This document provides information on various photography composition techniques, including:
- Deep depth of field and shallow depth of field
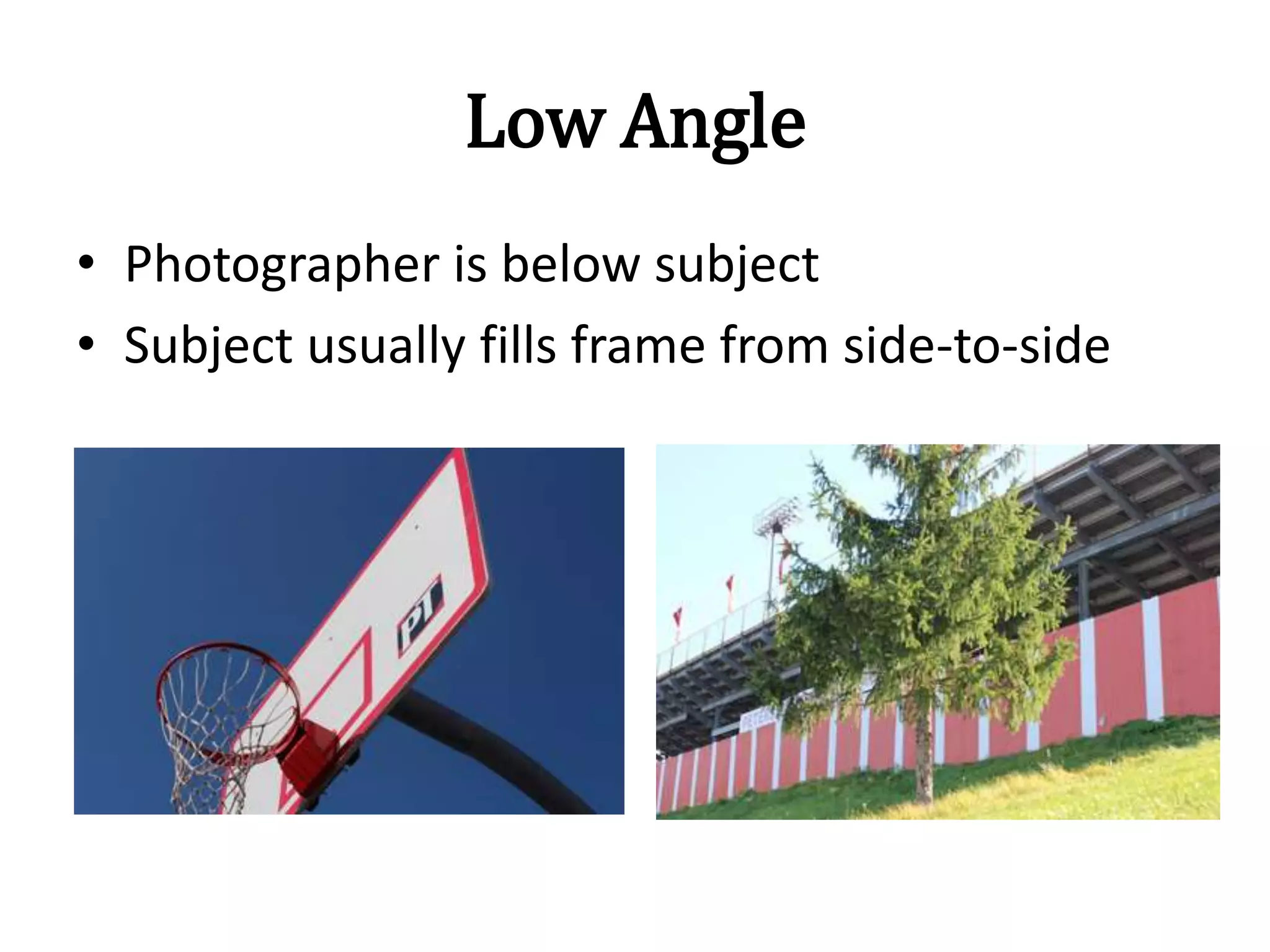
- High and low camera angles
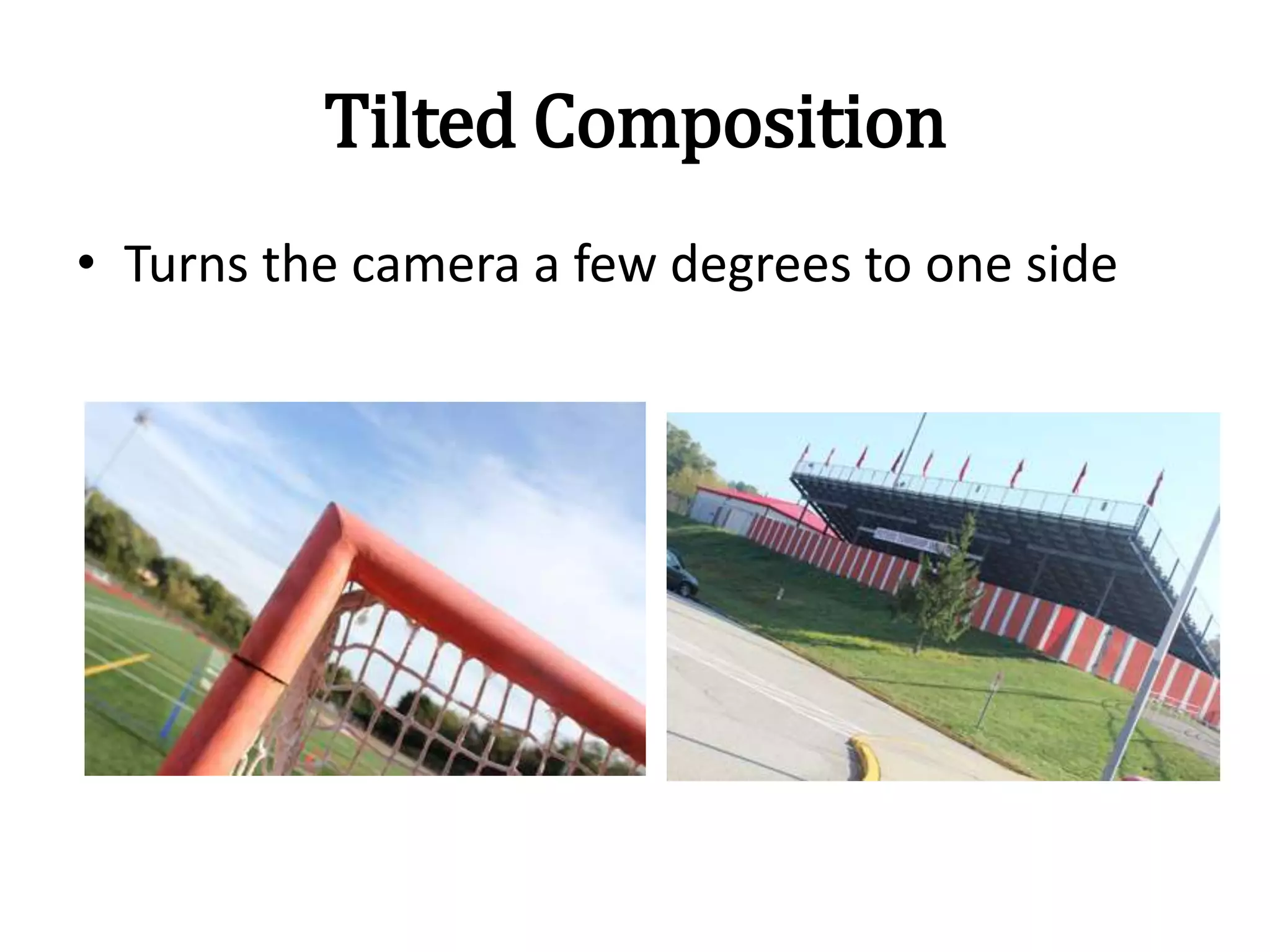
- Tilted frames, subject positioning, and nose room
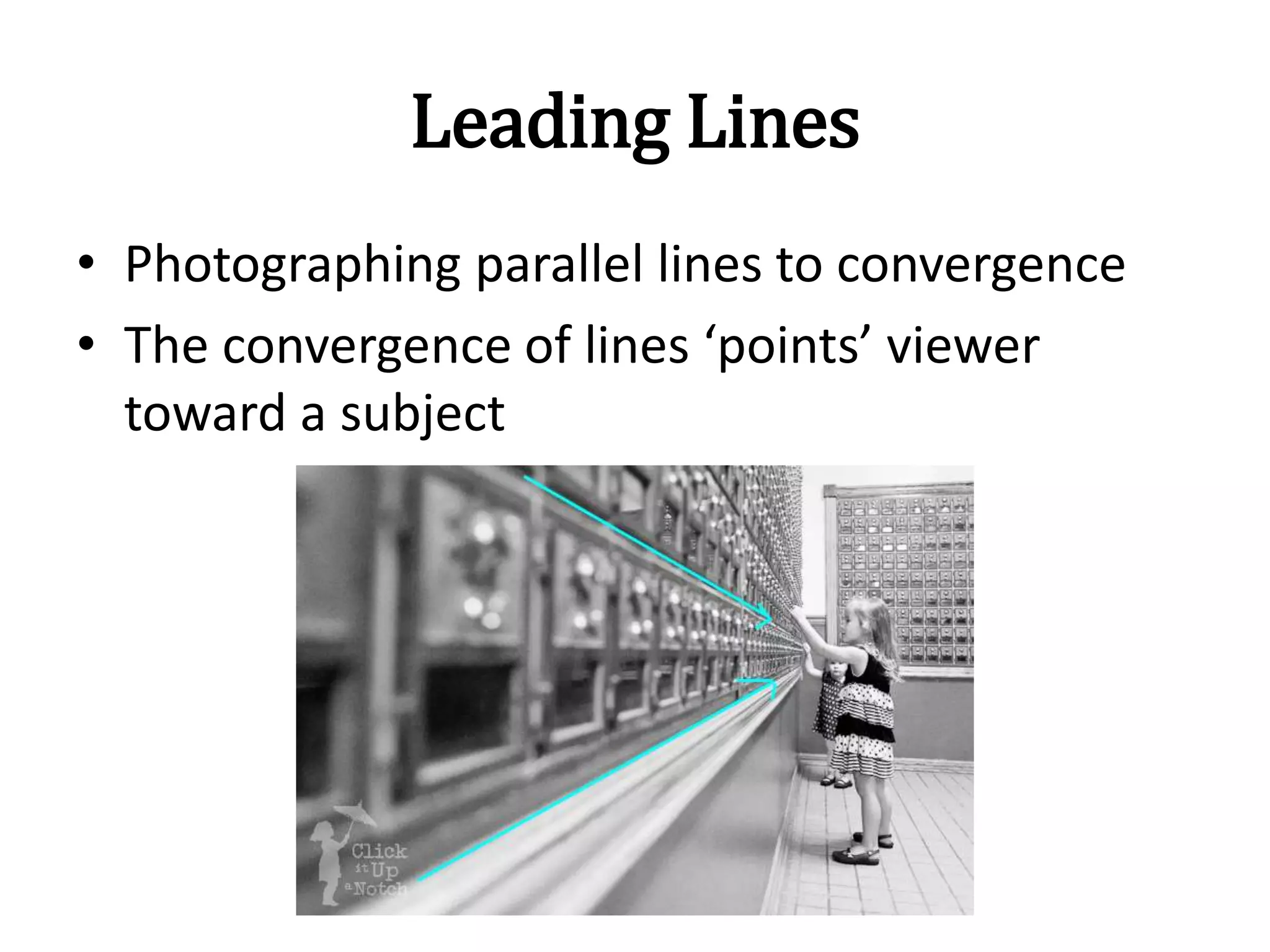
- Use of color, texture, leading lines, and framing
It describes each technique and gives examples of when and how it could be used to enhance photographs. The goal is to teach students best practices for intentional composition choices.