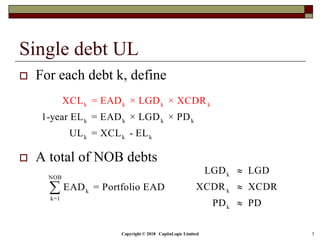
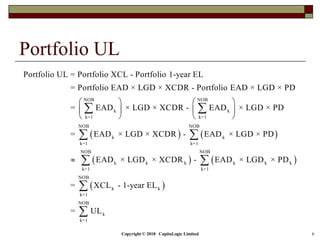
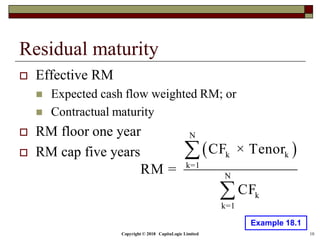
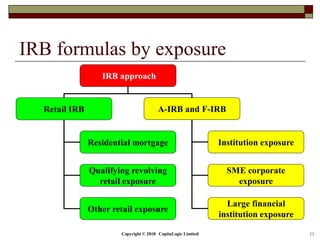
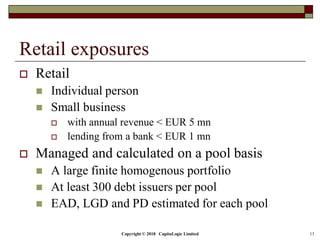
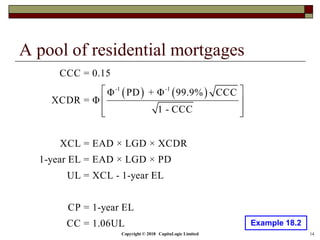
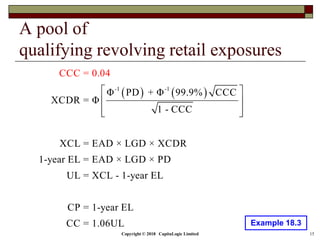
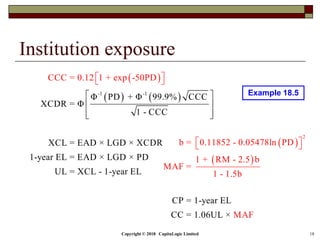
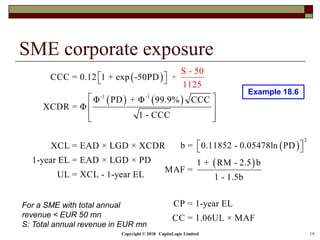
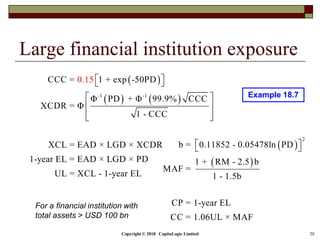
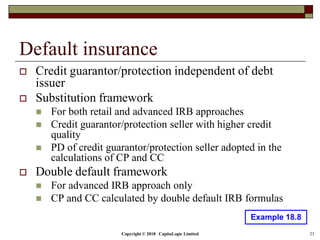
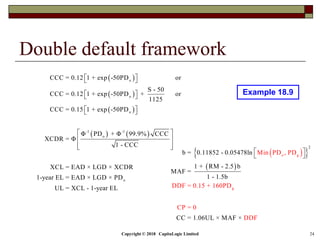
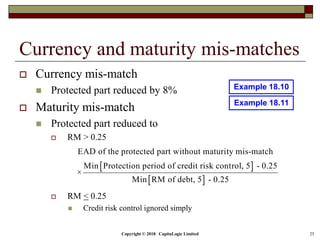
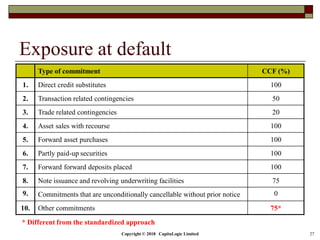
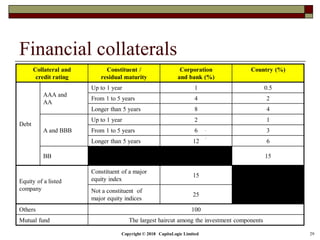
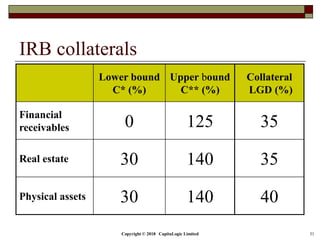
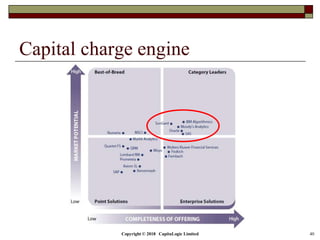
This document is a presentation on the internal ratings-based (IRB) approach for calculating capital requirements under Basel III. It includes outlines, definitions, formulas and examples for calculating key risk metrics like exposure at default, loss given default, probability of default, expected loss, unexpected loss and capital requirements under the retail, advanced, and foundation IRB approaches. Formulas vary depending on the type of exposure, such as residential mortgages, corporate exposures, or financial institutions. The document also discusses credit risk mitigation techniques.