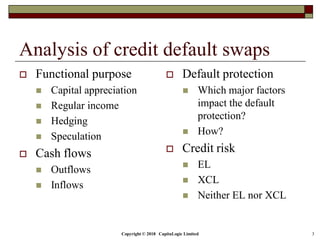
This document provides an overview of credit default swaps (CDS) and analyzes them in three sentences or less:
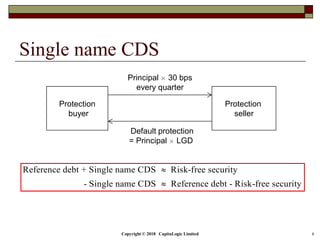
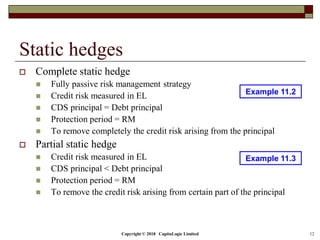
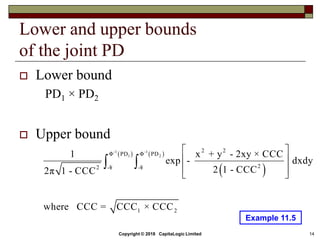
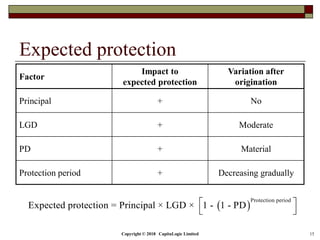
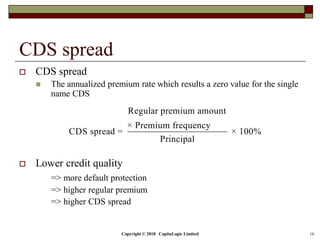
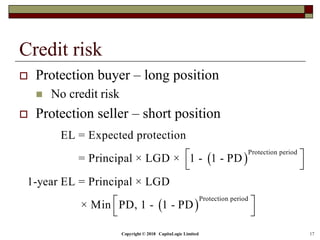
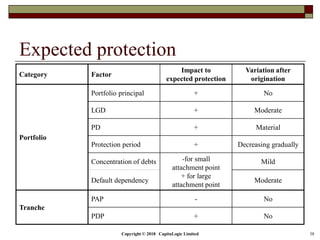
The document outlines different types of CDS including single name, binary, basket, and portfolio CDS. It discusses the cash flows, hedging applications, and credit risks associated with each type. The document also analyzes how factors like principal, probability of default, and protection period impact the expected protection of CDS.