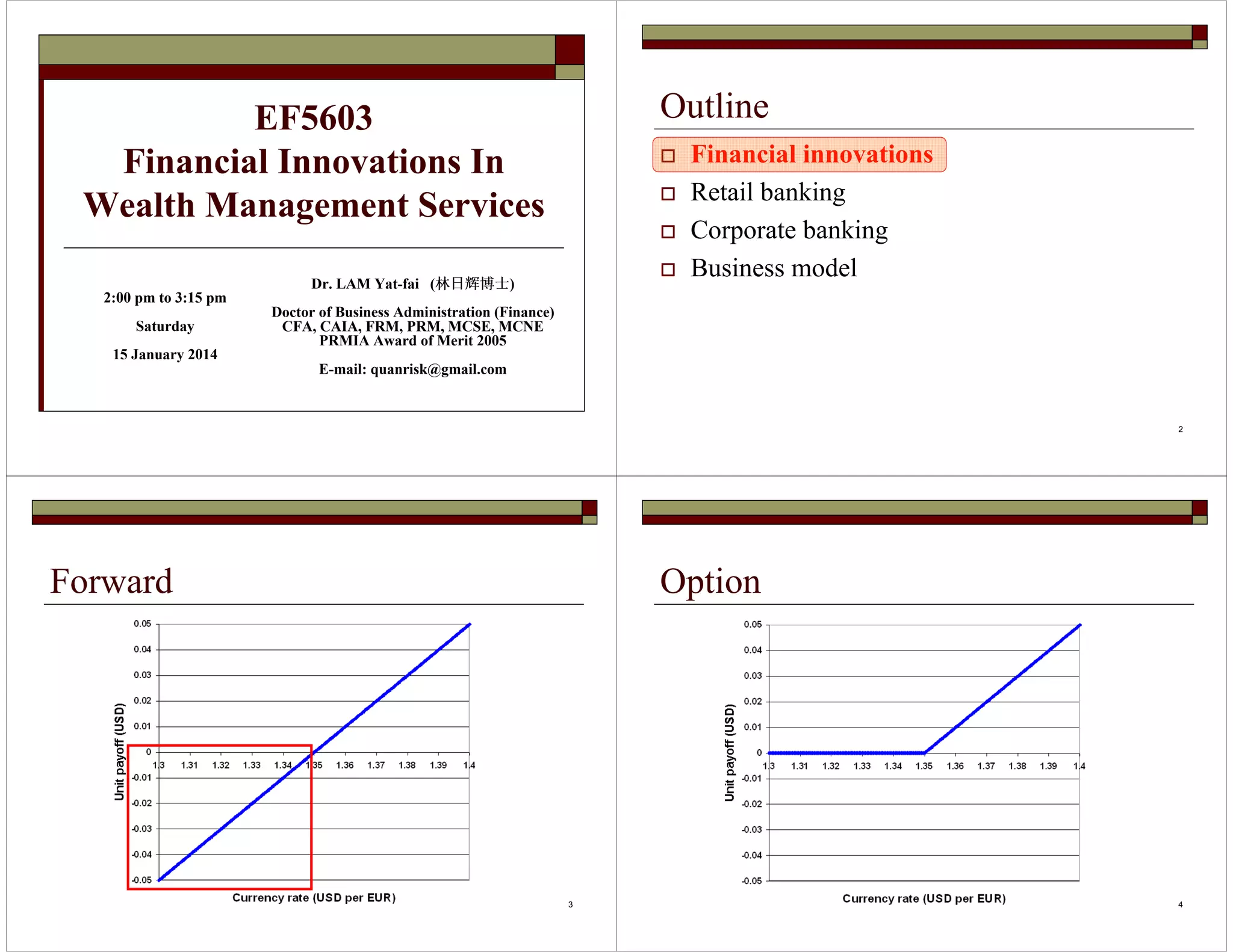
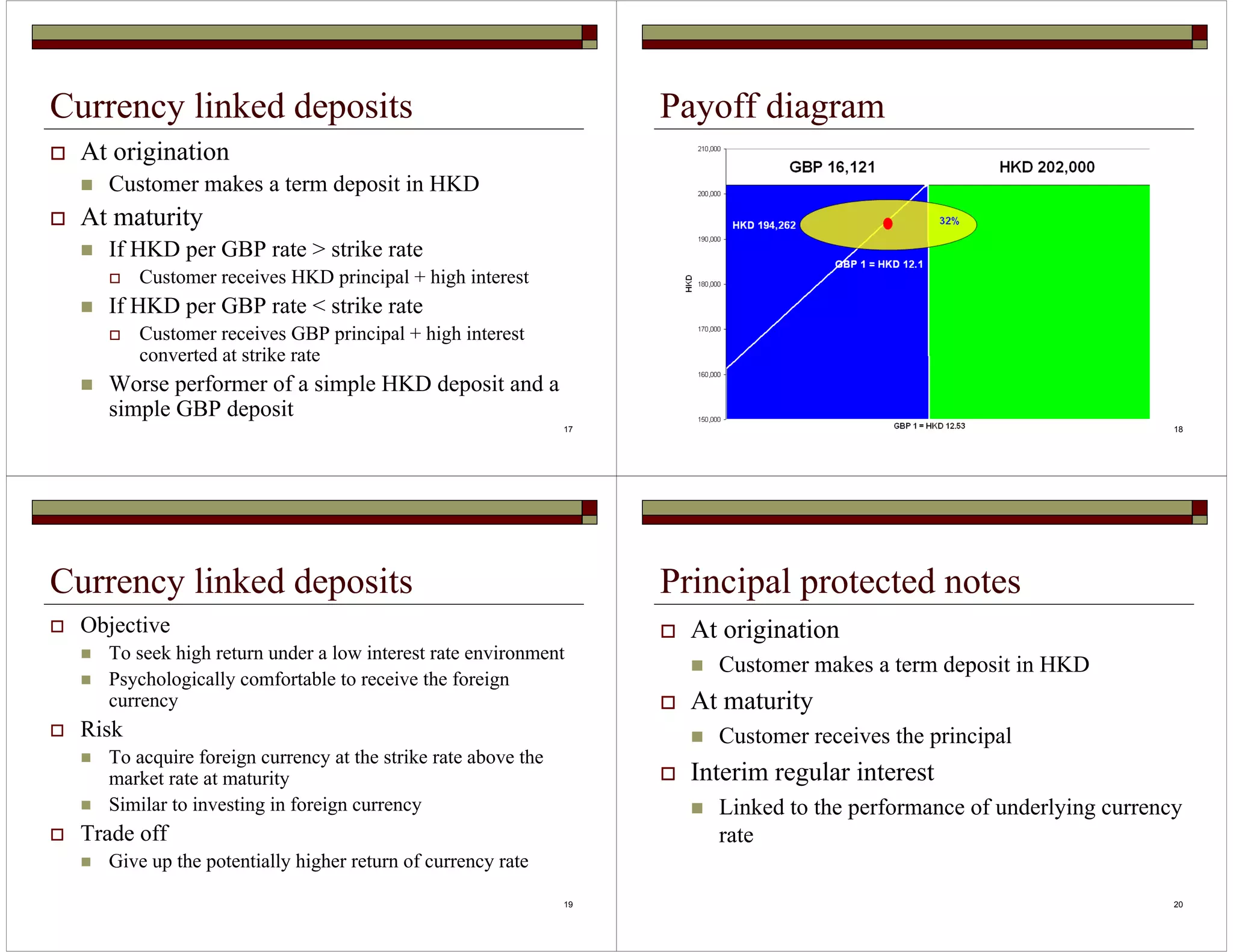
This document discusses financial innovations in wealth management services, focusing on currency-linked structured products. It describes common structured products used in retail and corporate banking like currency-linked deposits, principal protected notes, accumulators, and target accrual redemption forwards. It also discusses the business model of structured products including their valuation, pricing, sales channels and revenue/cost models.