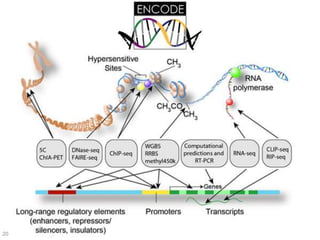
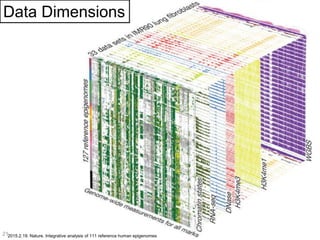
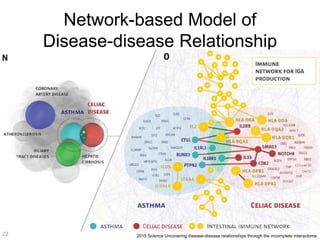
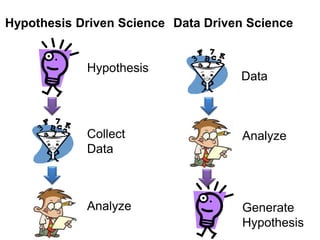
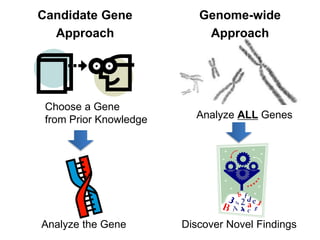
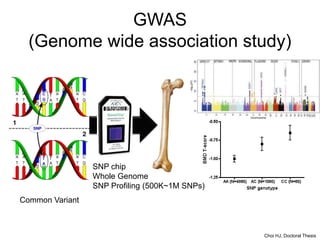
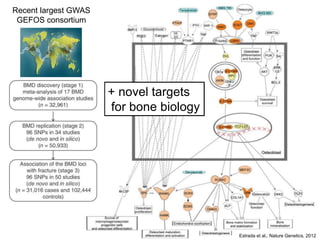
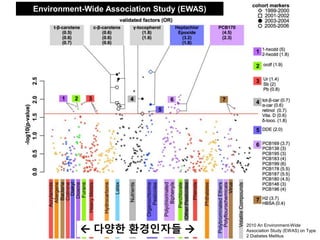
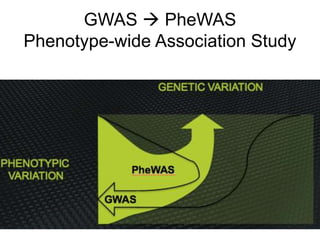
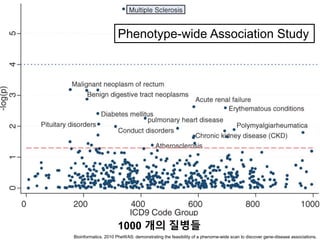
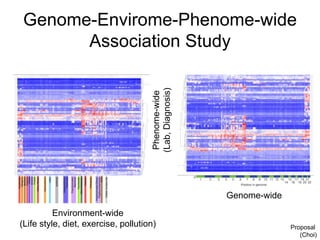
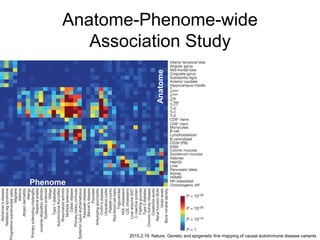
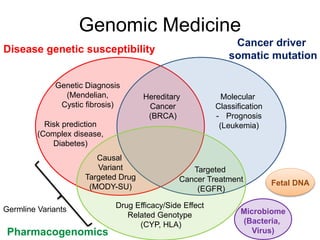
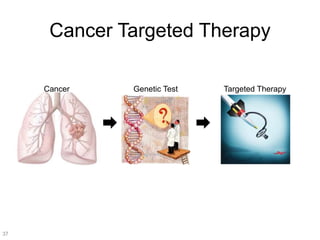
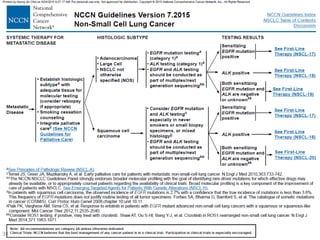
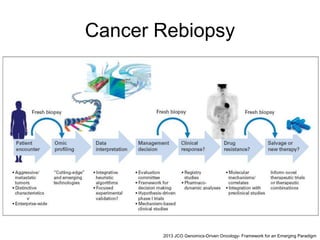
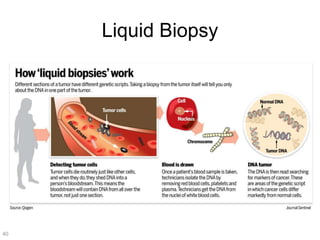
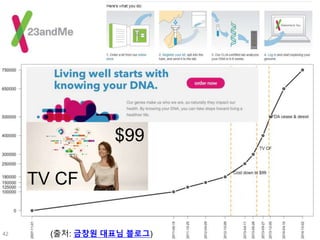
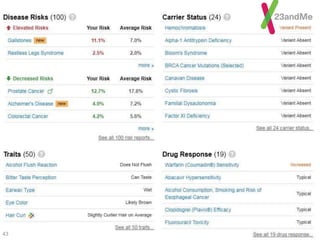
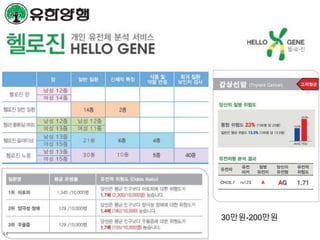
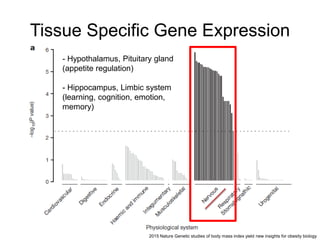
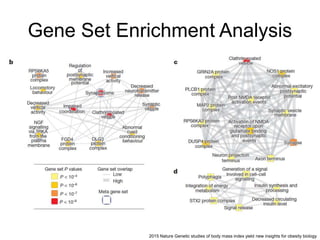
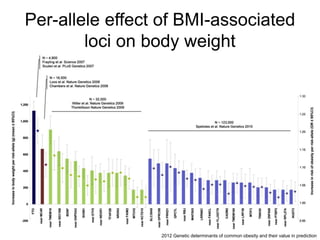
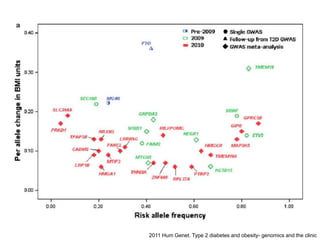
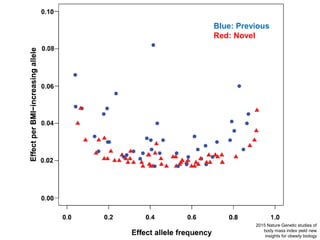
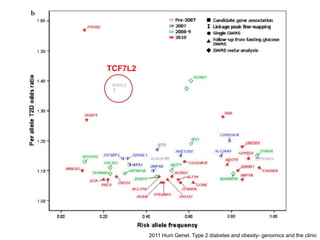
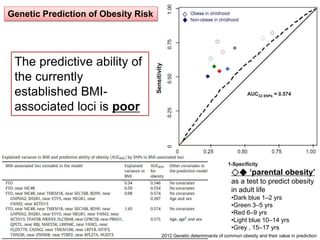
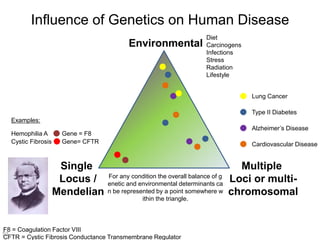
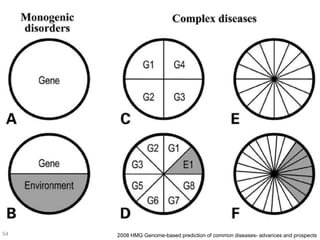
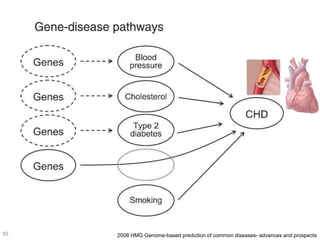
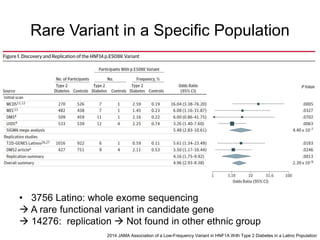
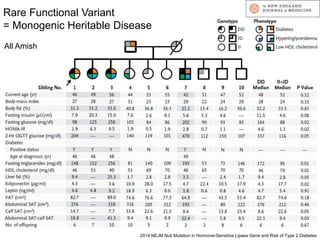
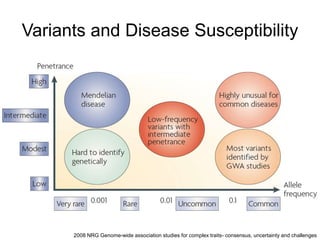
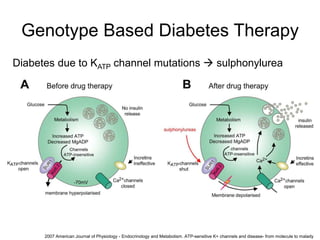
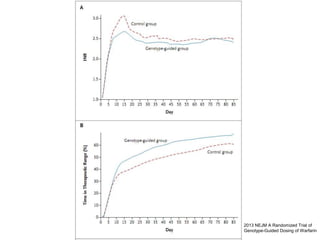
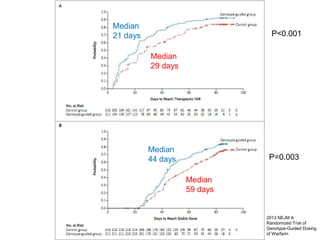
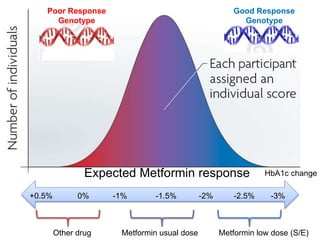
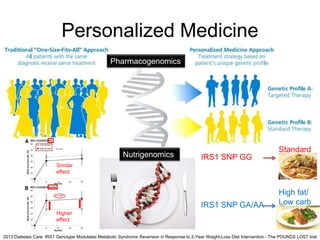
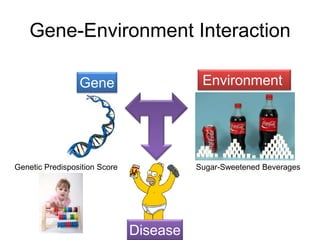
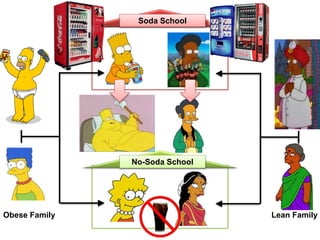
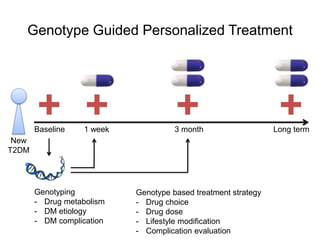
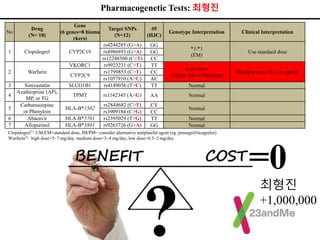
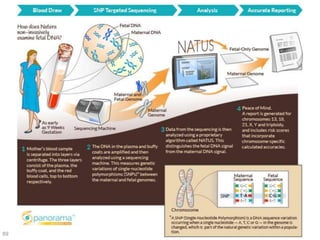
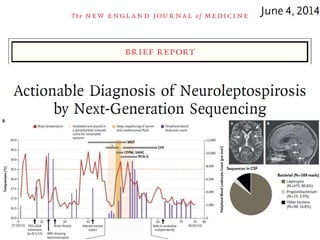
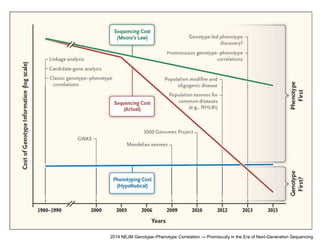
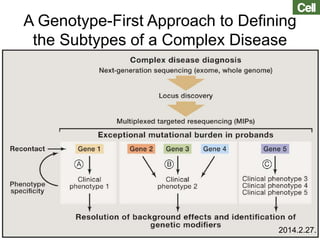
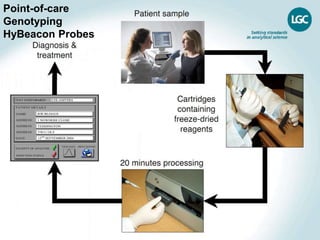
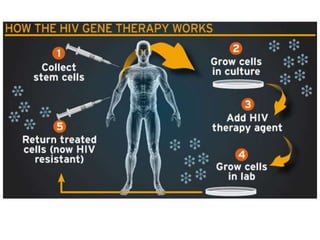
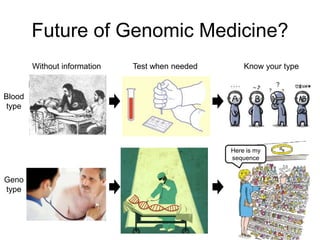
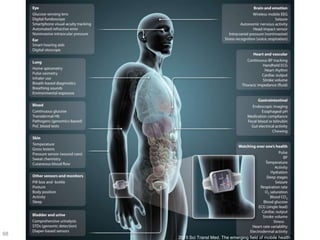
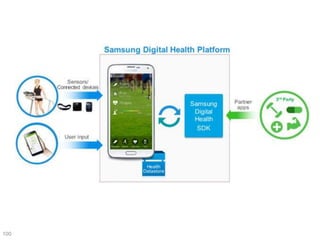
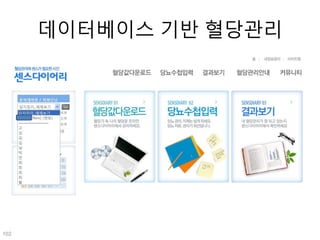
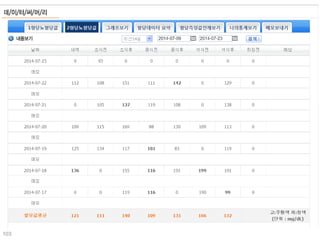
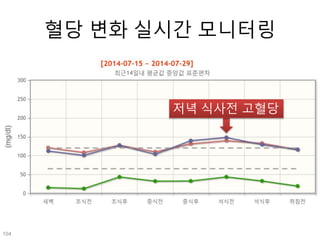
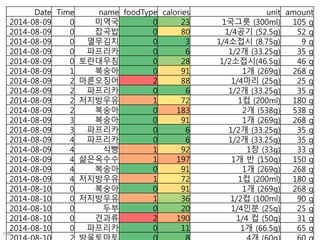
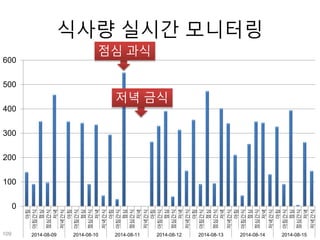
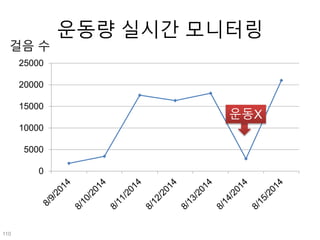
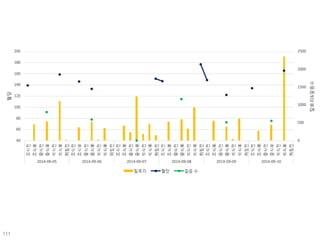
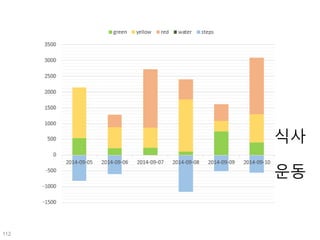
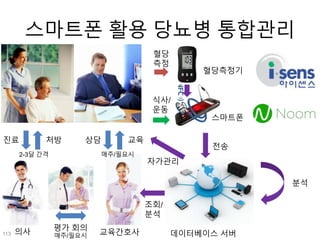
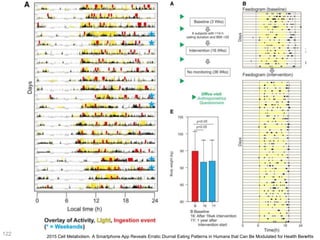
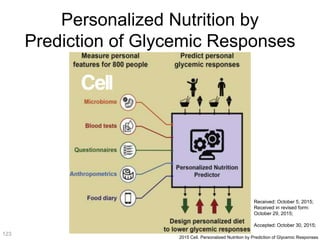
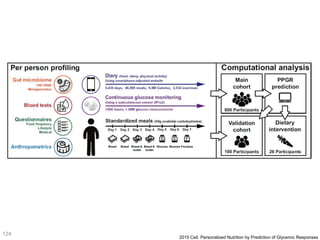
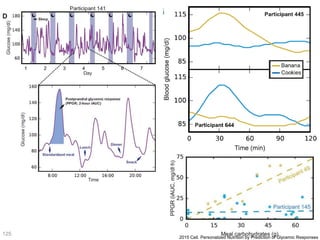
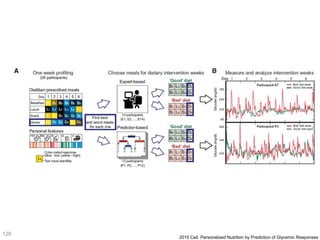
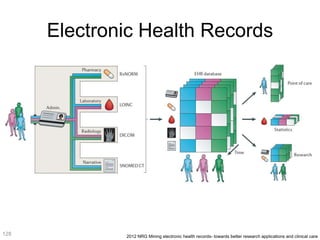
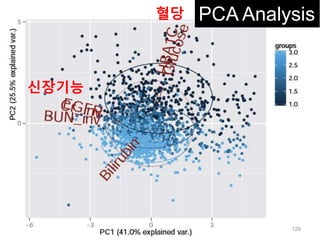
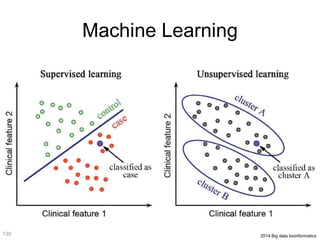
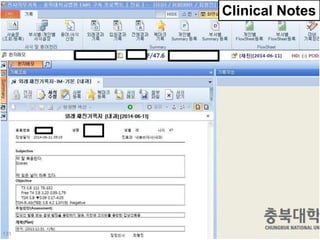
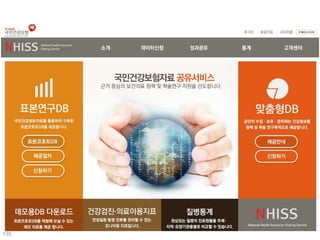
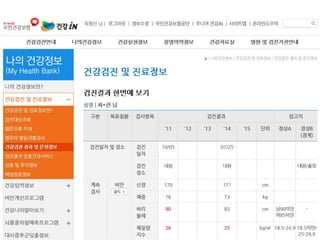
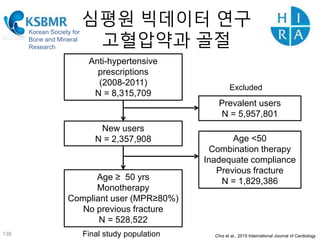
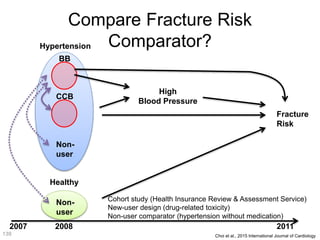
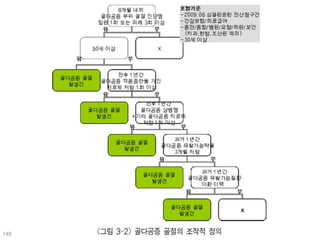
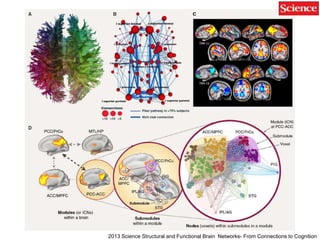
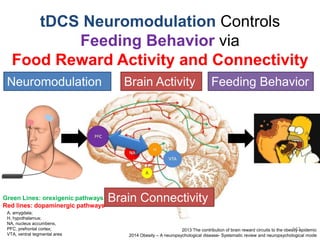
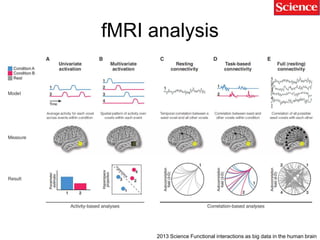
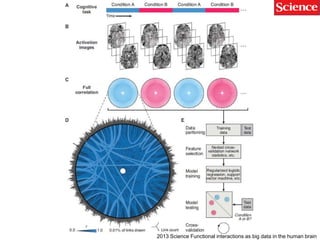
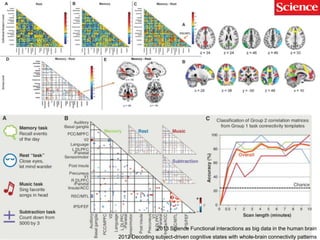
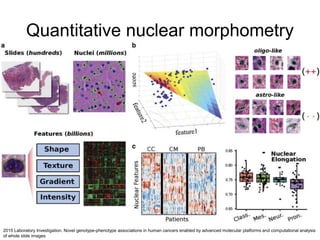
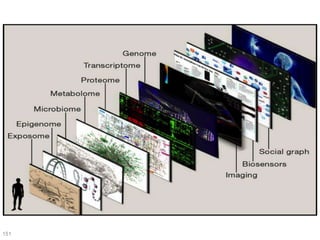
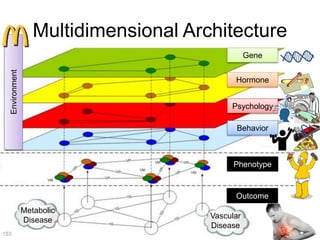
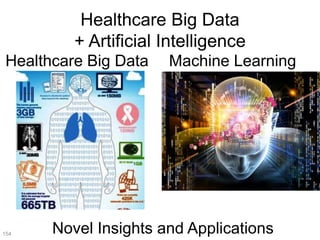
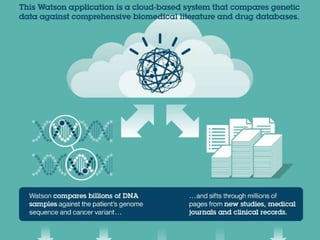
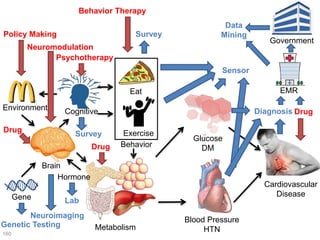
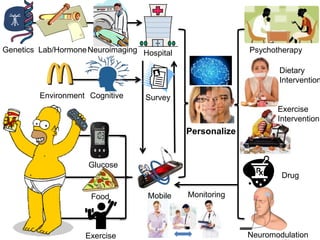
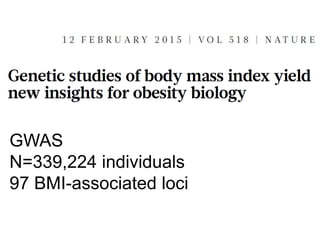This document discusses using genomic and lifelogging data for big data analysis in healthcare. It covers topics like the Human Genome Project, disease risk prediction using genomic data, targeted cancer therapies, use of sensor/mobile data, electronic health records, and applying artificial intelligence to biomedical big data. The goal is to integrate diverse types of healthcare data through big data analysis to enable more personalized medicine.