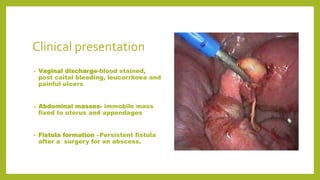
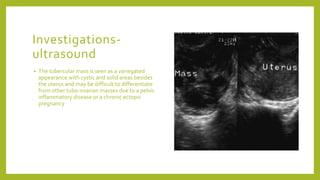
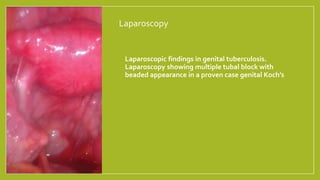
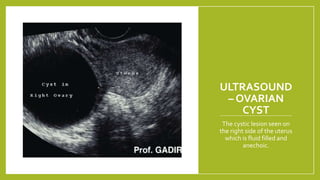
Genital tuberculosis is a secondary infection that primarily affects the fallopian tubes and is a significant cause of infertility, with symptoms often presenting long after primary pulmonary infection has healed. Diagnosis involves a combination of clinical, radiological, and laboratory tests, while treatment typically requires chemotherapy and may necessitate surgical intervention for severe cases. The prognosis for fertility restoration is low, with only about 10% of patients achieving conception post-treatment.