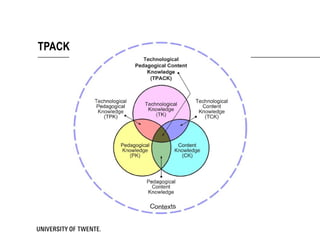
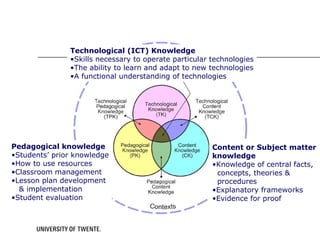
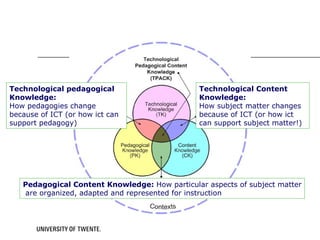
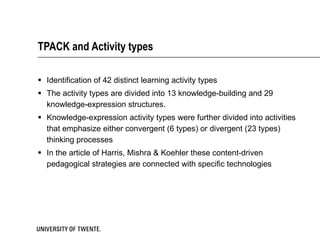
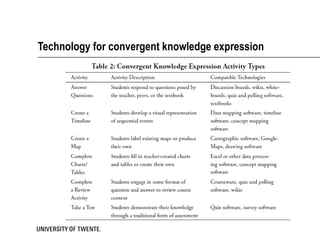
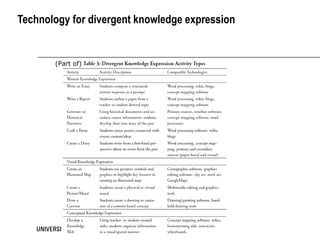
The document discusses the TPACK framework, which emphasizes the integration of content, pedagogy, and technology for effective teaching in the 21st century. It highlights the importance of teachers developing competencies in various areas, such as ICT literacy, creativity, and critical thinking, to enhance student learning. Additionally, it introduces activities like the TPACK game to facilitate discussion and reflection on the relationships between technology, pedagogy, and content in educational contexts.










![Want to know more? Literature study (in translation at the moment) Development of TPACK interventions & instruments Studies in the Netherlands, Belgium, Kuwait, Tanzania, Ghana, ….. and Poland???? Please contact me! Petra Fisser University of Twente http://users.gw.utwente.nl/fisser [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2010-12-13warschauworkshop21sttpackpetrafisser-101216162907-phpapp02/85/21st-Century-Skills-TPACK-Workshop-17-320.jpg)