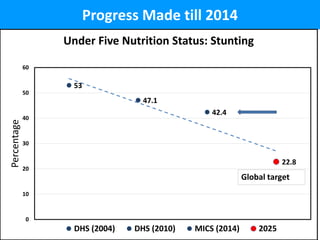
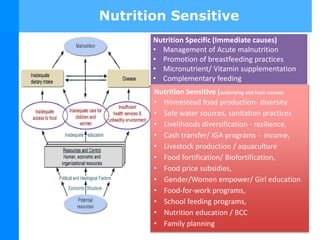
The document defines nutrition-sensitive interventions as multi-sectorial strategies designed to improve nutrition outcomes by addressing underlying determinants of malnutrition. It highlights the importance of these approaches in combating malnutrition, especially in contexts like Malawi, where specific targets need to be met within a decade. The text further discusses various specific and sensitive nutrition actions necessary for effectively tackling malnutrition and outlines the complexity of implementing such interventions.