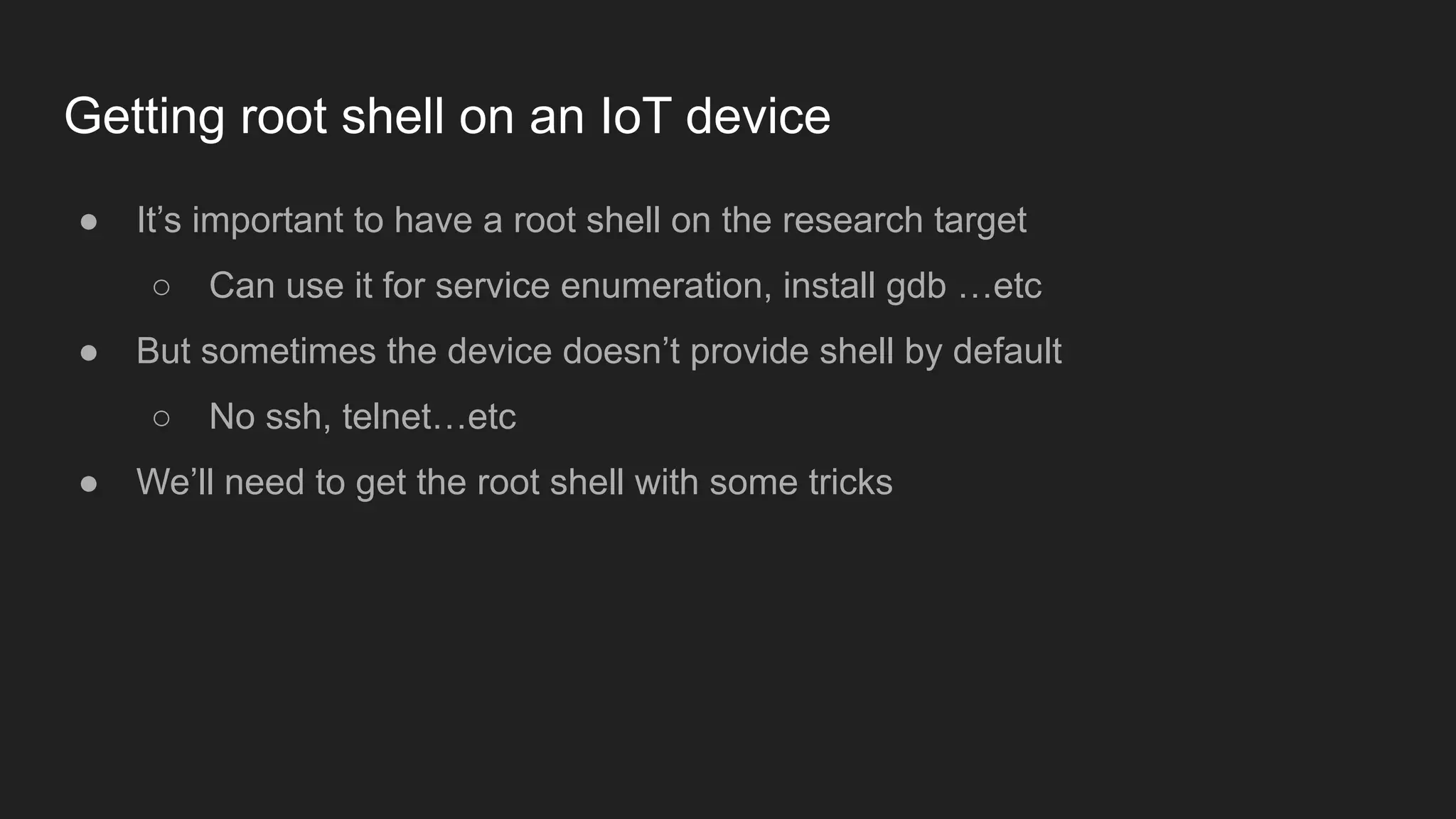
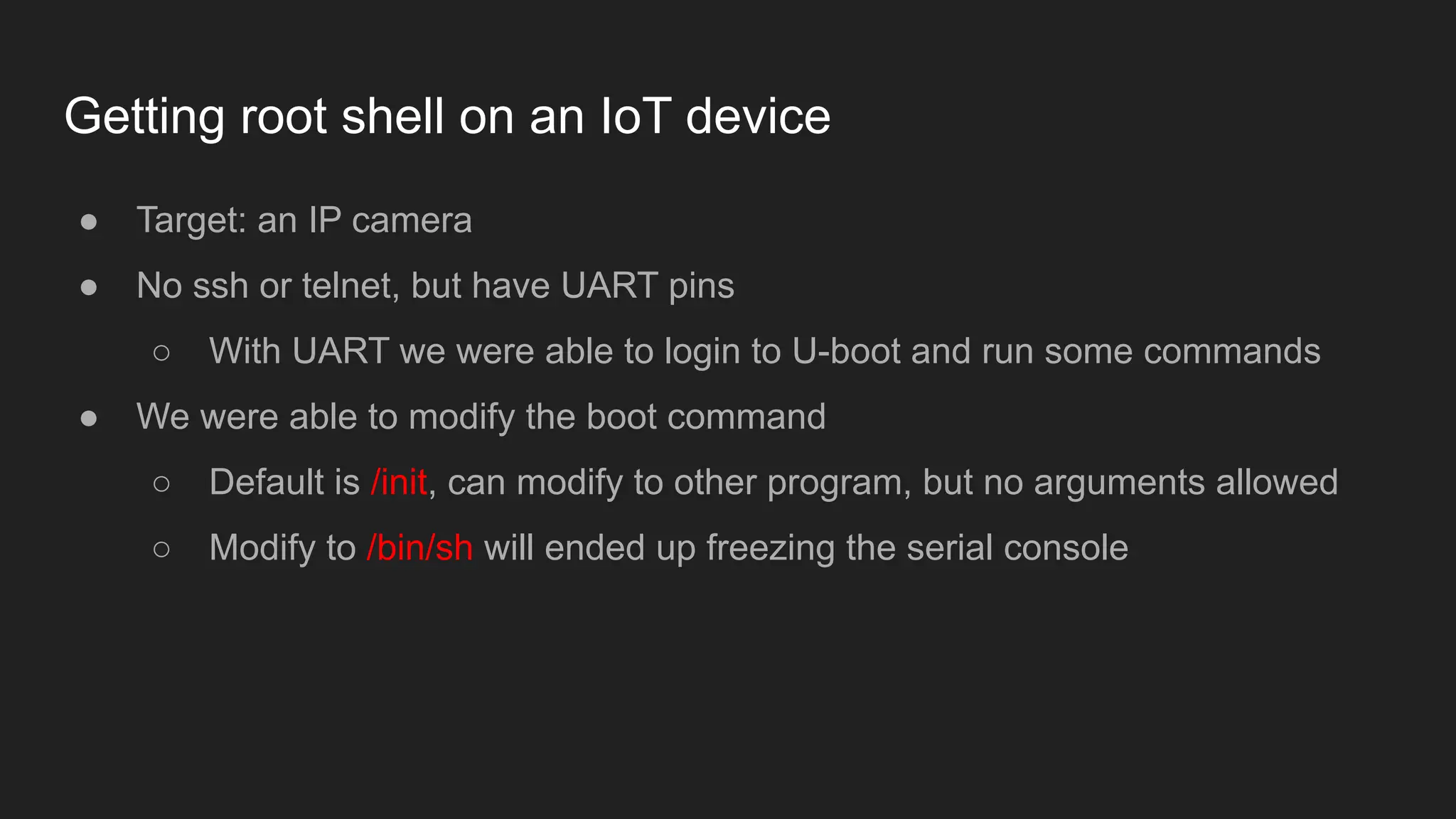
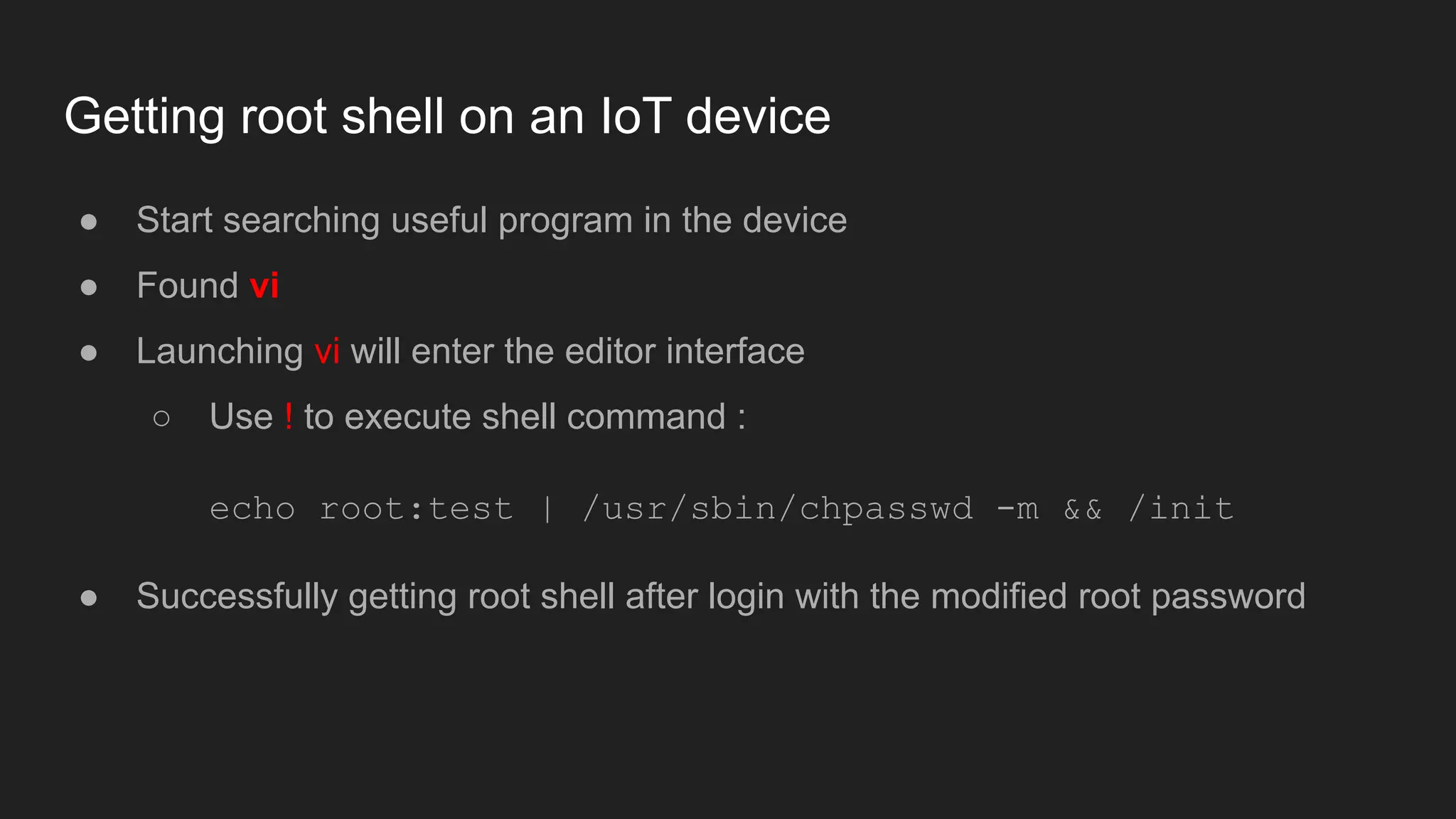
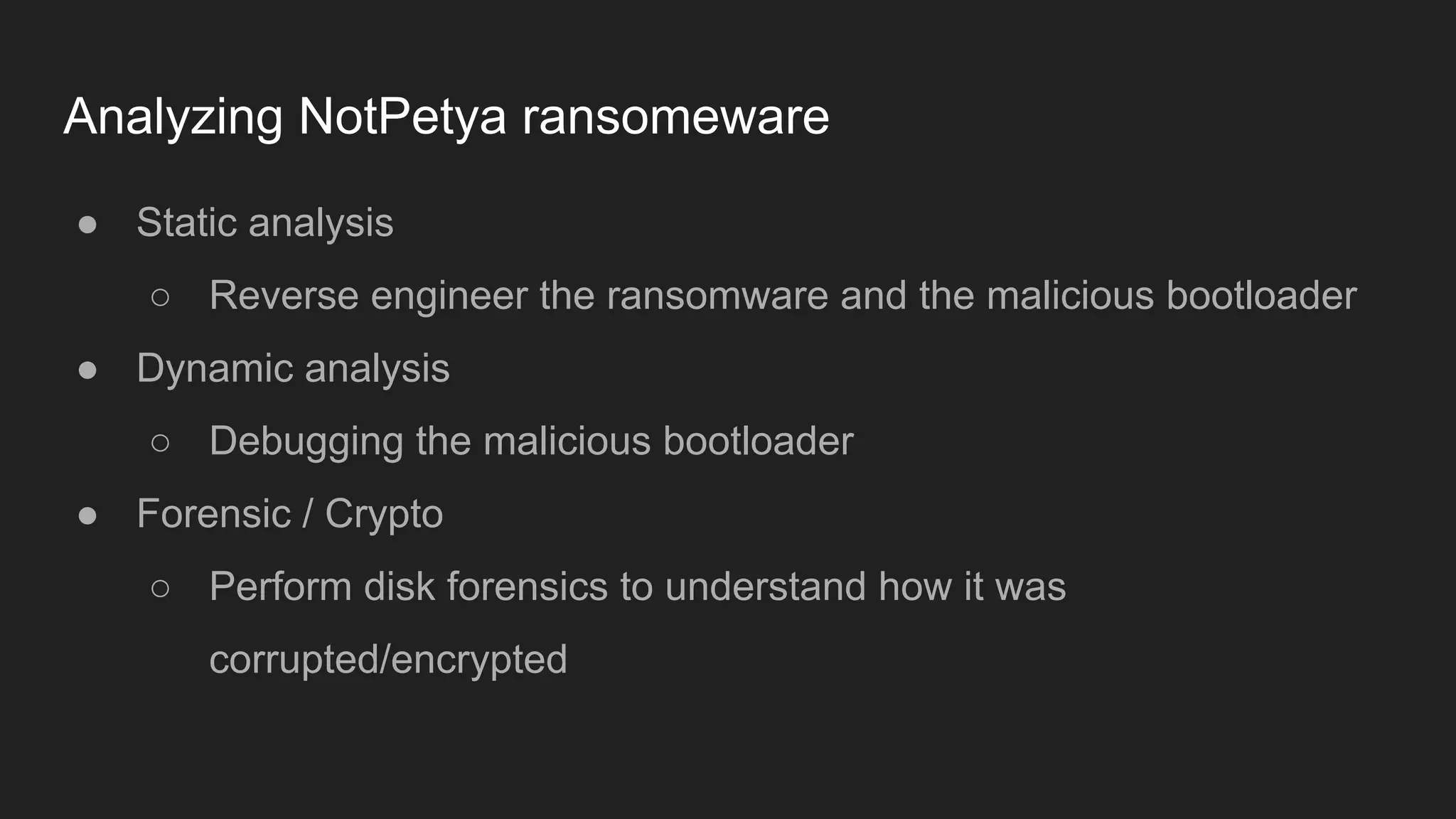
Bruce Chen, a vulnerability researcher, shares insights on how participating in CTFs enhanced his skills in vulnerability discovery and exploitation, particularly in IoT and browser security. He provides examples of overcoming challenges, such as gaining root access to an IP camera and bypassing control flow guard in the Windows Chrome browser. He concludes that CTFs are beneficial for skill improvement and advises aspiring researchers to focus on real-world challenges and documentation.