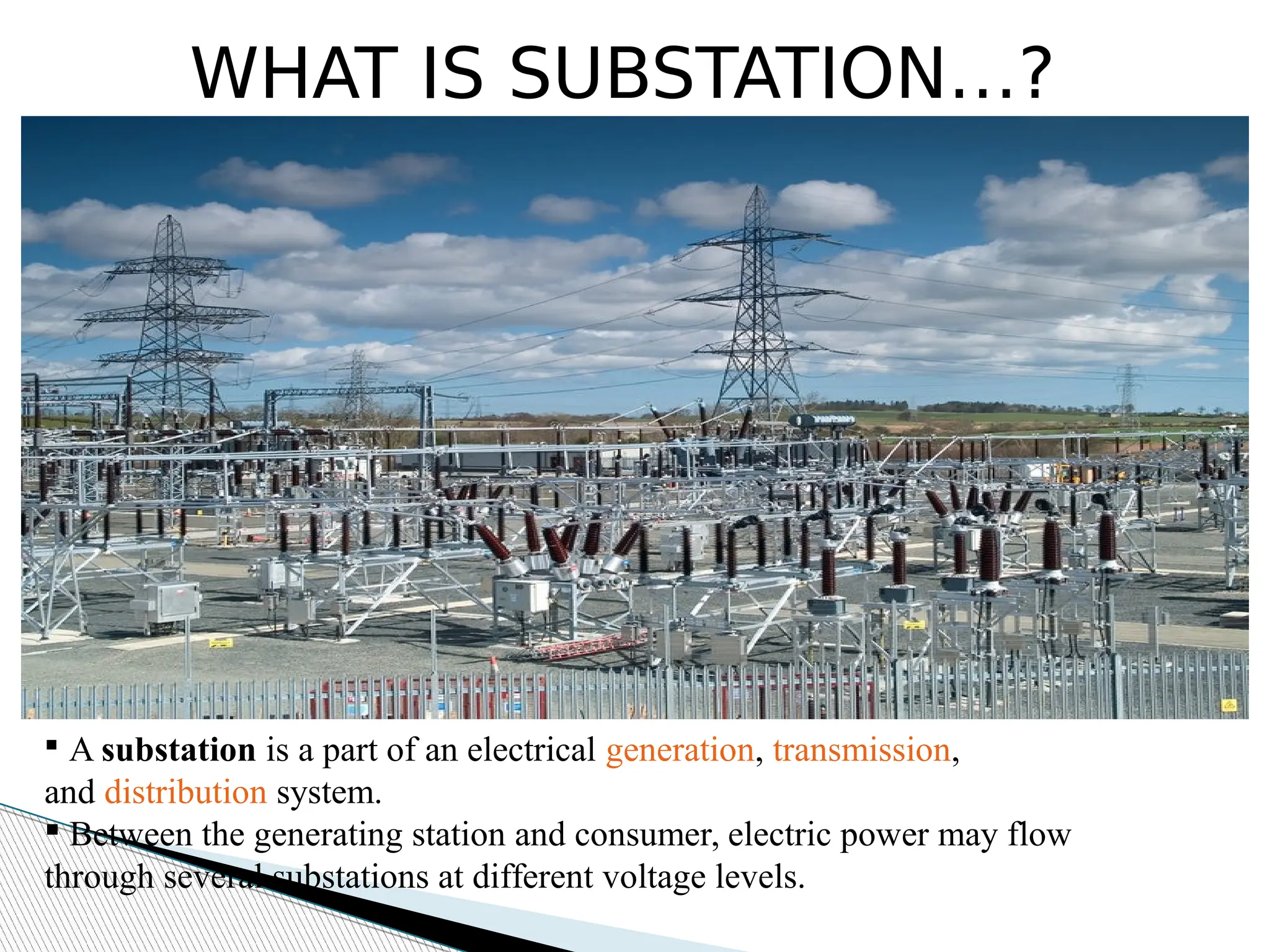
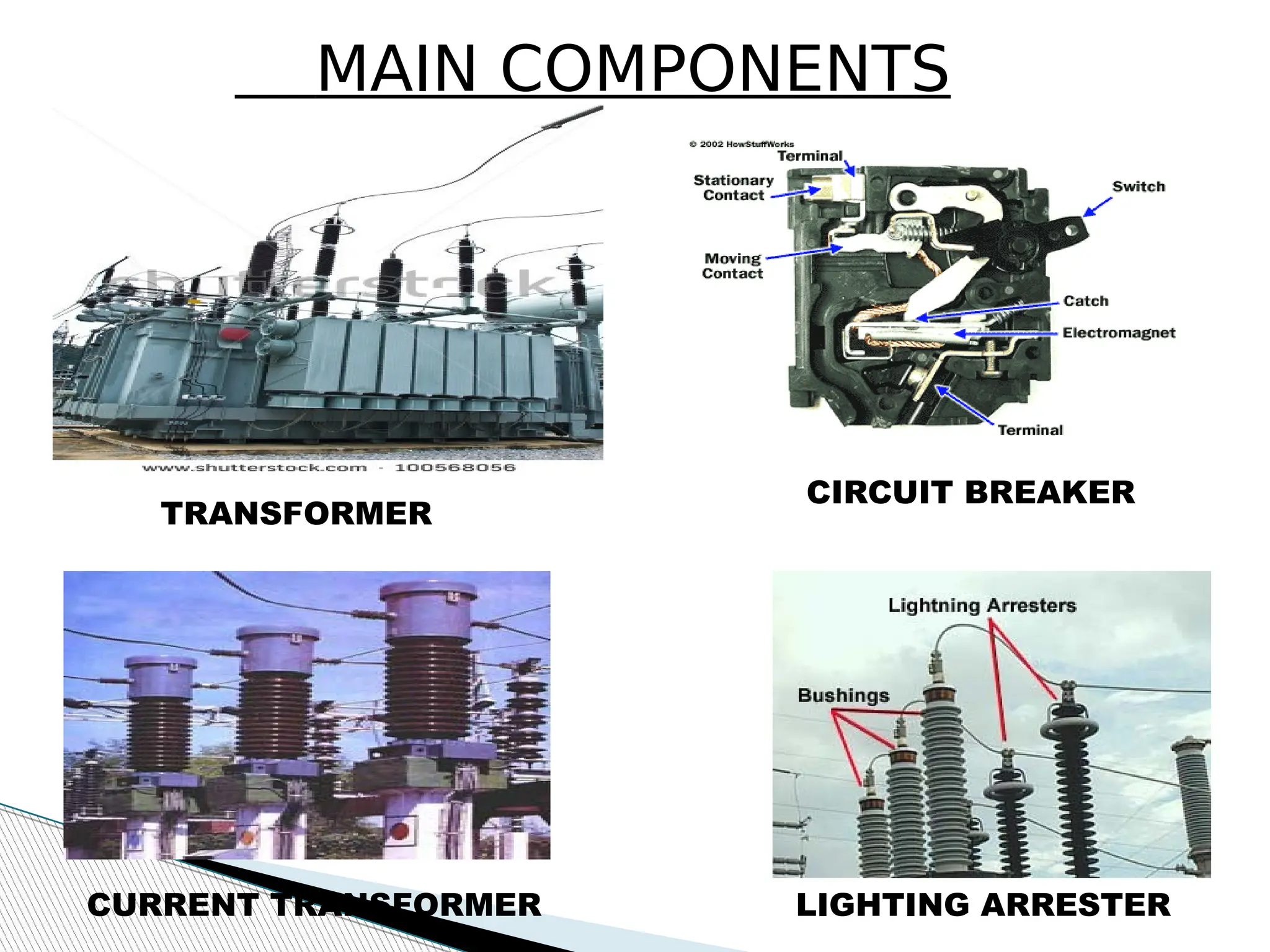
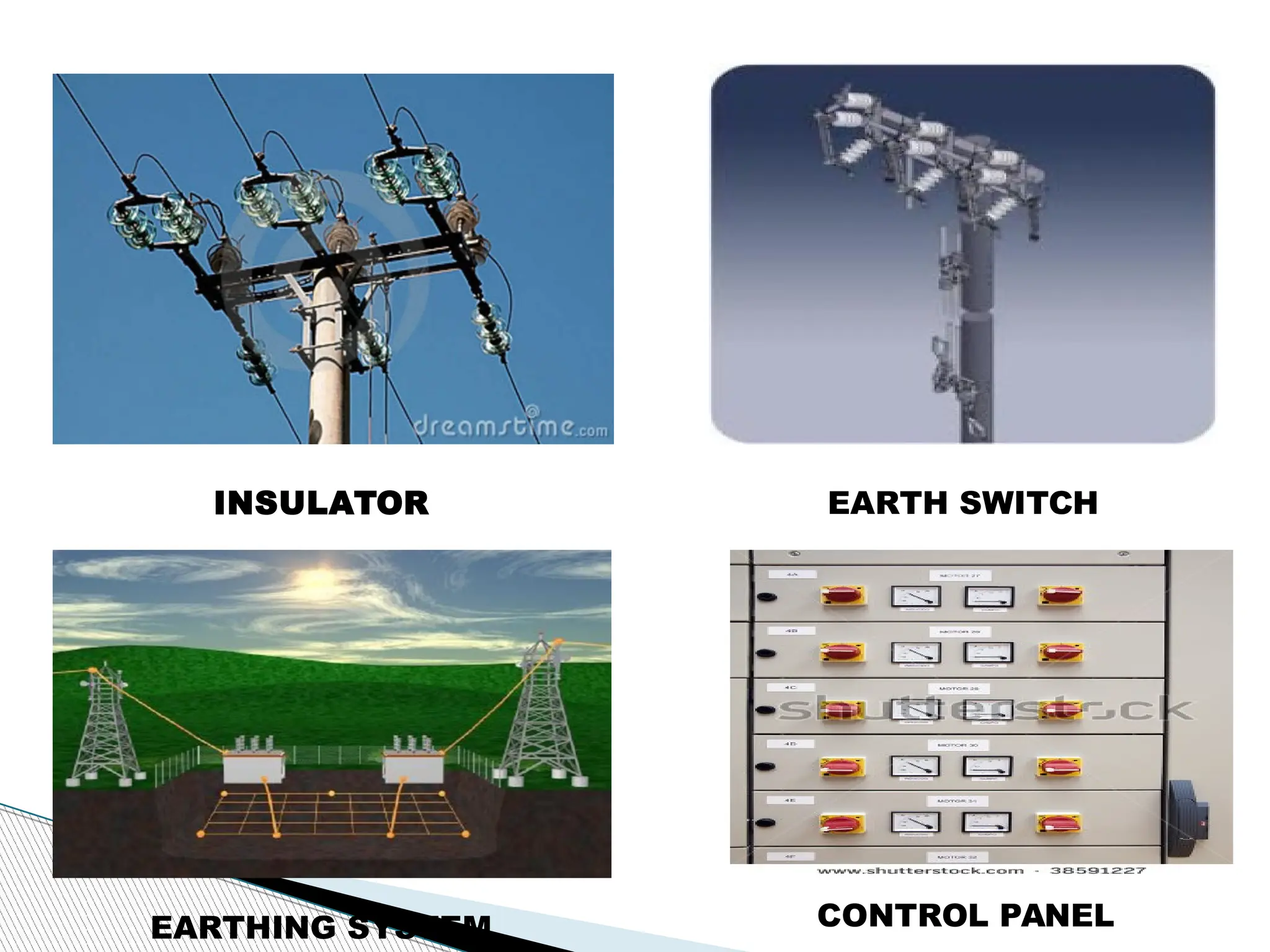
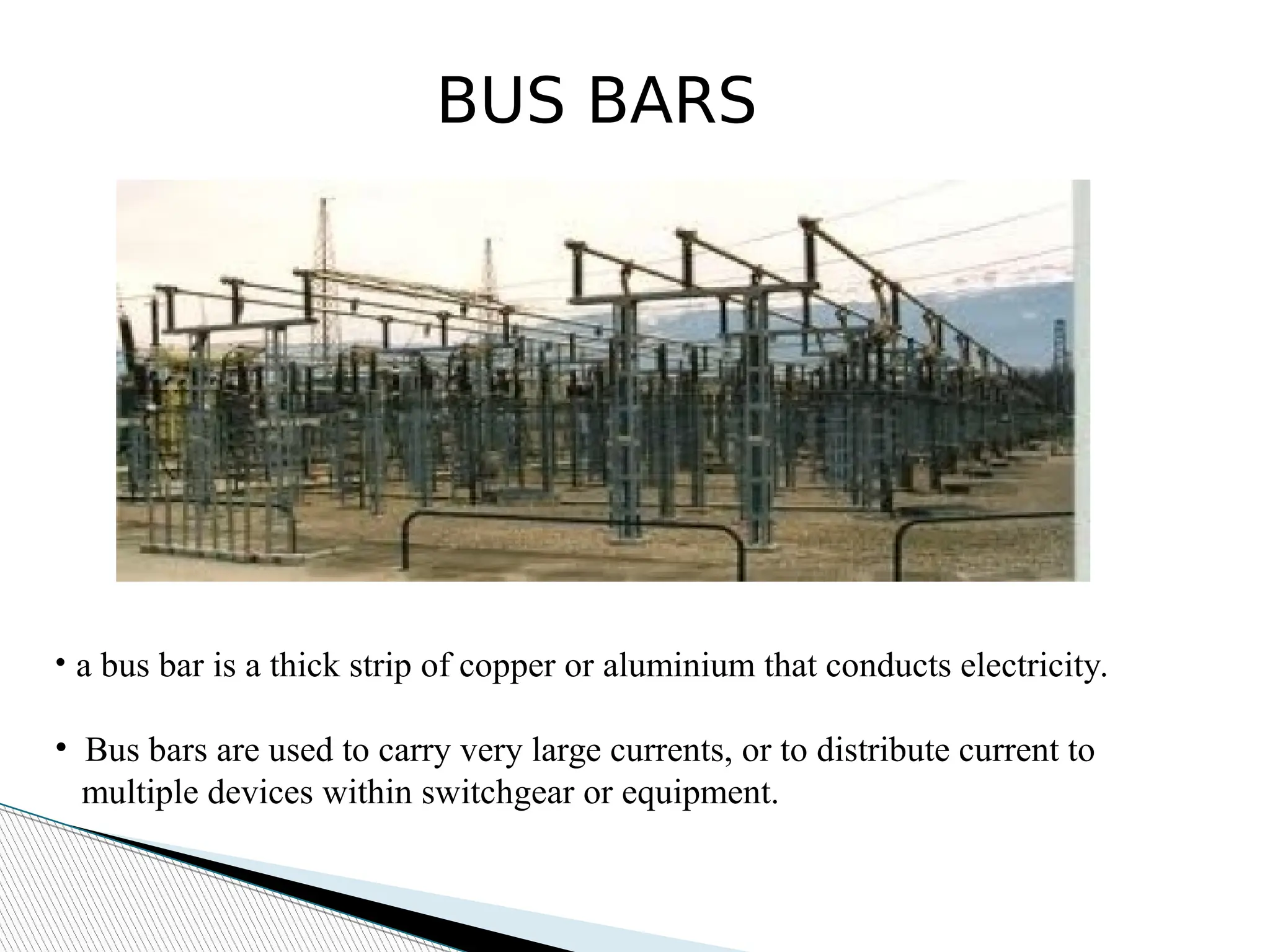
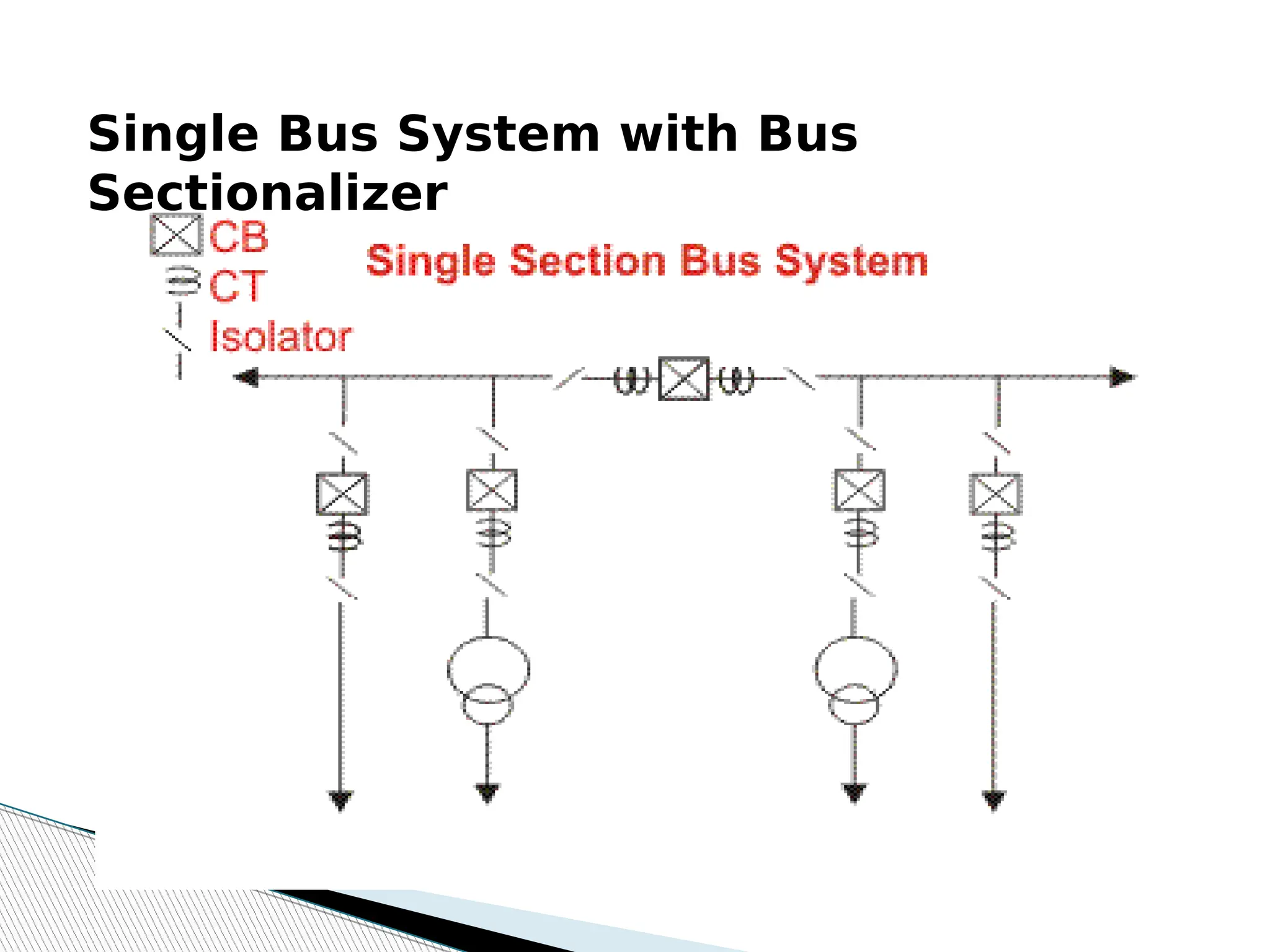
A substation is a critical component of electrical generation, transmission, and distribution systems that facilitates voltage transformation and power flow management. Key components include transformers, circuit breakers, isolators, current transformers, and earthing systems, each fulfilling specific roles in safety and operational efficiency. Various bus systems such as single bus, double bus, and ring bus configurations enable varying levels of flexibility and reliability in maintaining power distribution without interruptions during maintenance.