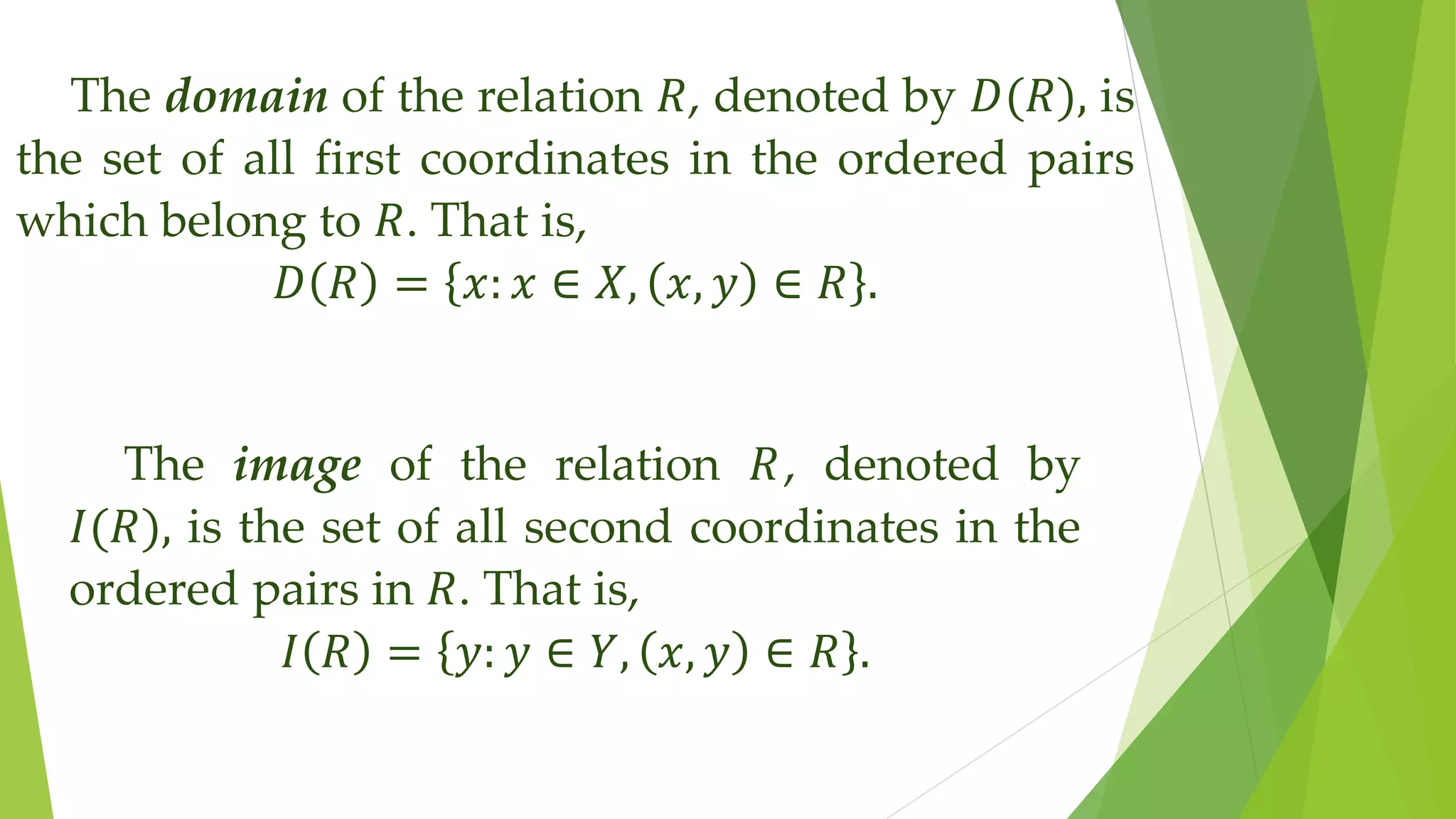
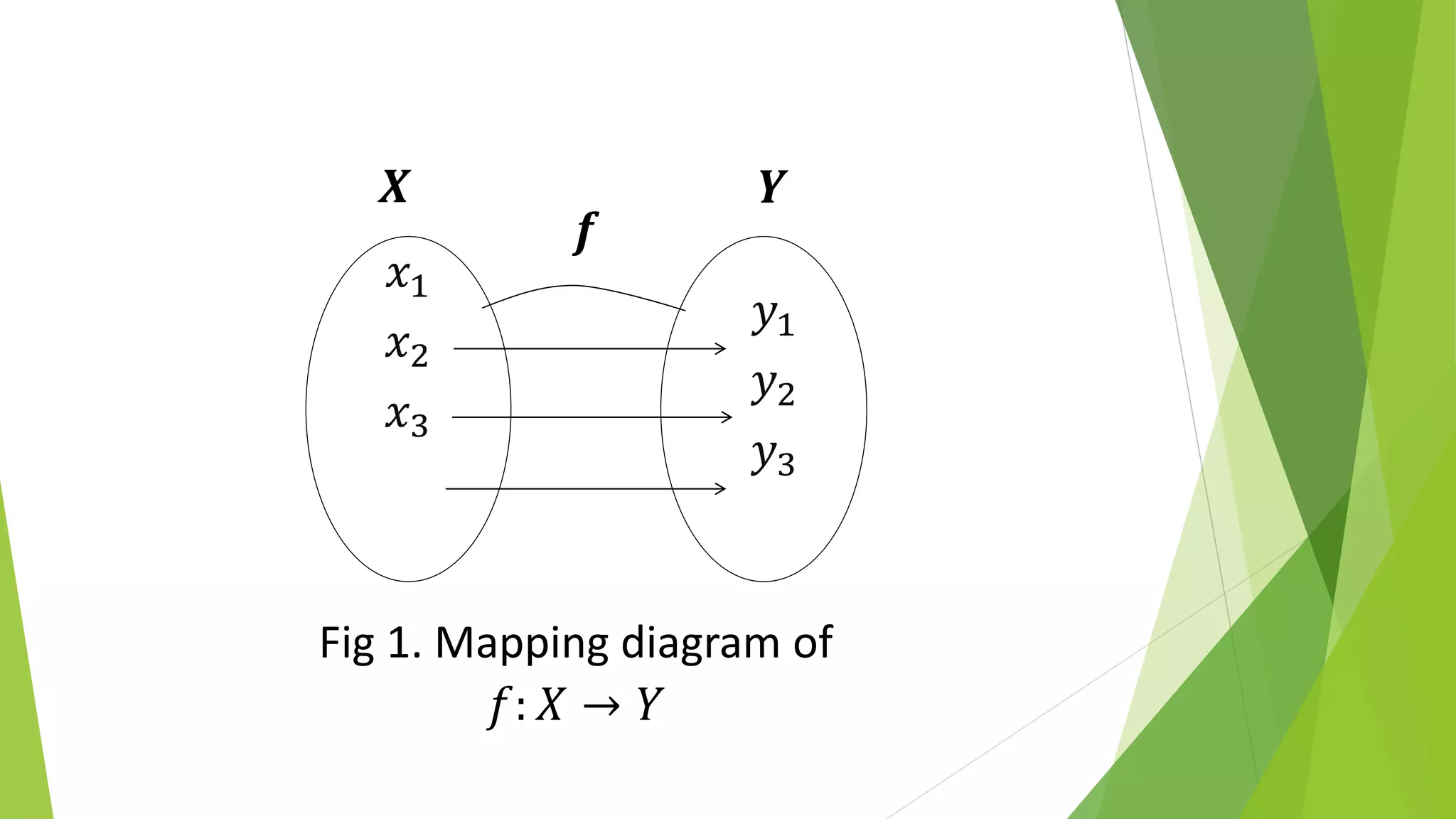
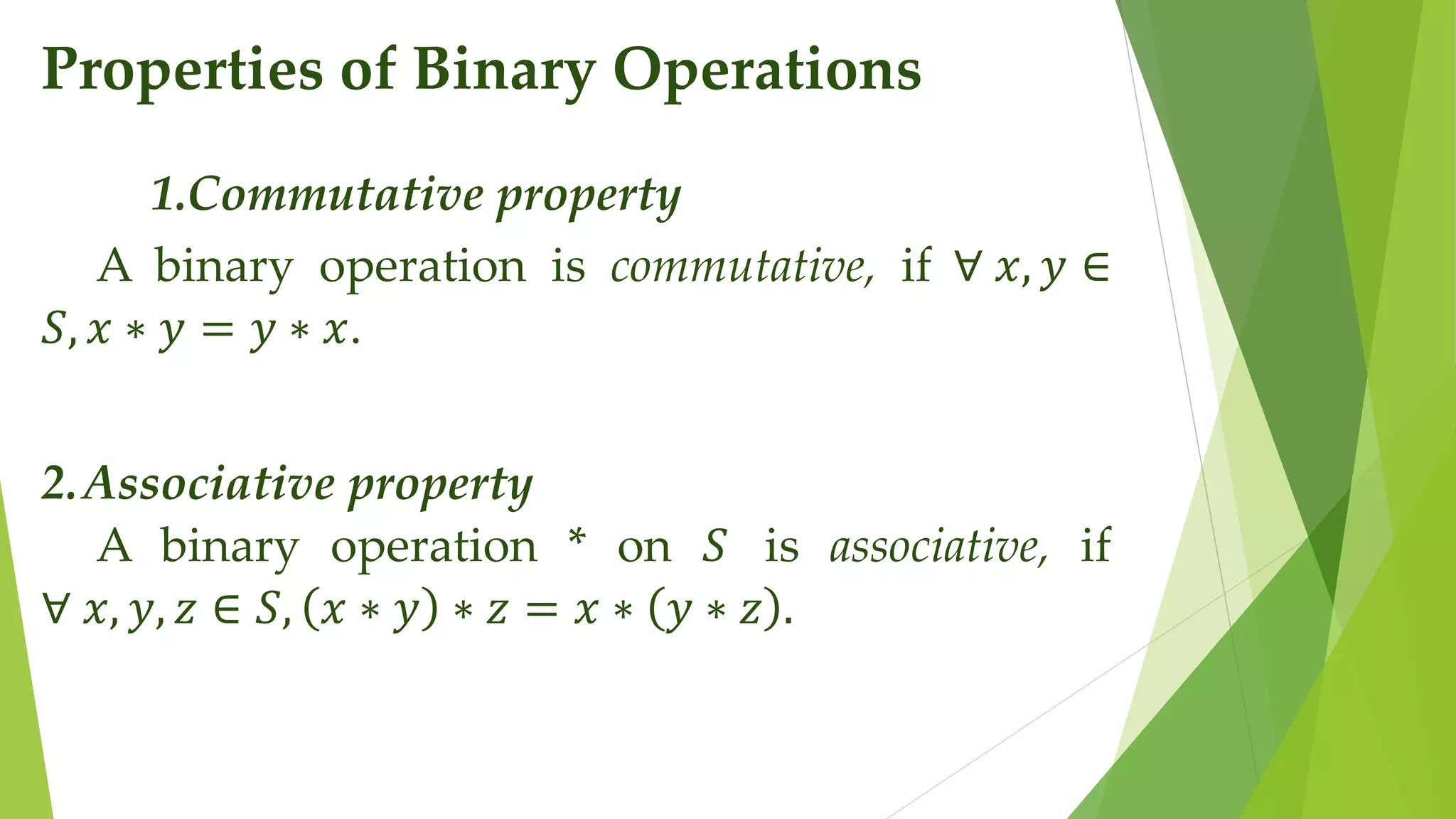
This document discusses mathematical language and symbols. It defines key concepts such as sets, relations, functions, and binary operations. Sets are collections of distinct objects that can be defined using a roster or rule. Relations pair elements between two sets. A function is a special type of relation where each input is paired with exactly one output. Binary operations take two inputs from a set and return an output in that same set. Common properties of binary operations include commutativity and associativity.




![Some Classification of Symbols
4. Grouping Symbols include parentheses ( ),
curly brackets or braces { }, or square brackets [ ].
5. Variables are another form of mathematical
symbol. These are used when quantities take
different values. These usually include letters of
the alphabet.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2mathematicallanguageandsymbols-221111044330-6001c77f/75/Chapter-2-Mathematical-Language-and-Symbols-pdf-9-2048.jpg)