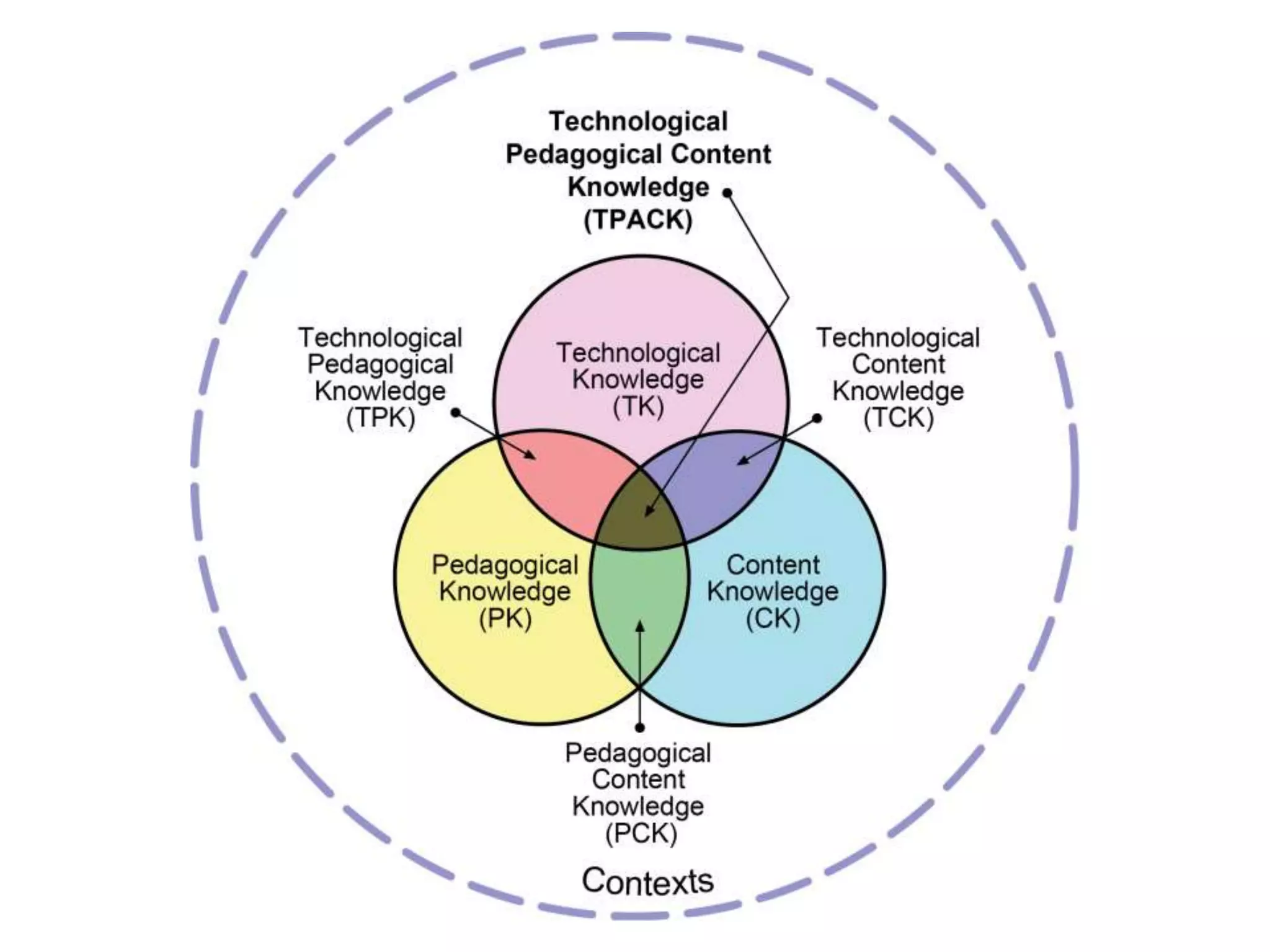
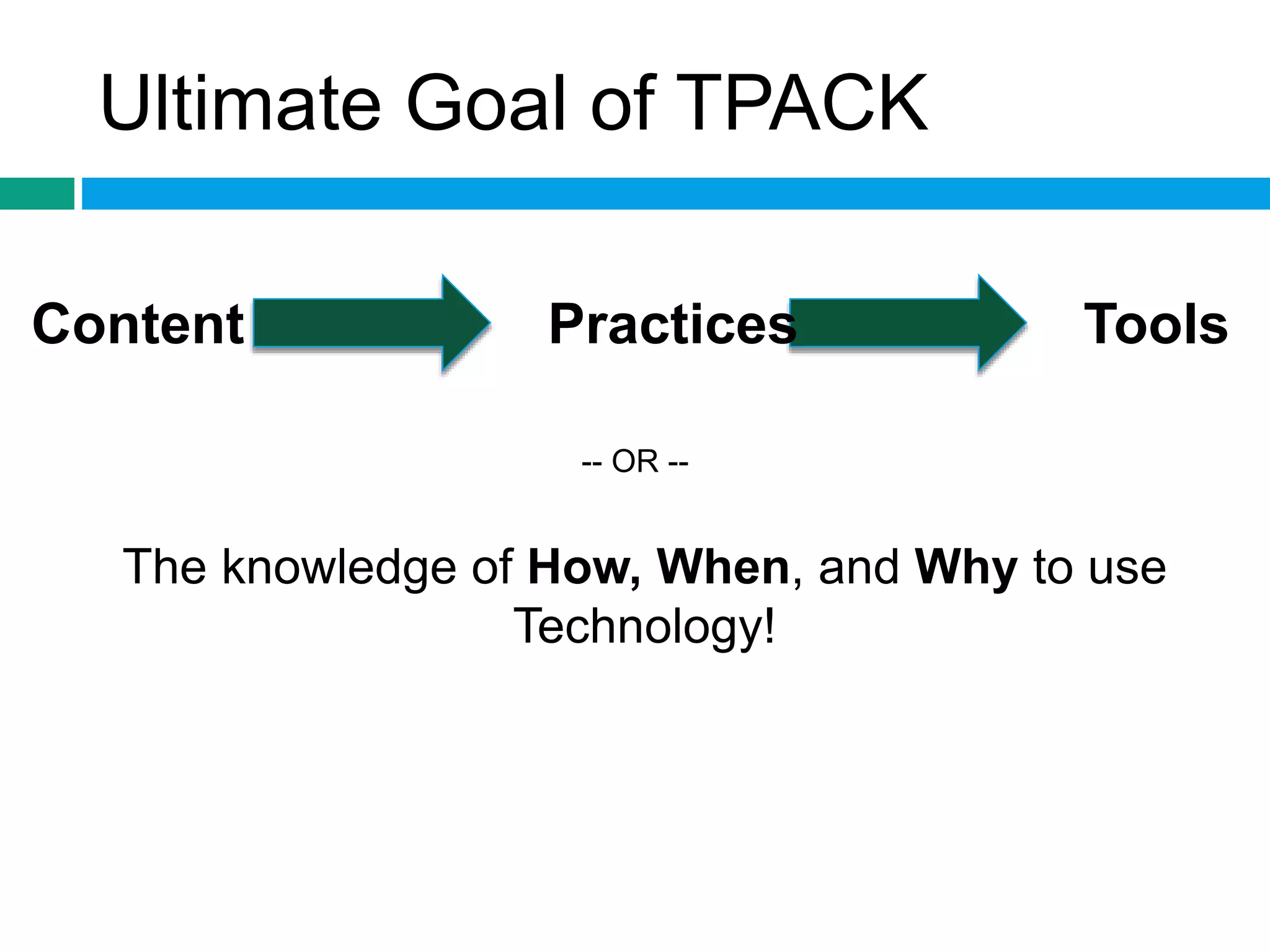
This document discusses the strategic integration of technology into instruction using the TPACK framework. TPACK stands for technological pedagogical content knowledge and refers to the interplay between a teacher's knowledge of technology, pedagogy and content. The document outlines the 7 components of TPACK, including content knowledge, pedagogical knowledge, technological knowledge, pedagogical content knowledge, technological content knowledge, technological pedagogical knowledge, and technological pedagogical content knowledge. It provides examples of each component and has teachers do activities to apply TPACK to choosing a technology to support a given content and pedagogical approach. The goal of TPACK is to understand how, when and why to use technology for effective