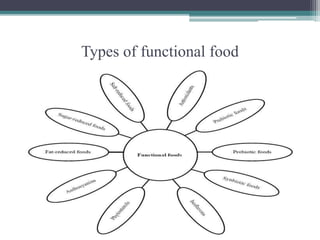
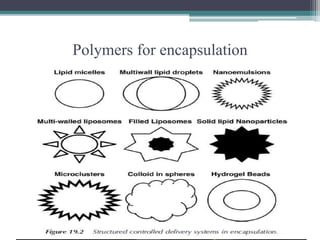
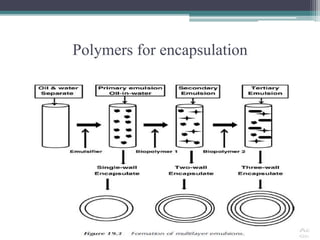
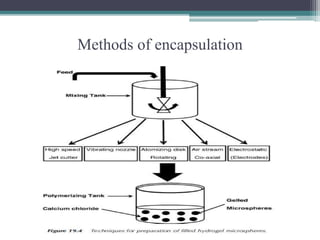
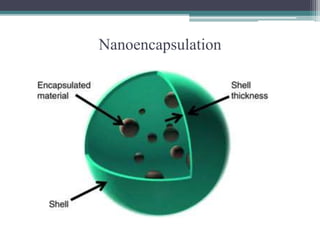
This document discusses bioencapsulation technologies for incorporating bioactive components into functional foods. It describes how there are several techniques for encapsulating functional ingredients, such as spray drying, fluid bed coating, and emulsification. These techniques involve coating droplets of active ingredients with carrier polymers. The document then discusses polymers used for encapsulation, different encapsulation methods like nanoencapsulation, and examples of encapsulating ingredients like fish oils, vitamins, and antioxidants. It concludes by discussing how nutrigenomics and biotechnology will influence the future of functional foods.