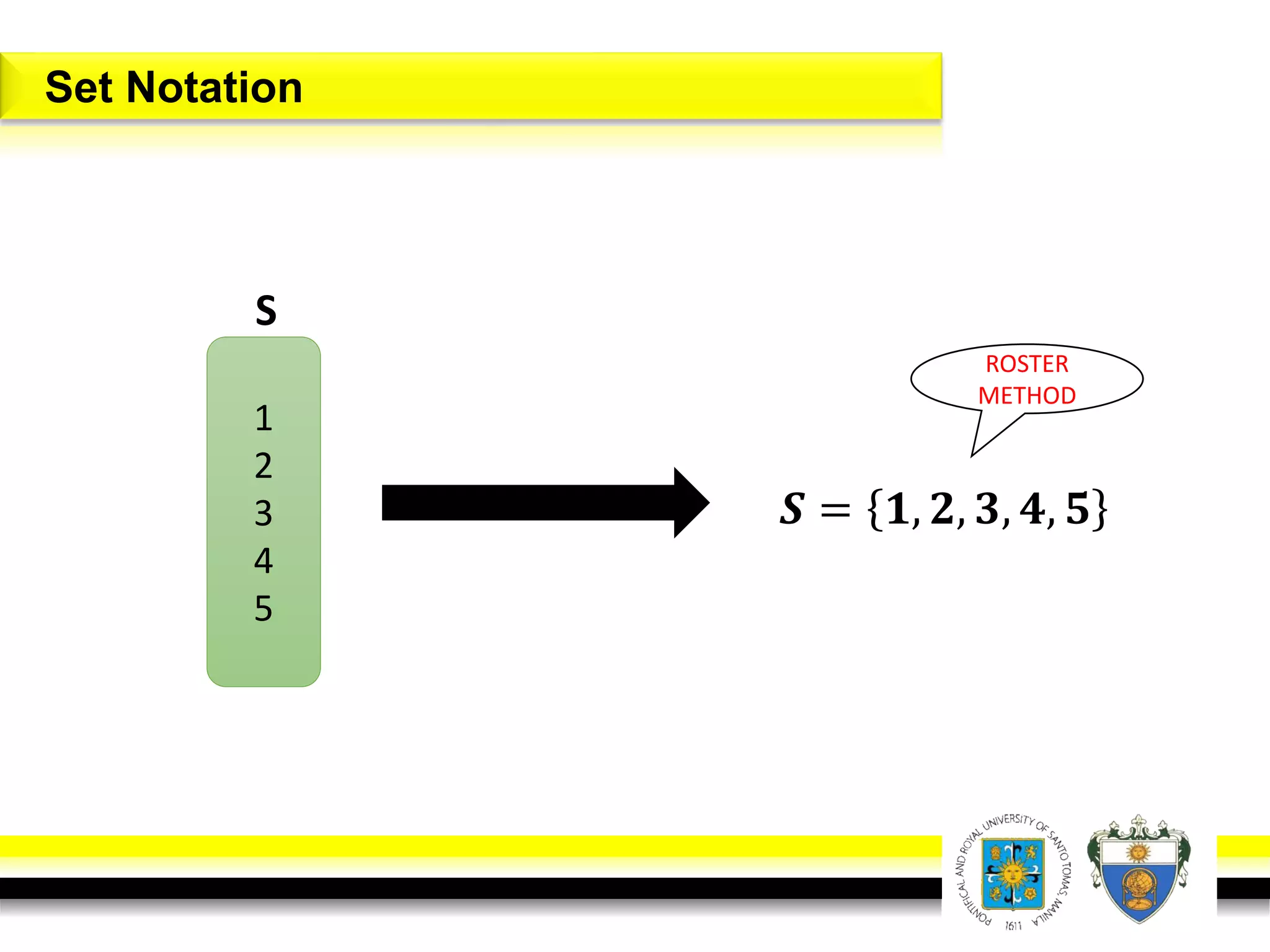
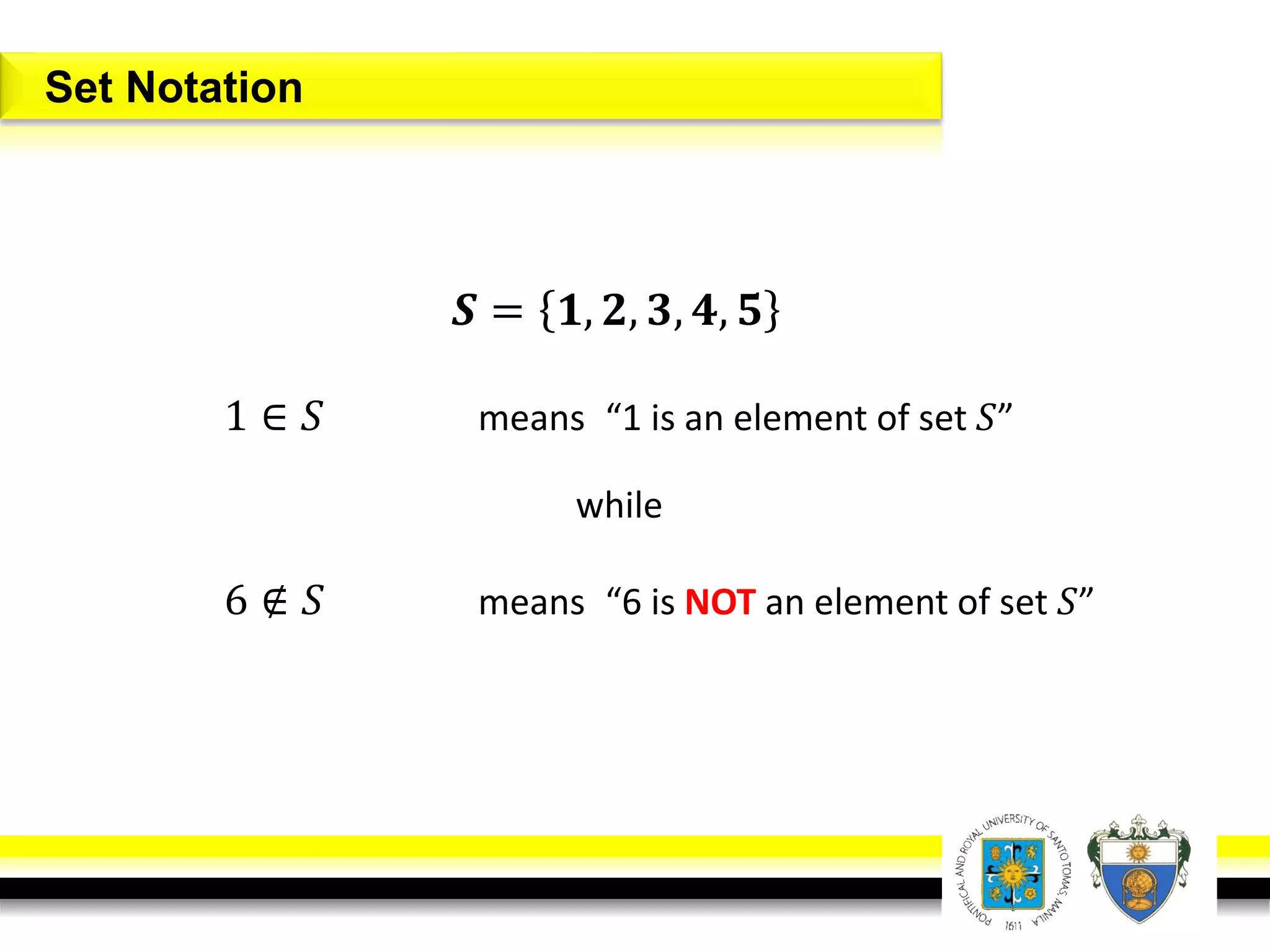
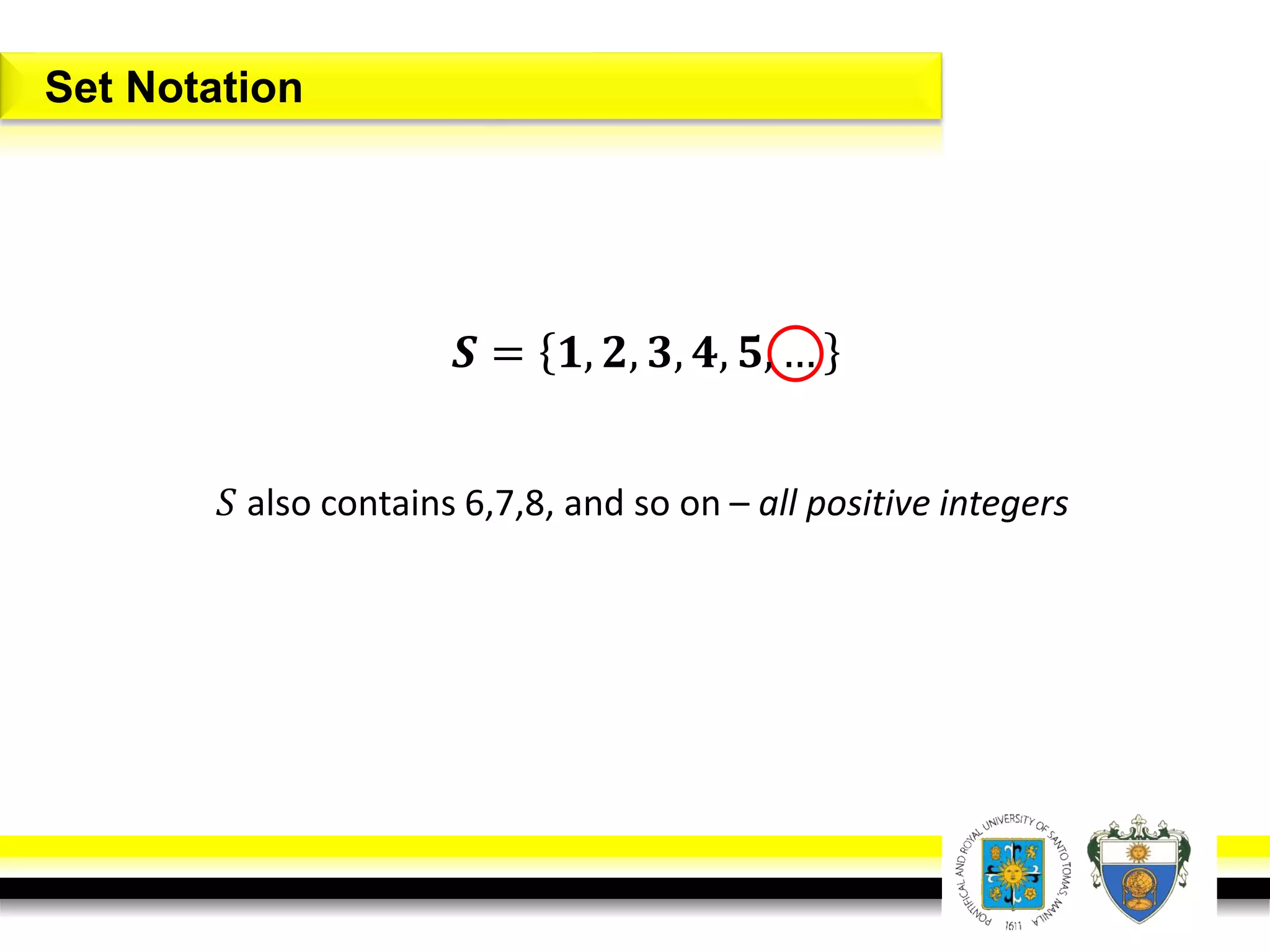
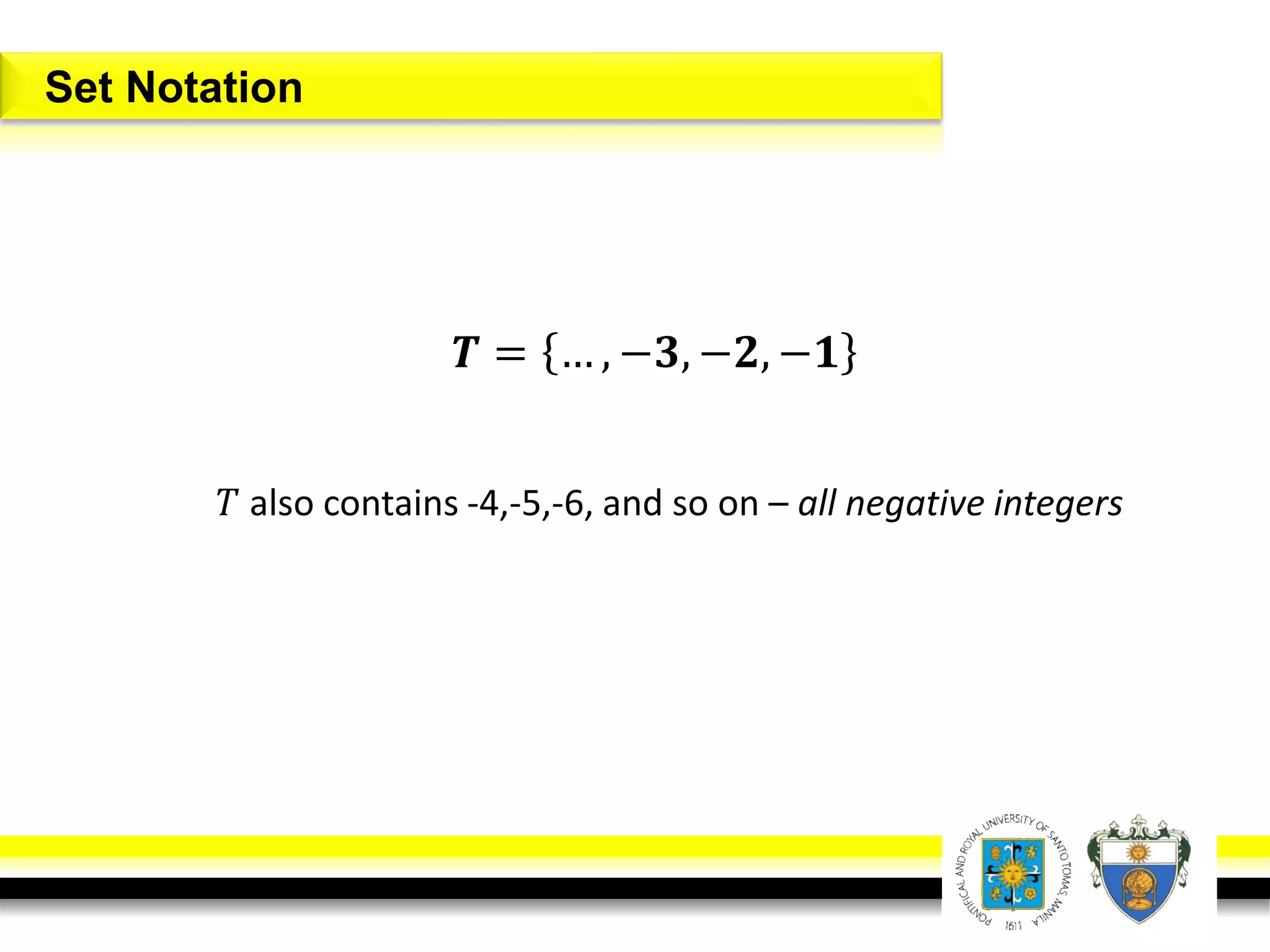
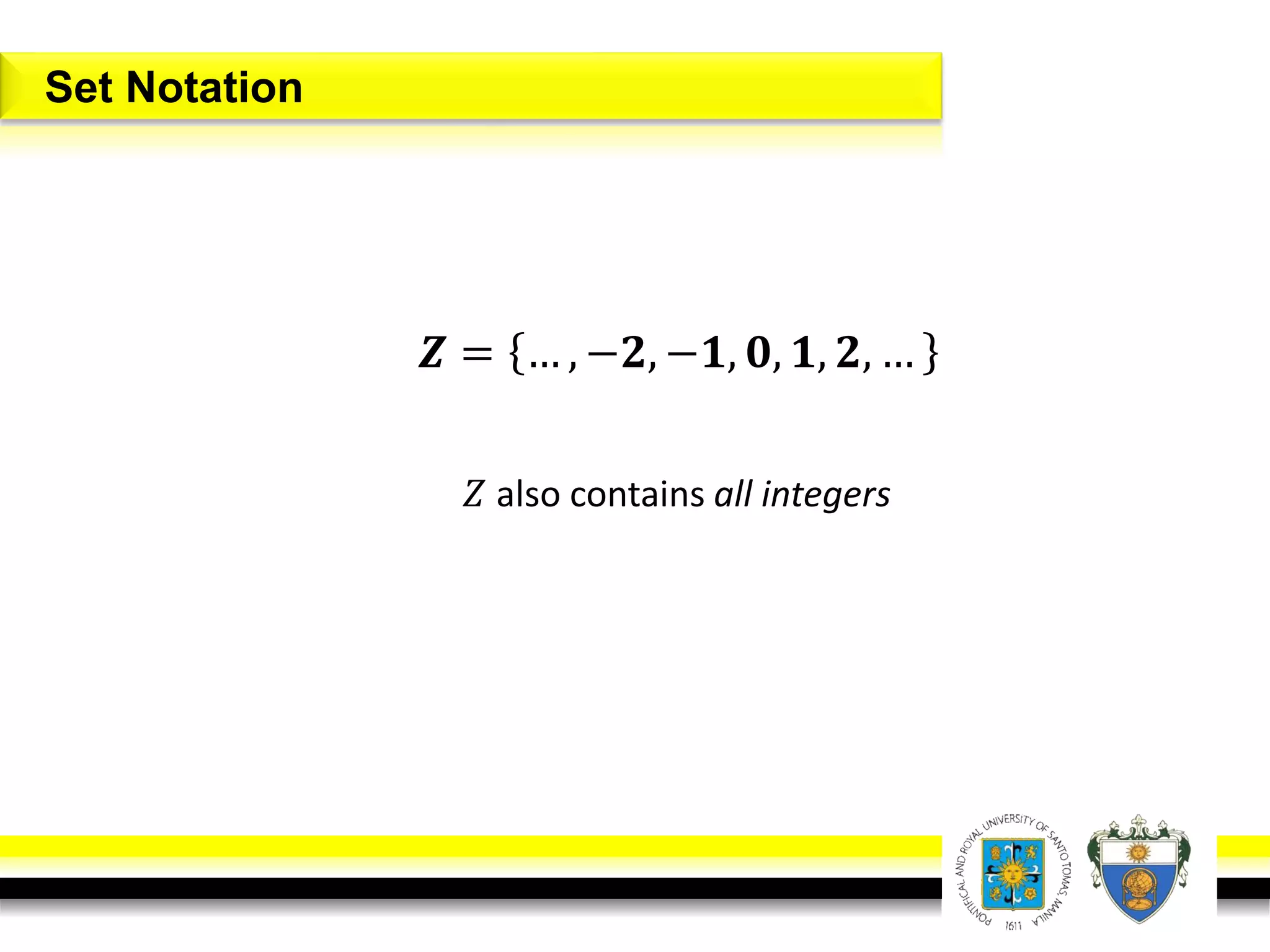
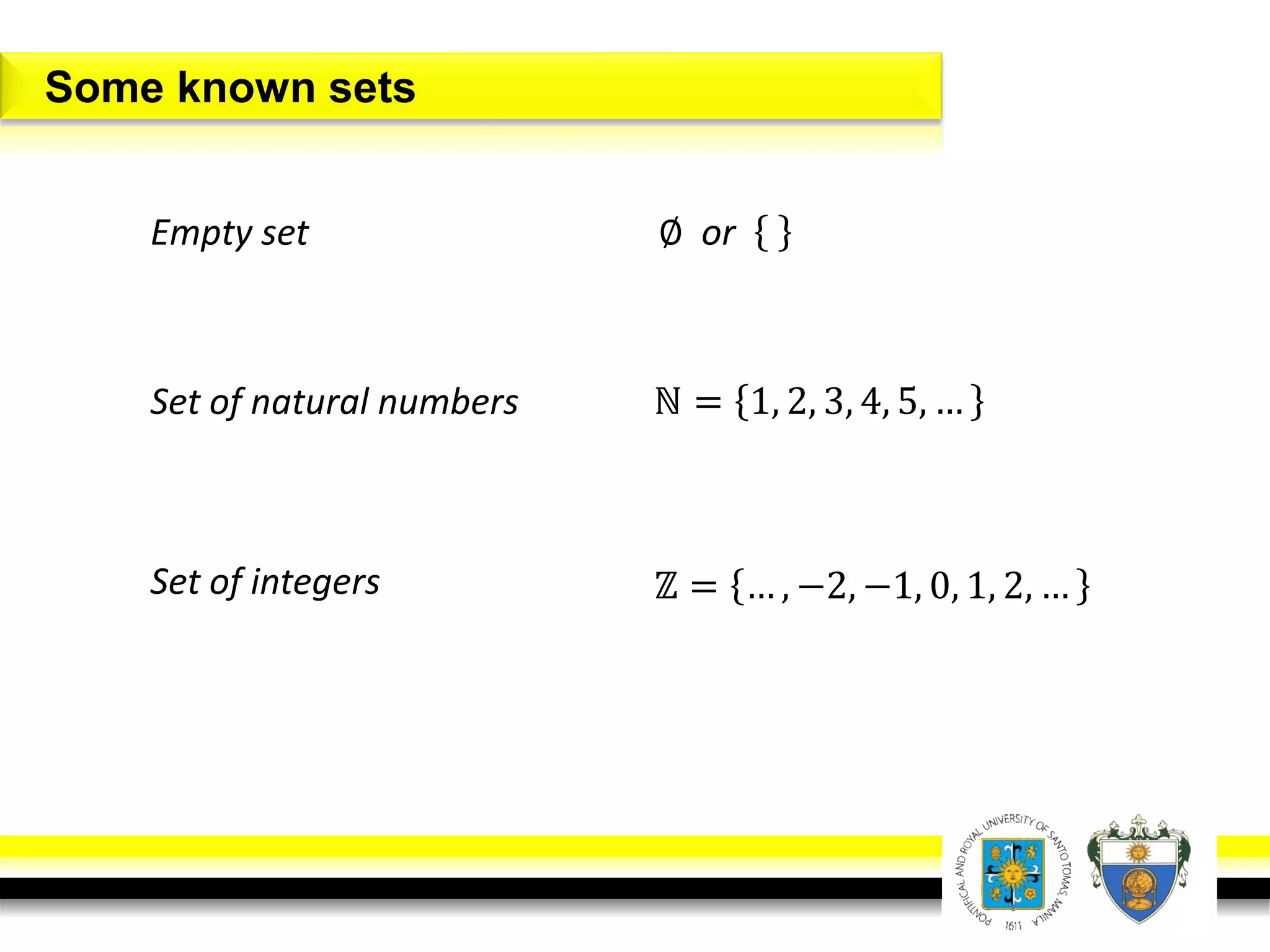
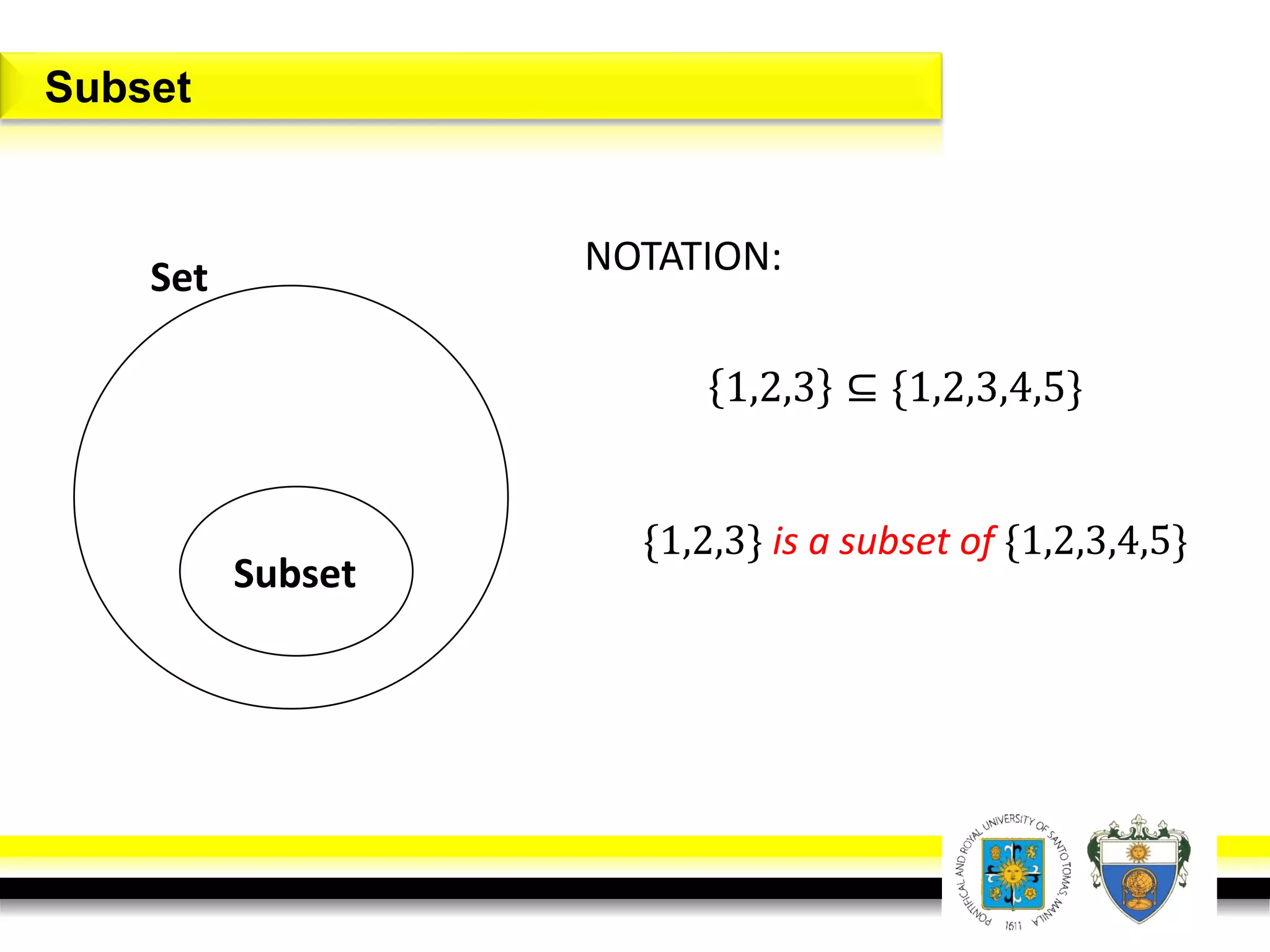
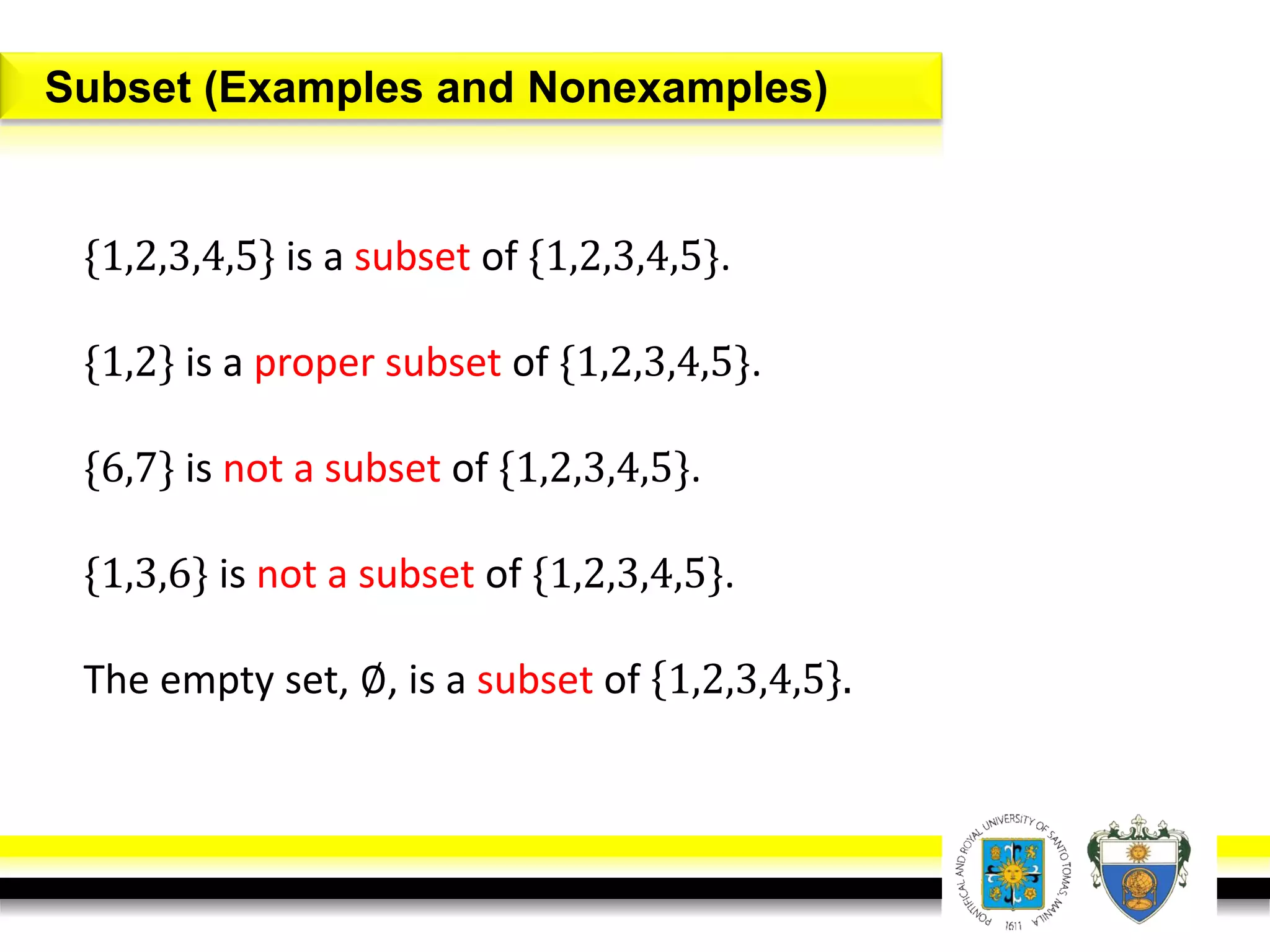
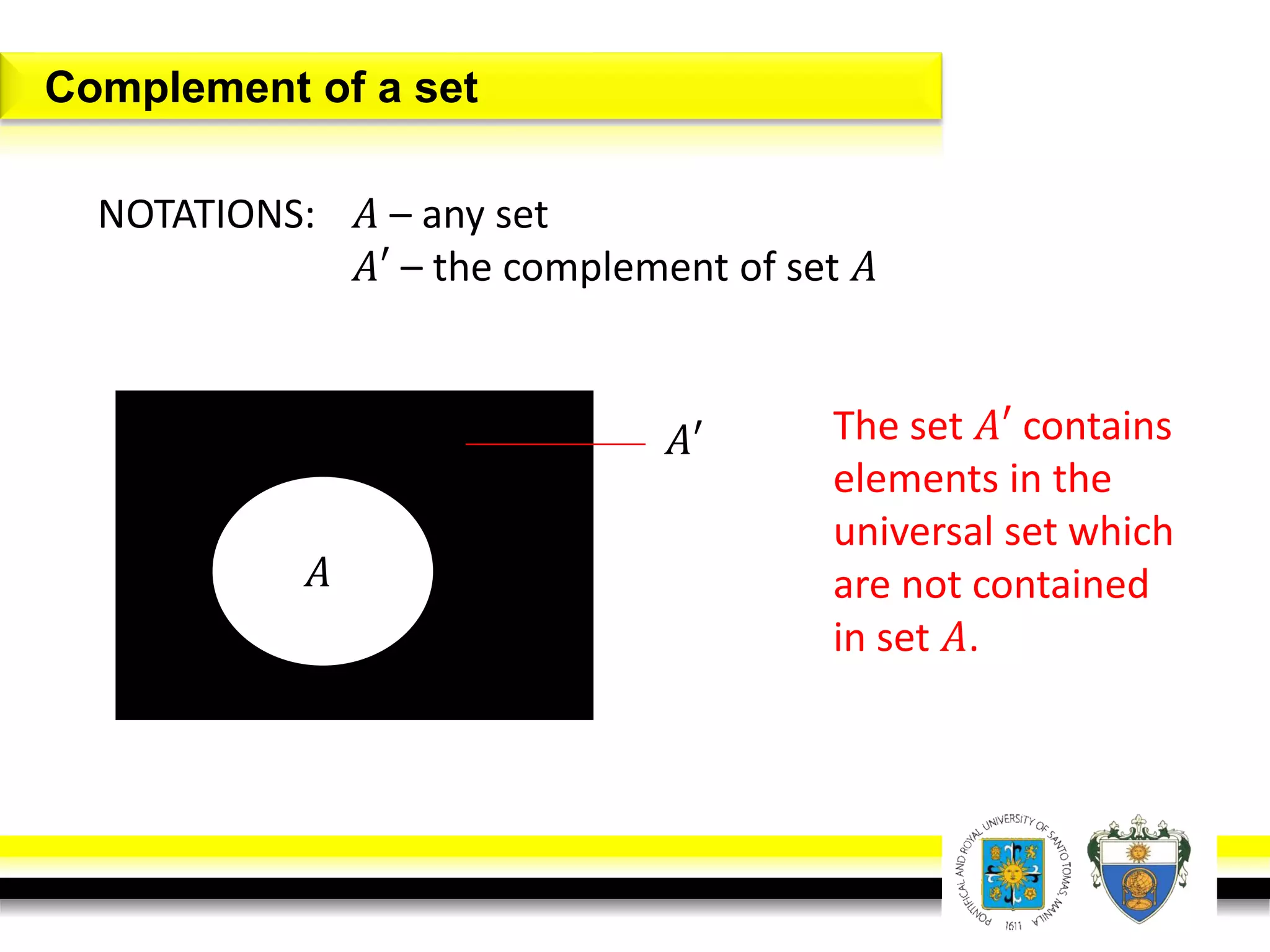
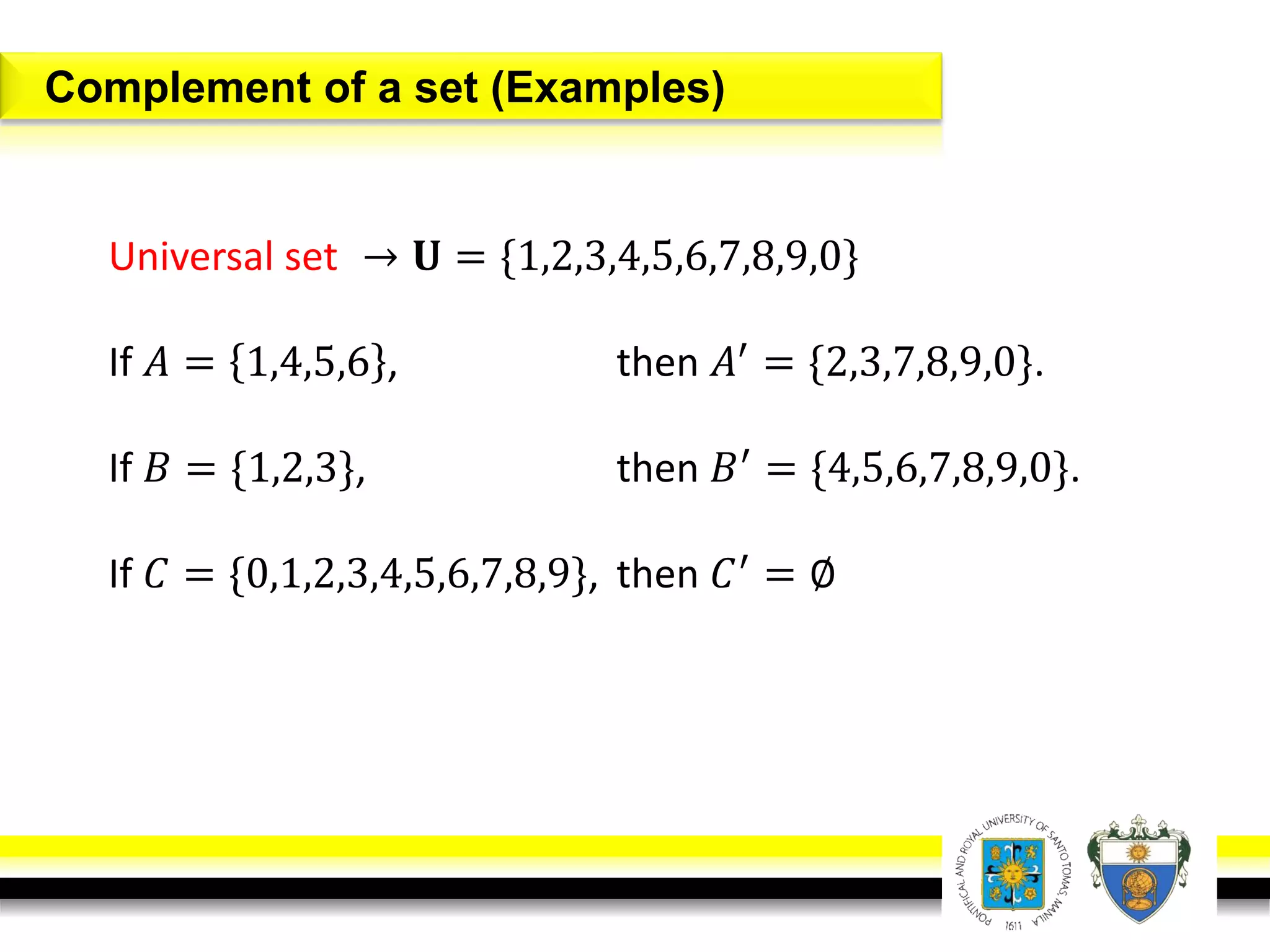
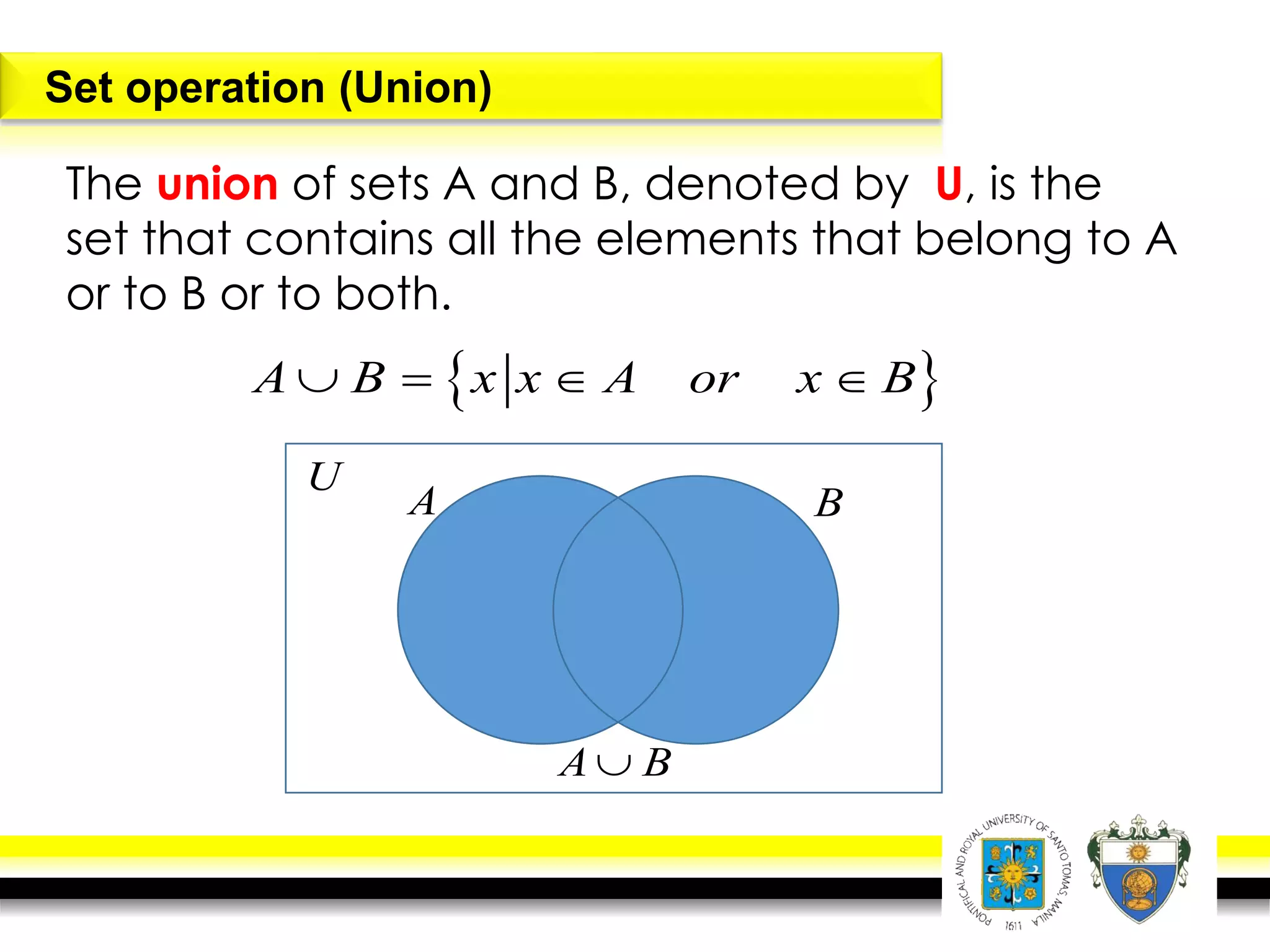
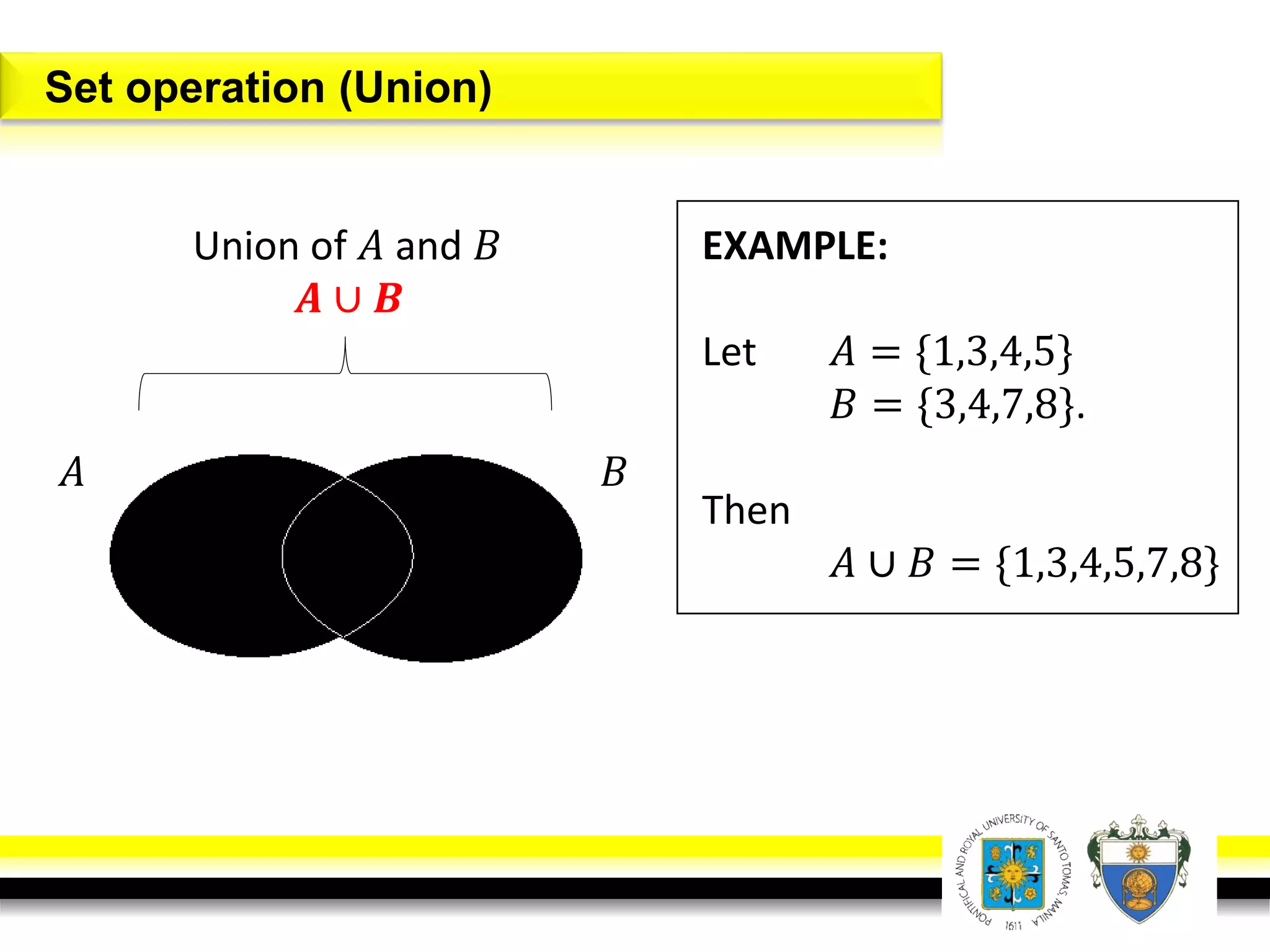
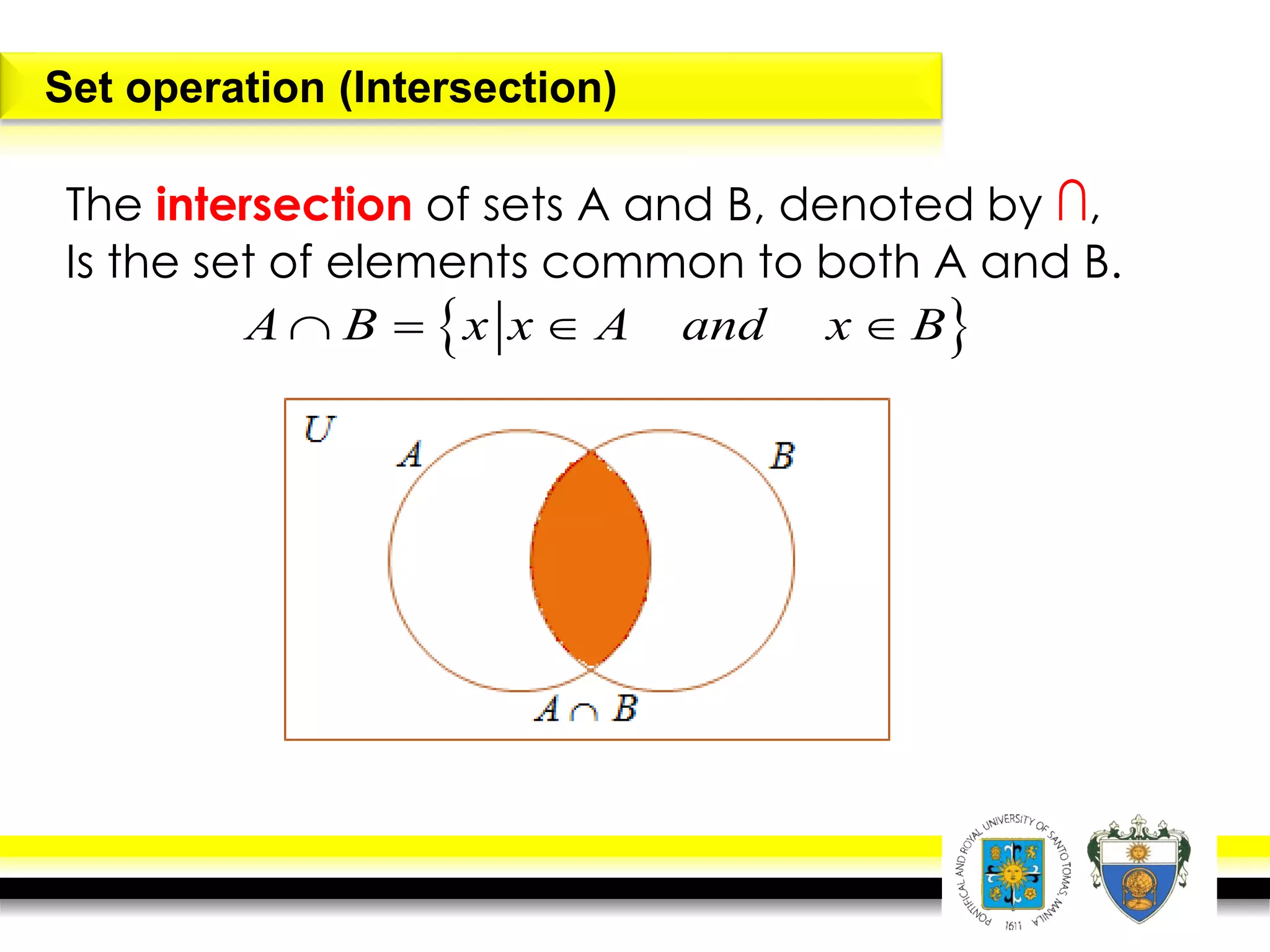
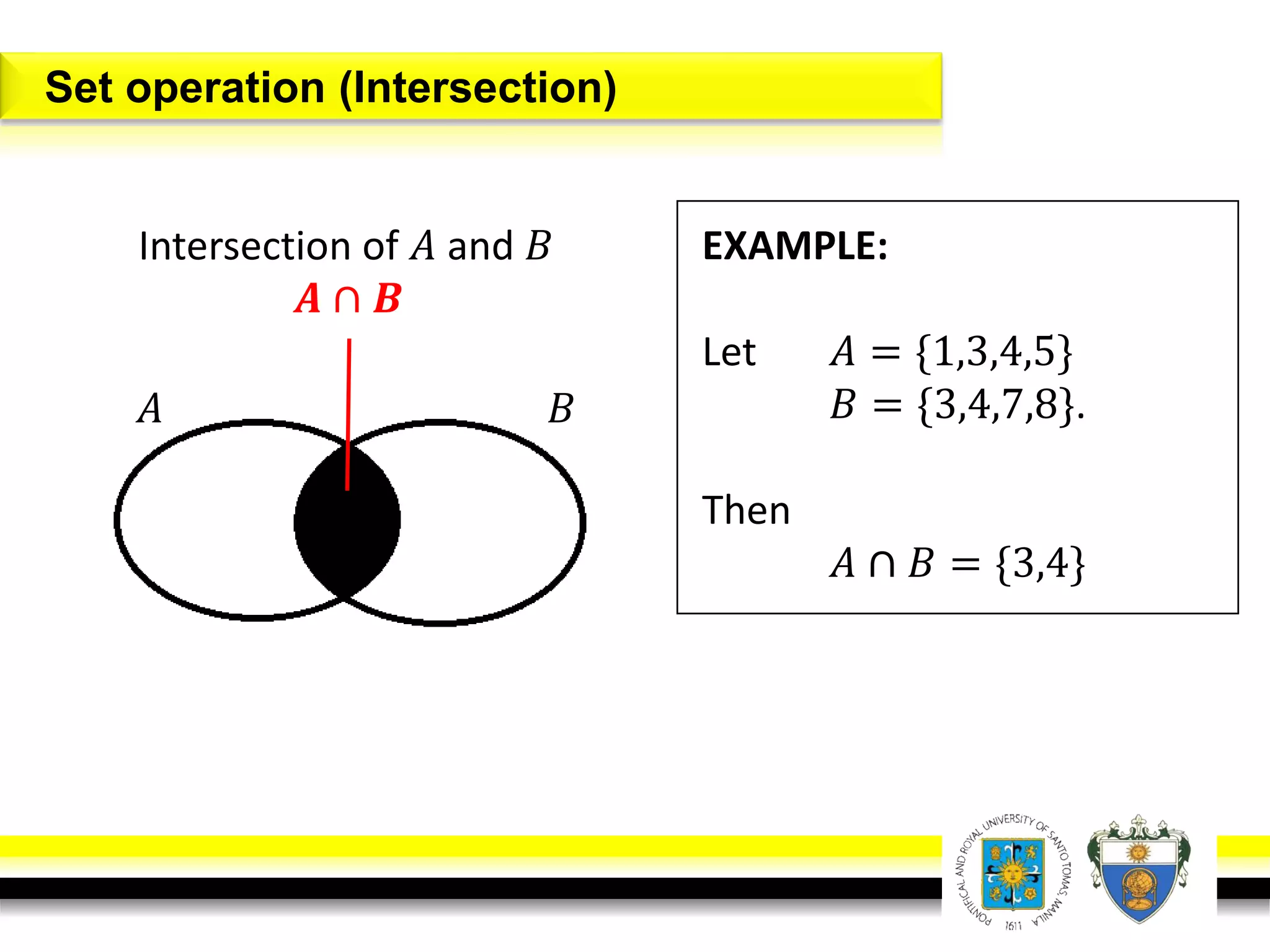
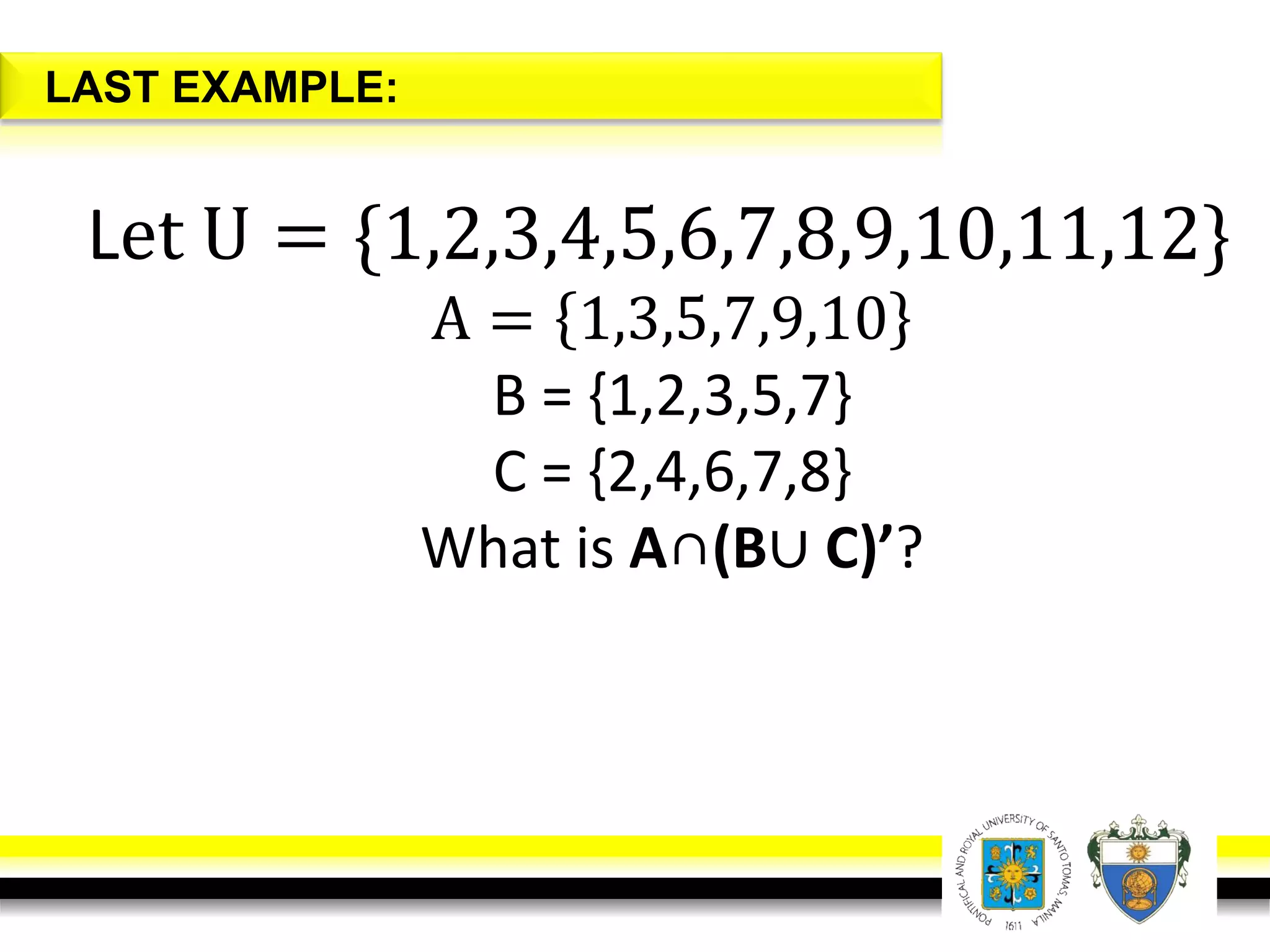
This document provides an overview of mathematical language and symbols. It discusses how mathematics can be considered a language with its own precise, concise and powerful means of communicating ideas using symbols. Examples of common symbols are presented, as well as how English phrases can be translated into mathematical expressions. Sets are then introduced as collections of objects or elements that can be represented using set notation. Operations on sets like union, intersection and complement are defined along with examples.