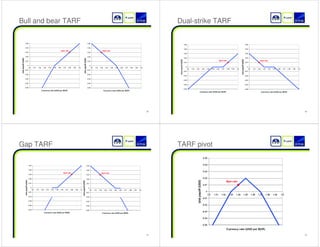
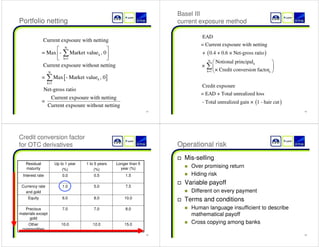
This document outlines a presentation on structured foreign exchange products for wealth management services in Greater China. The presentation covers why banks offer structured FX products, major product types including accumulators, currency linked deposits, and pivots. It also discusses international standards, sales and marketing strategies, and customer services considerations like pricing, hedging, and credit risk management. The target audience includes professionals seeking continuing education credits.