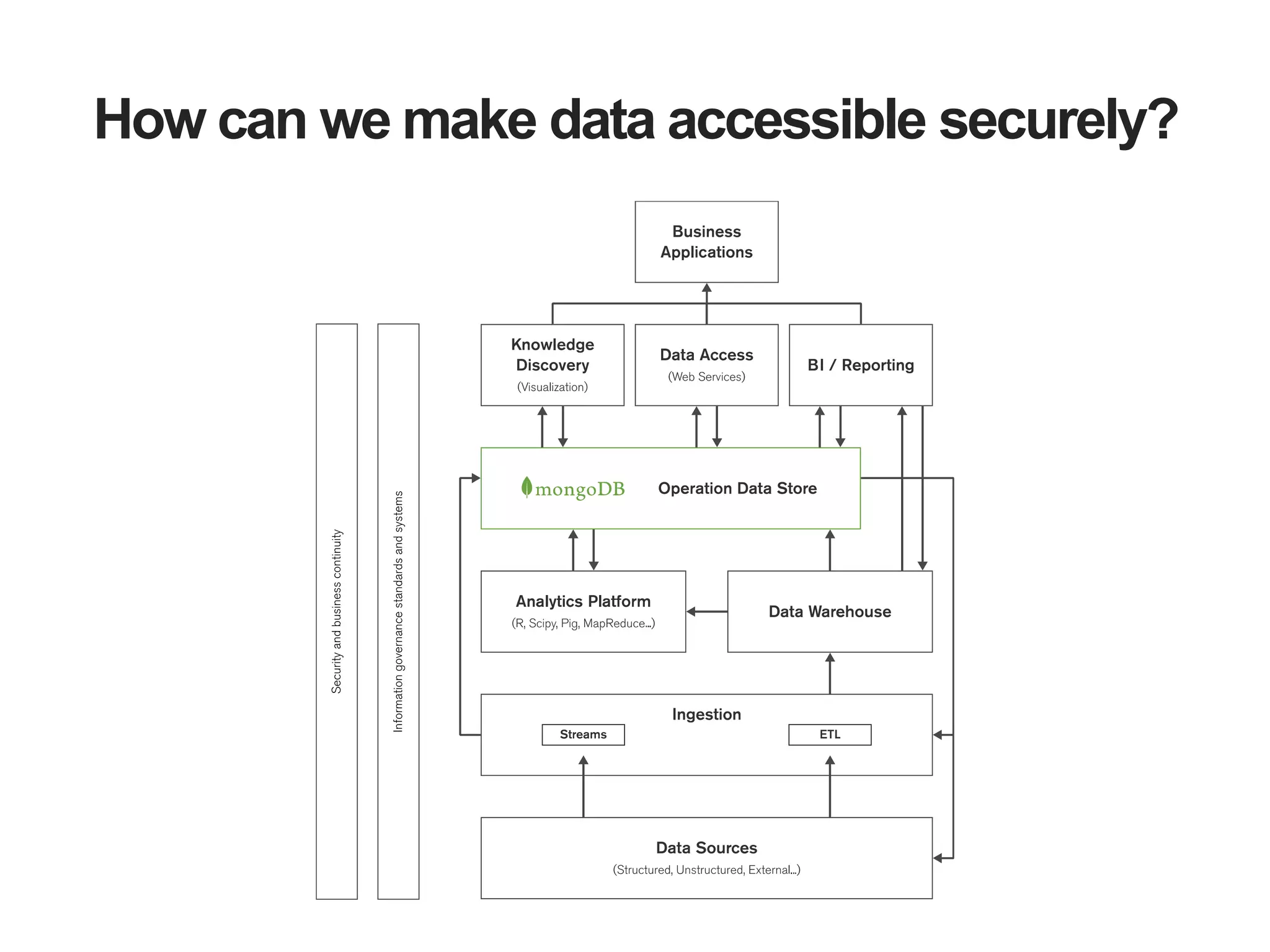
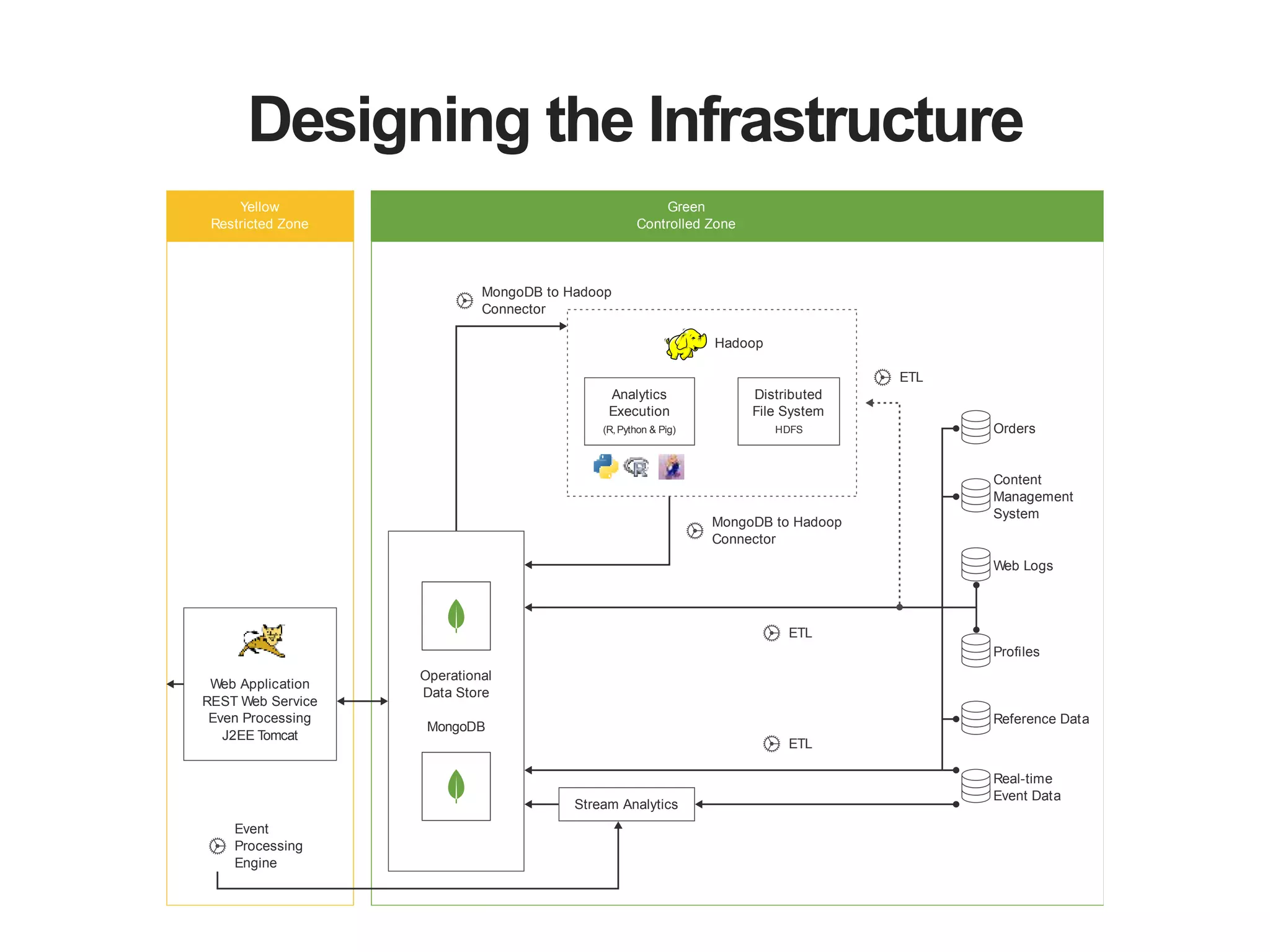
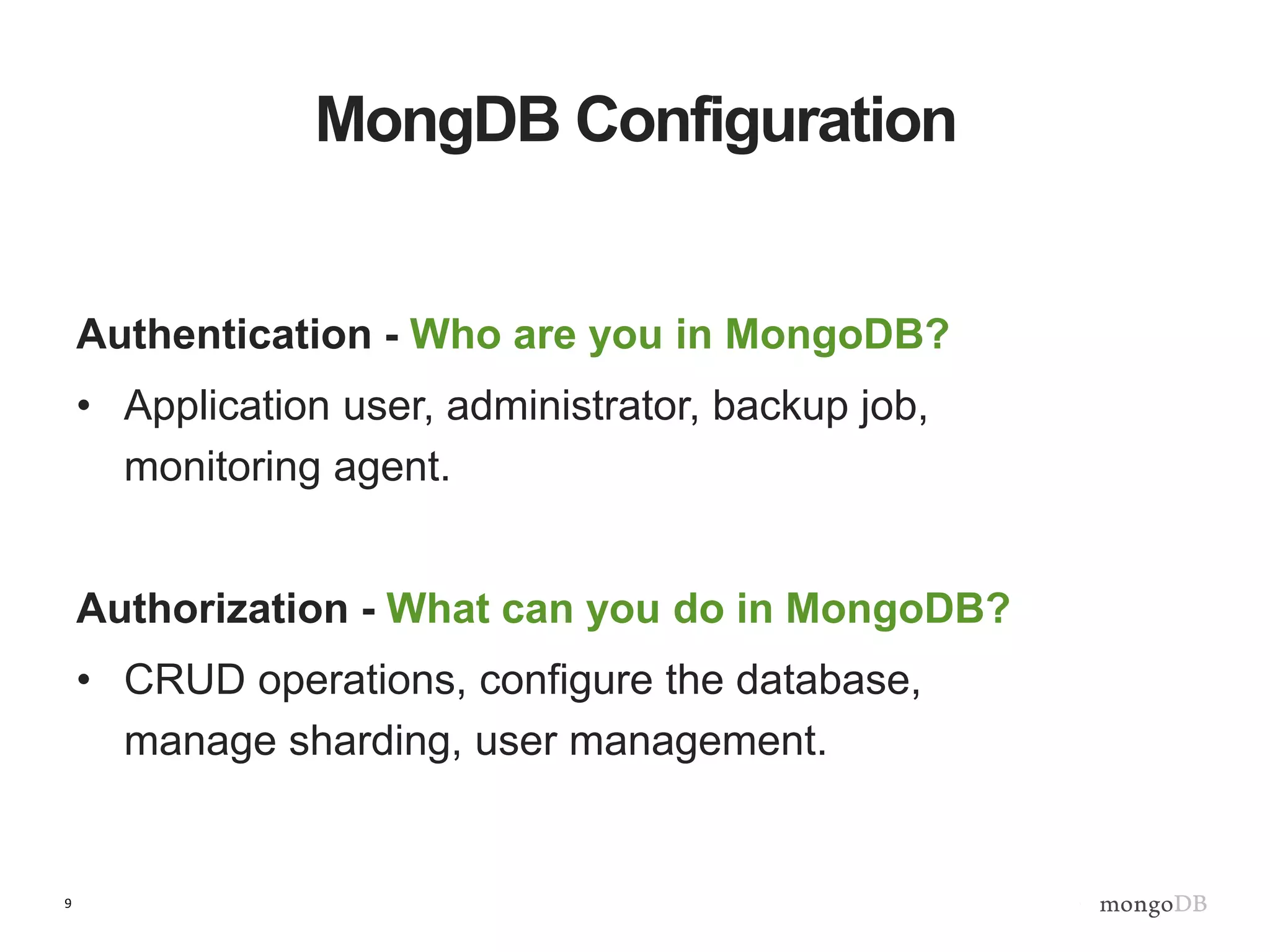
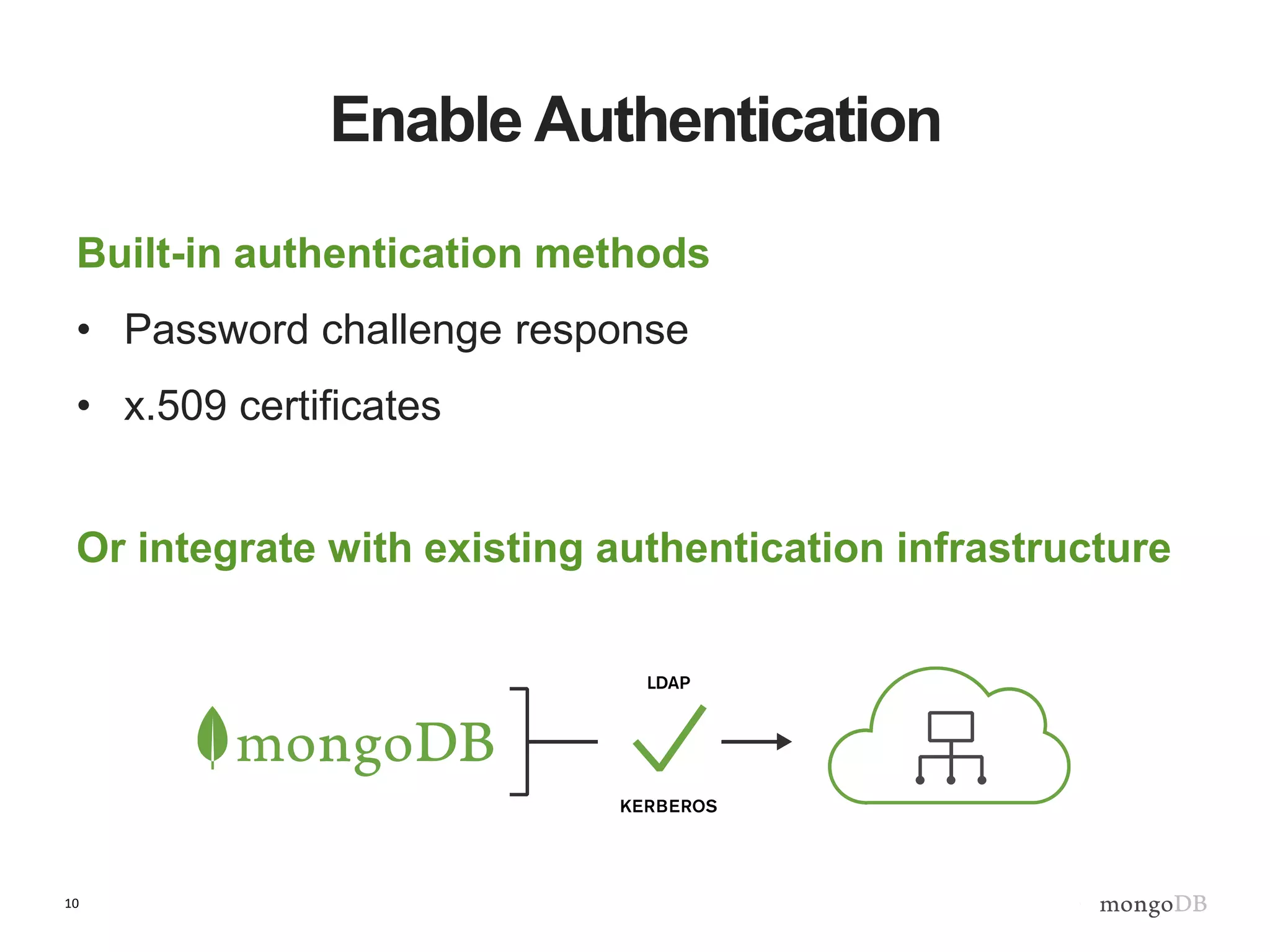
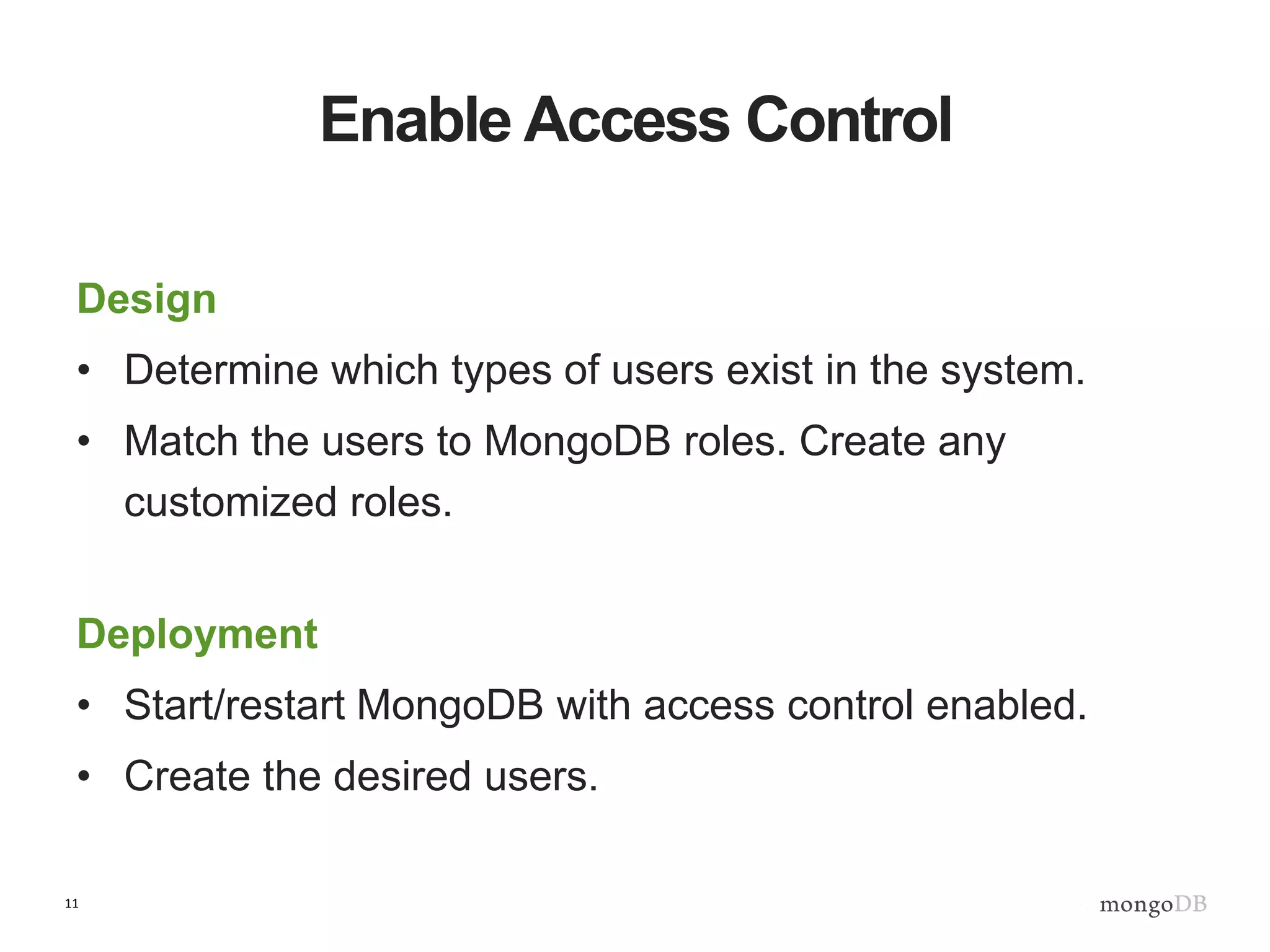
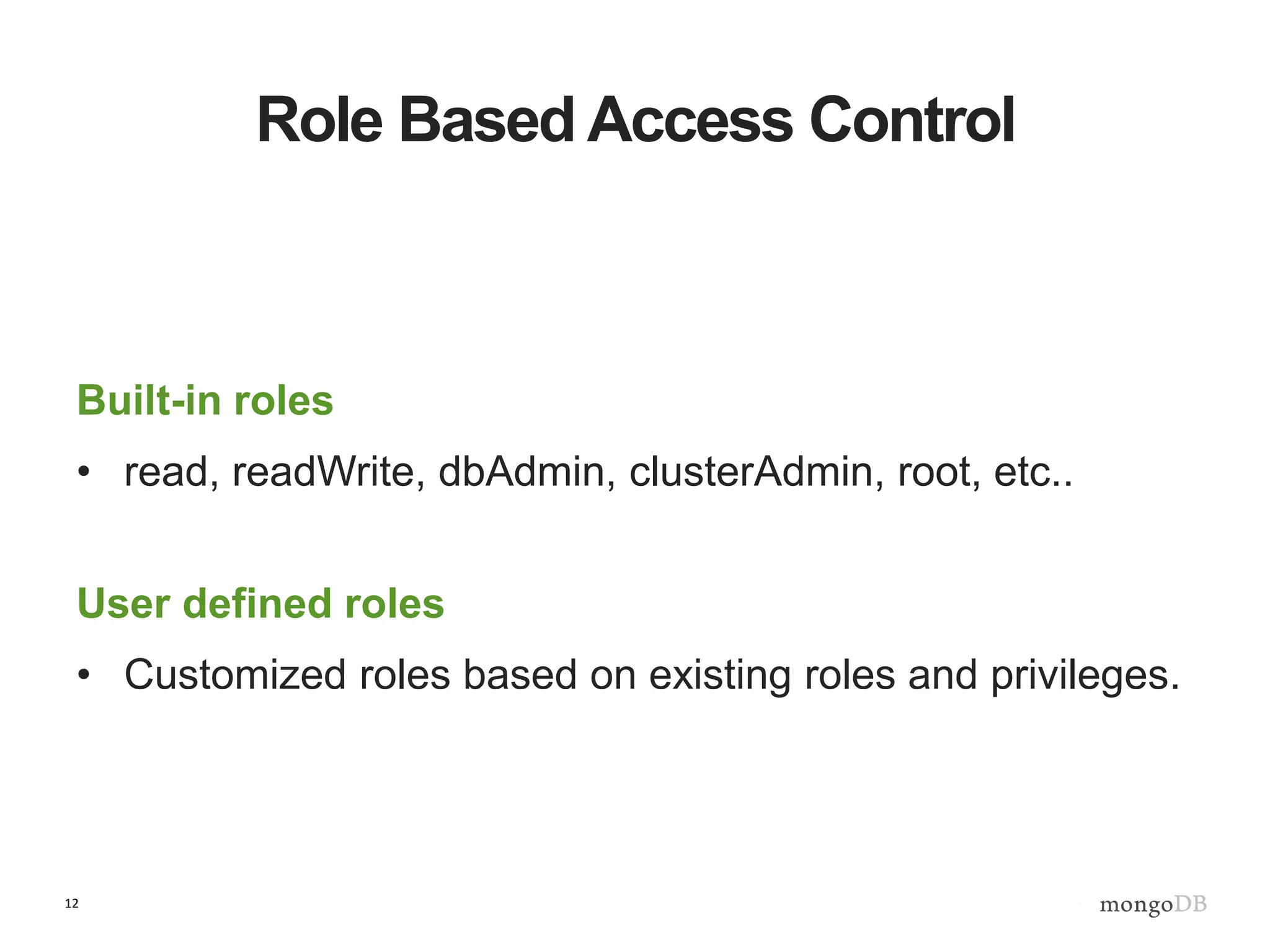
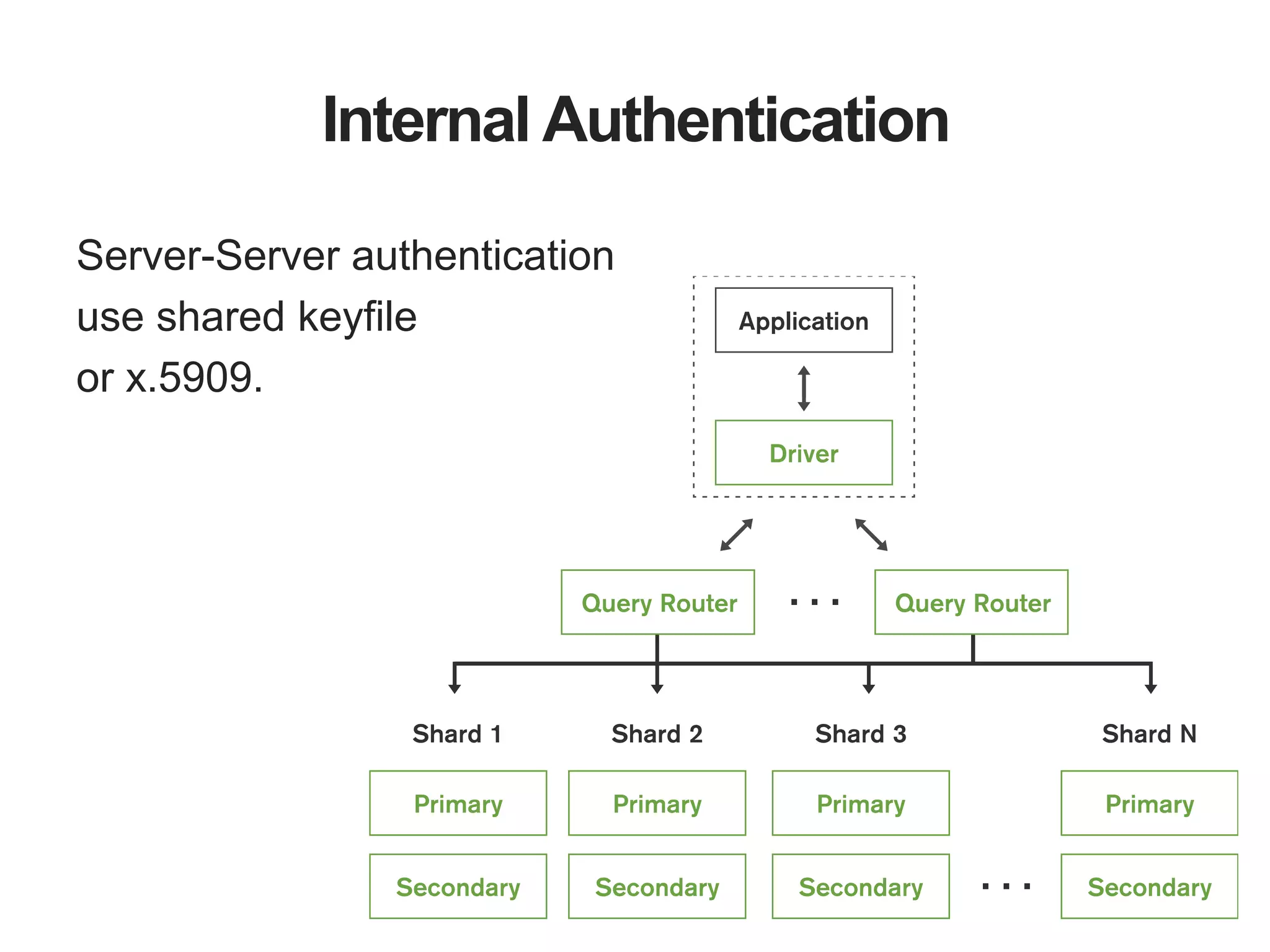
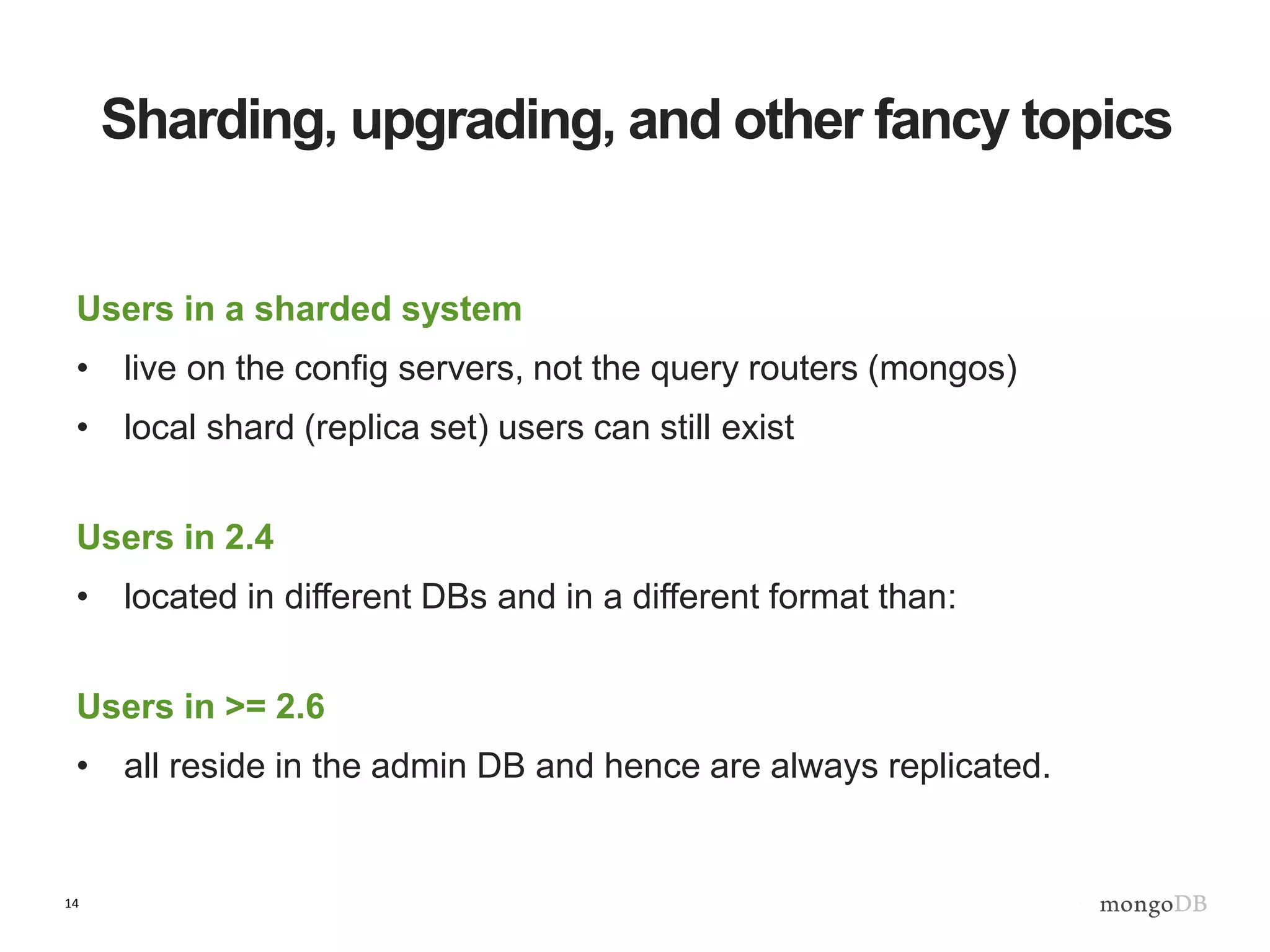
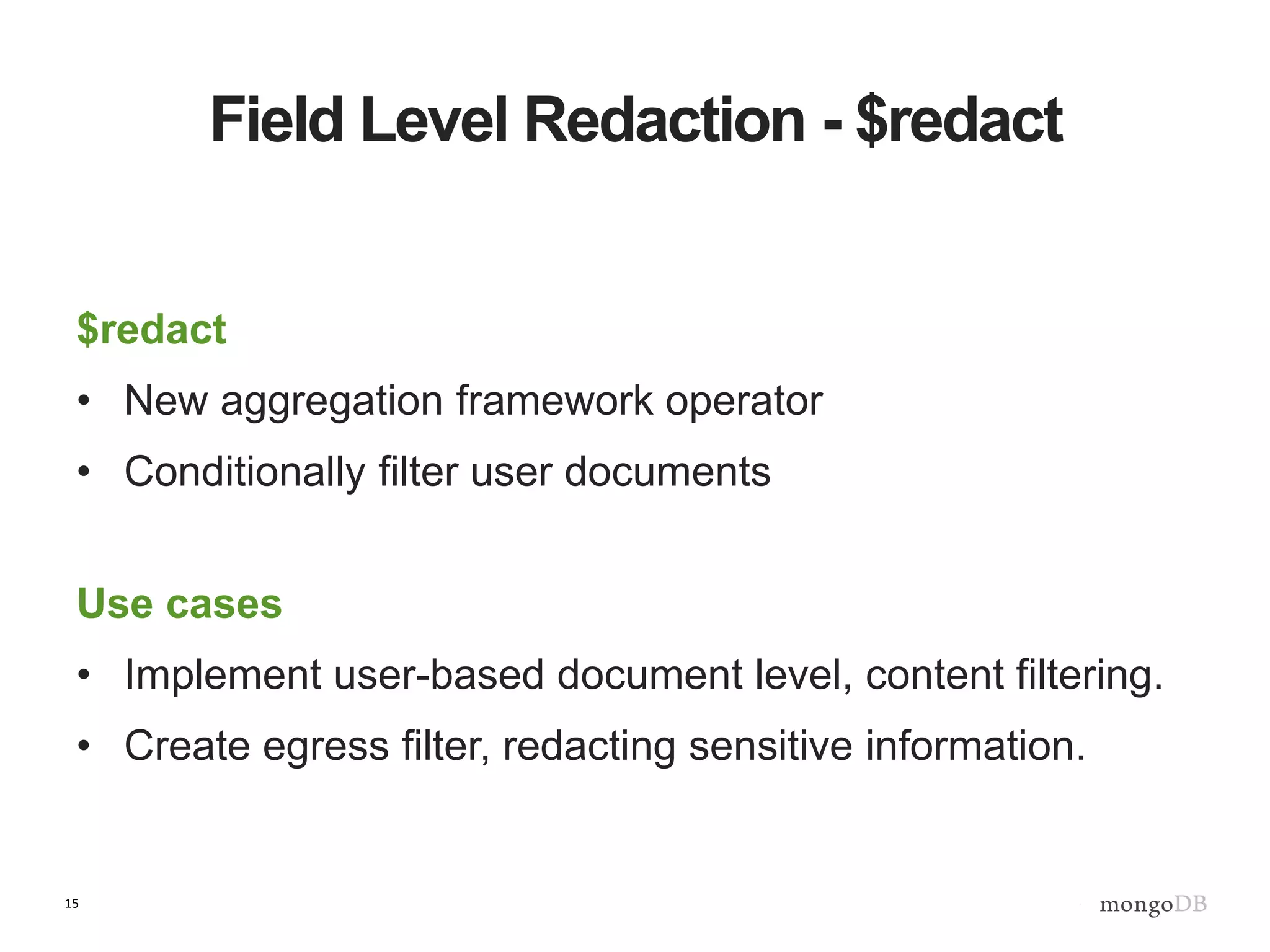
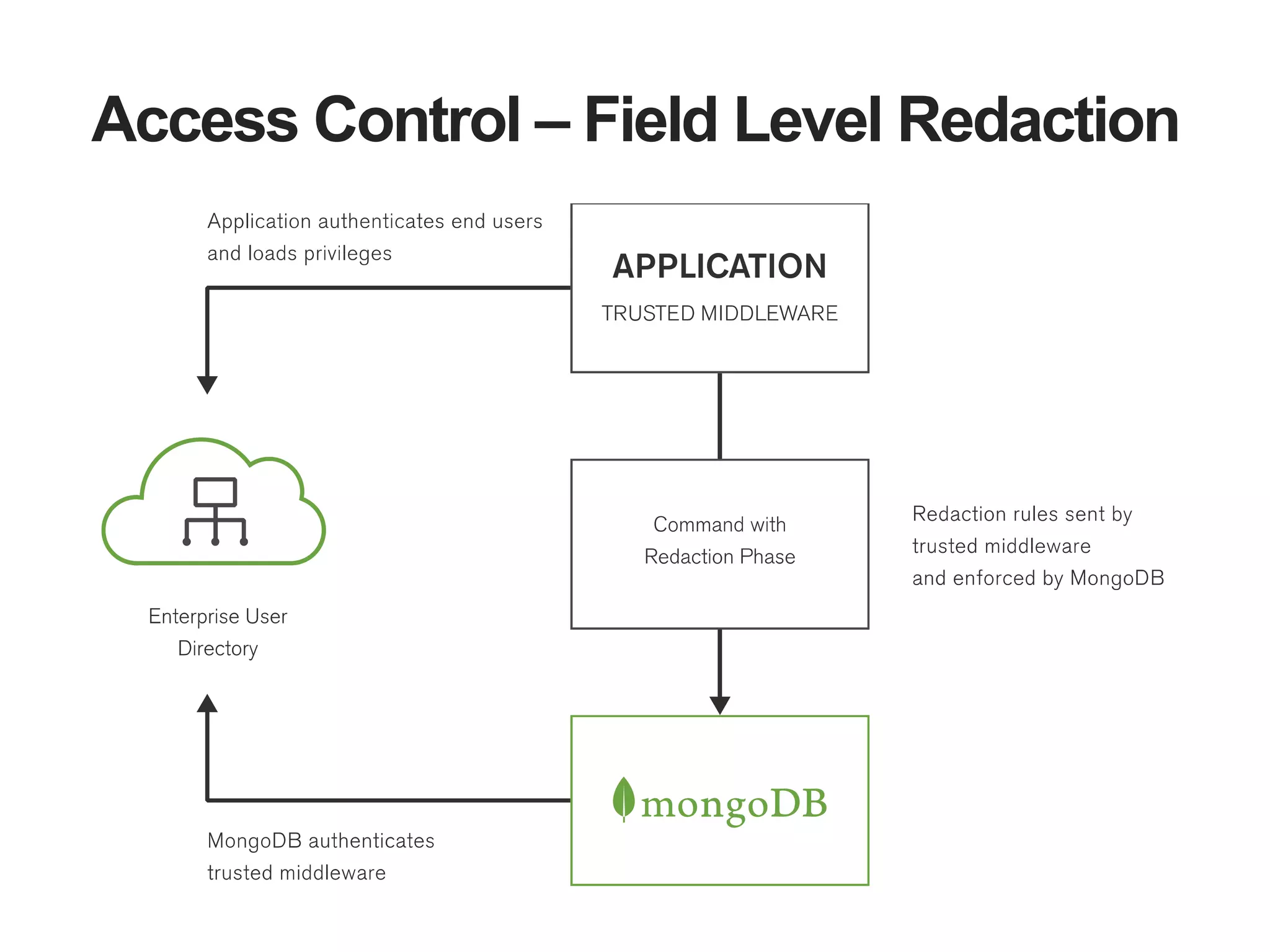
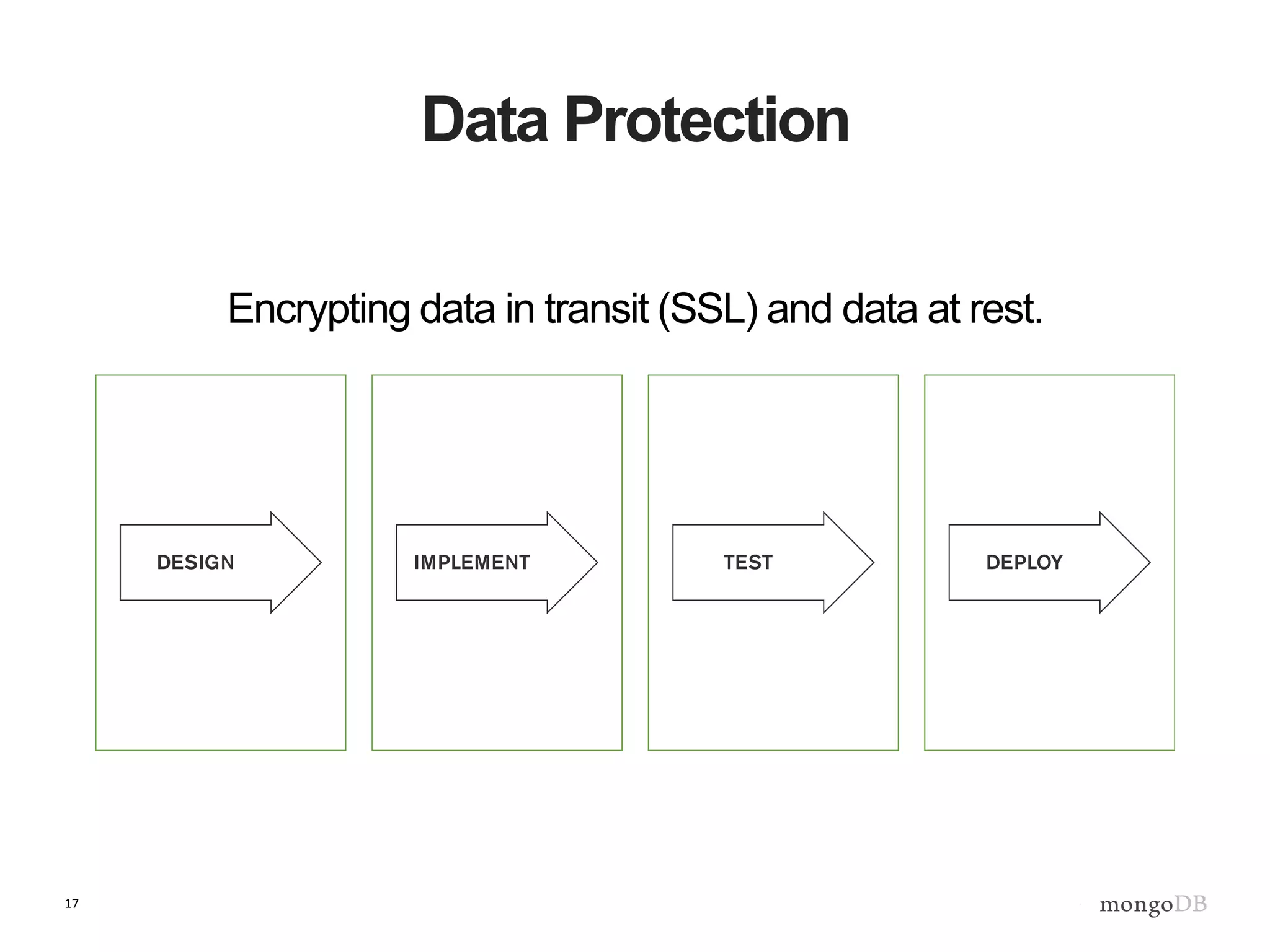
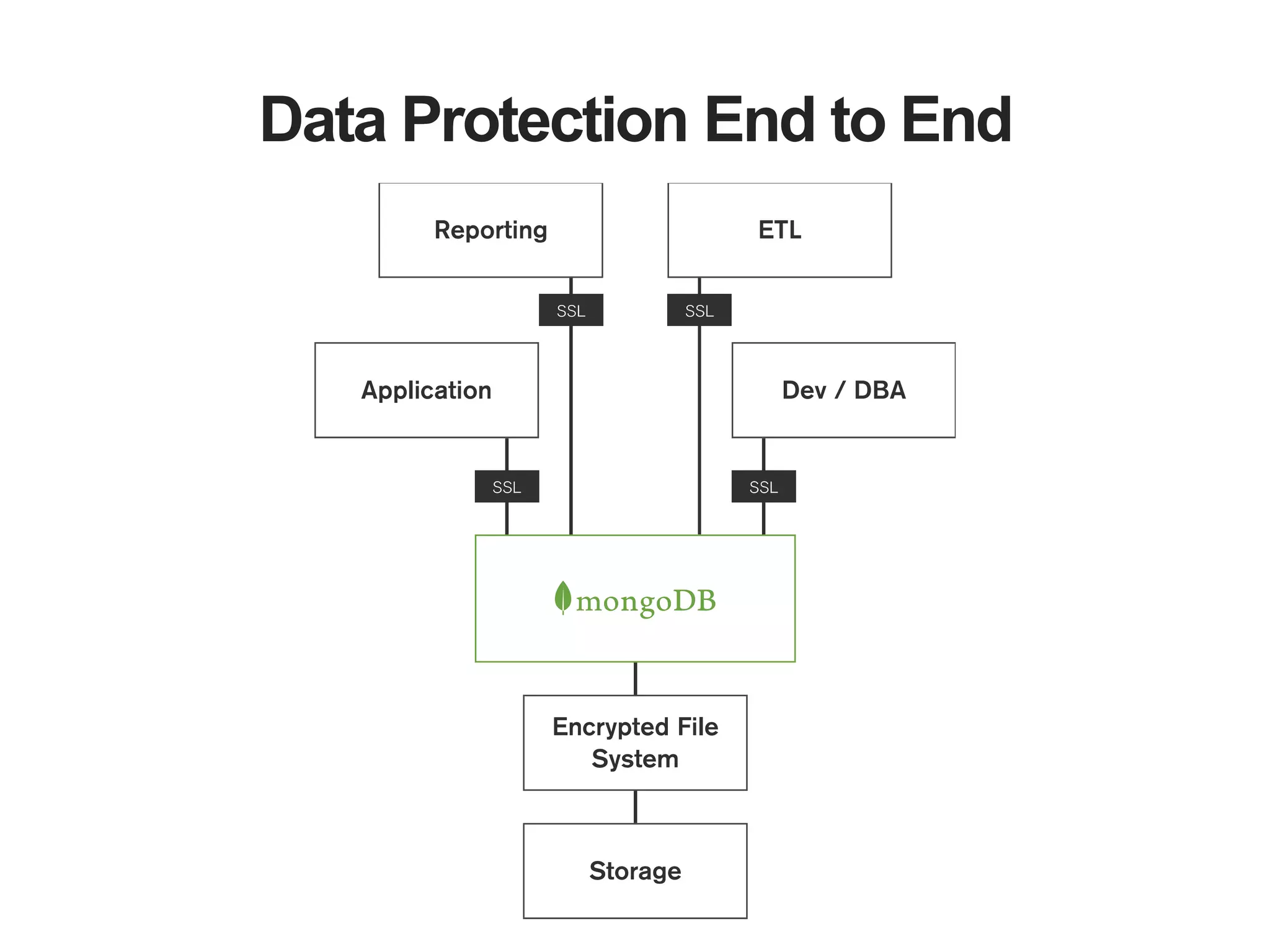
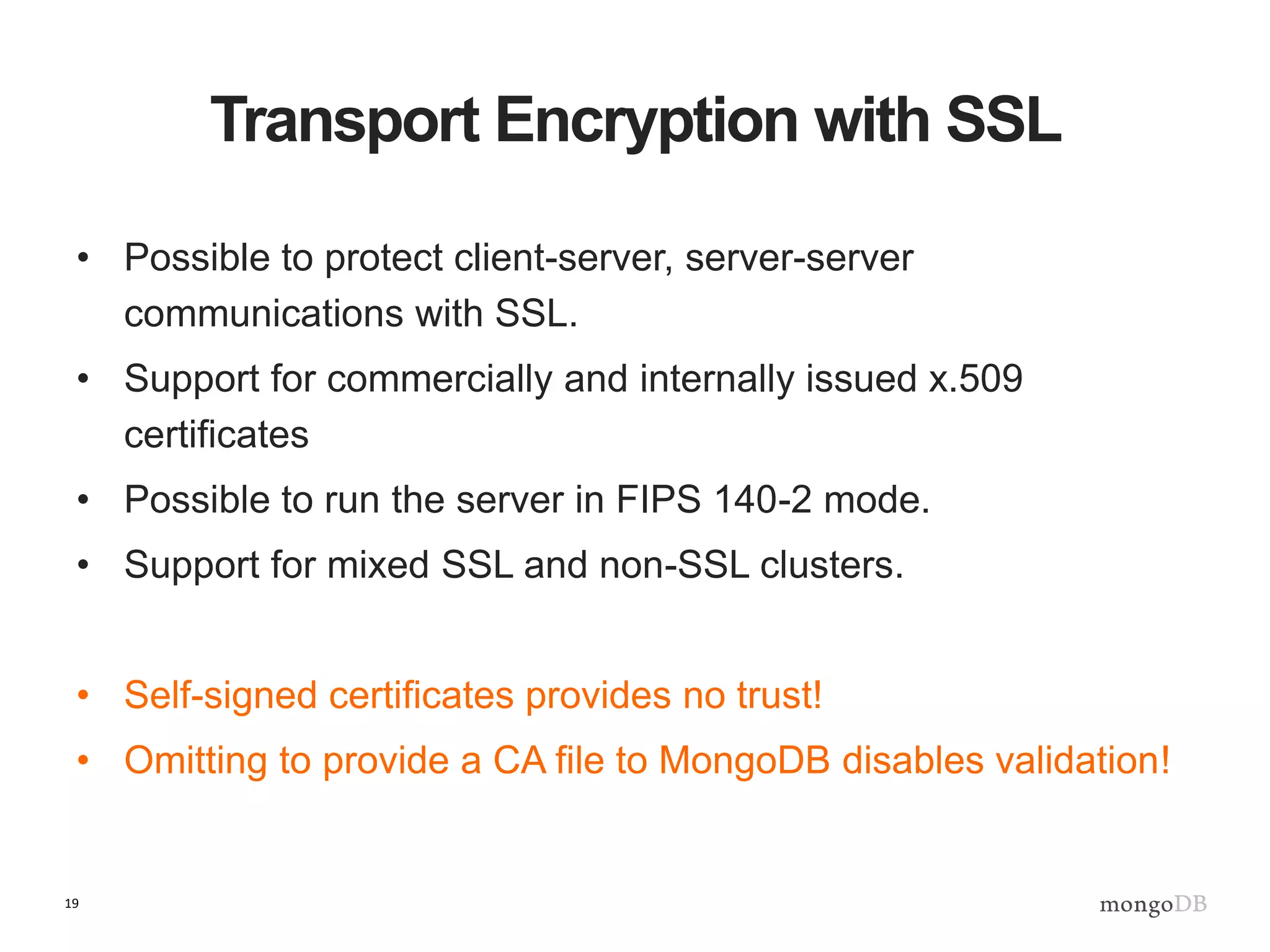
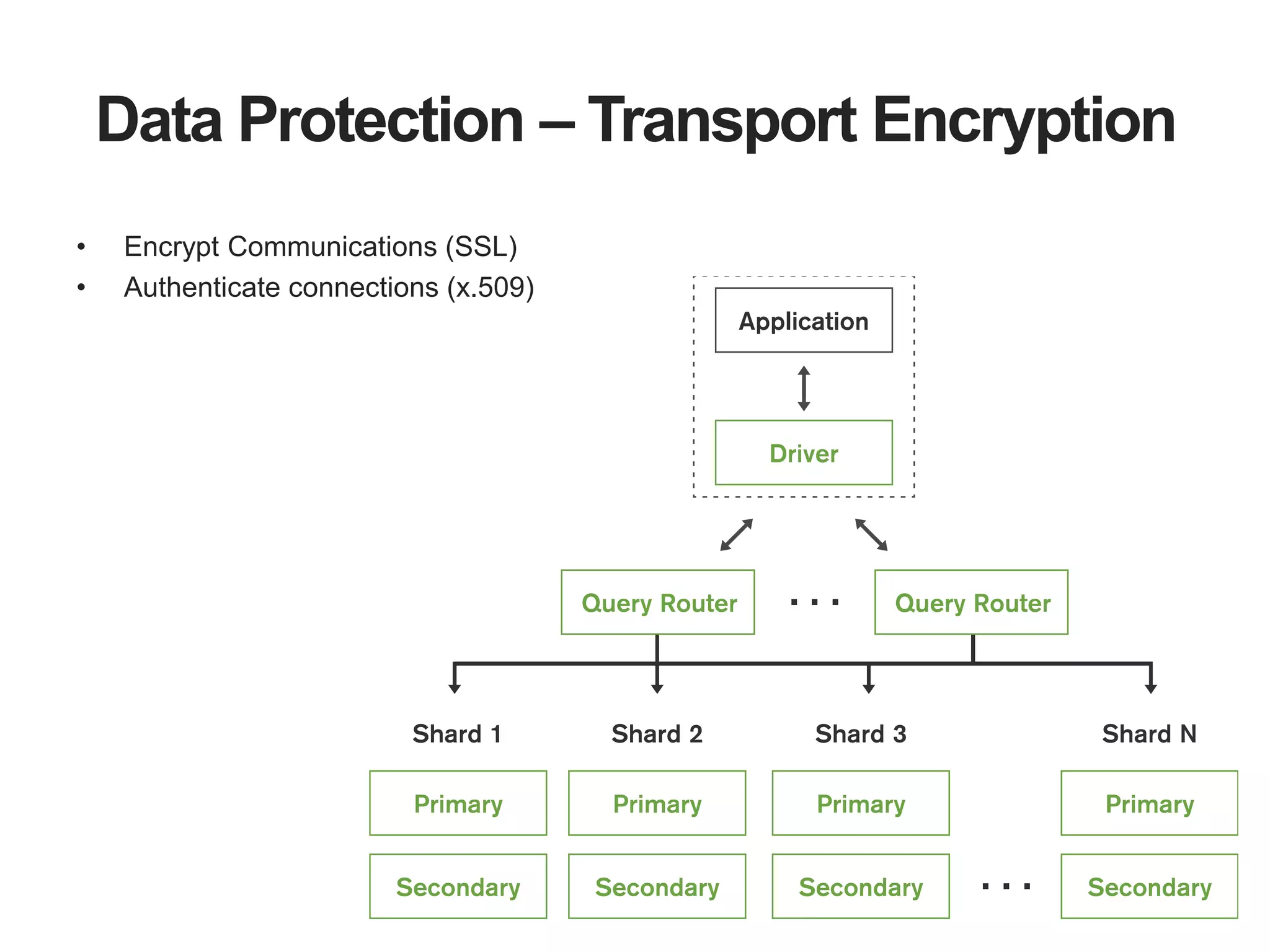
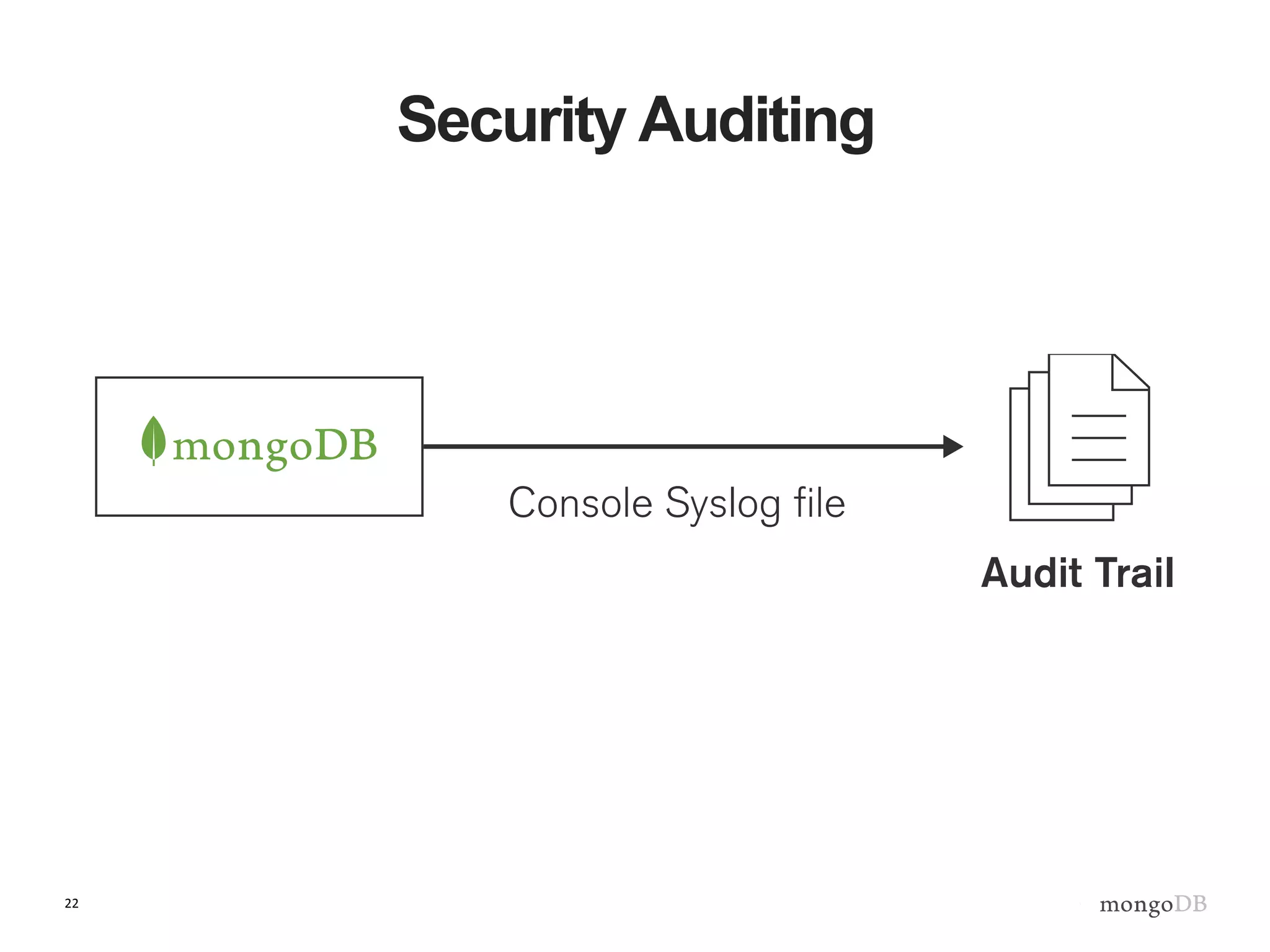
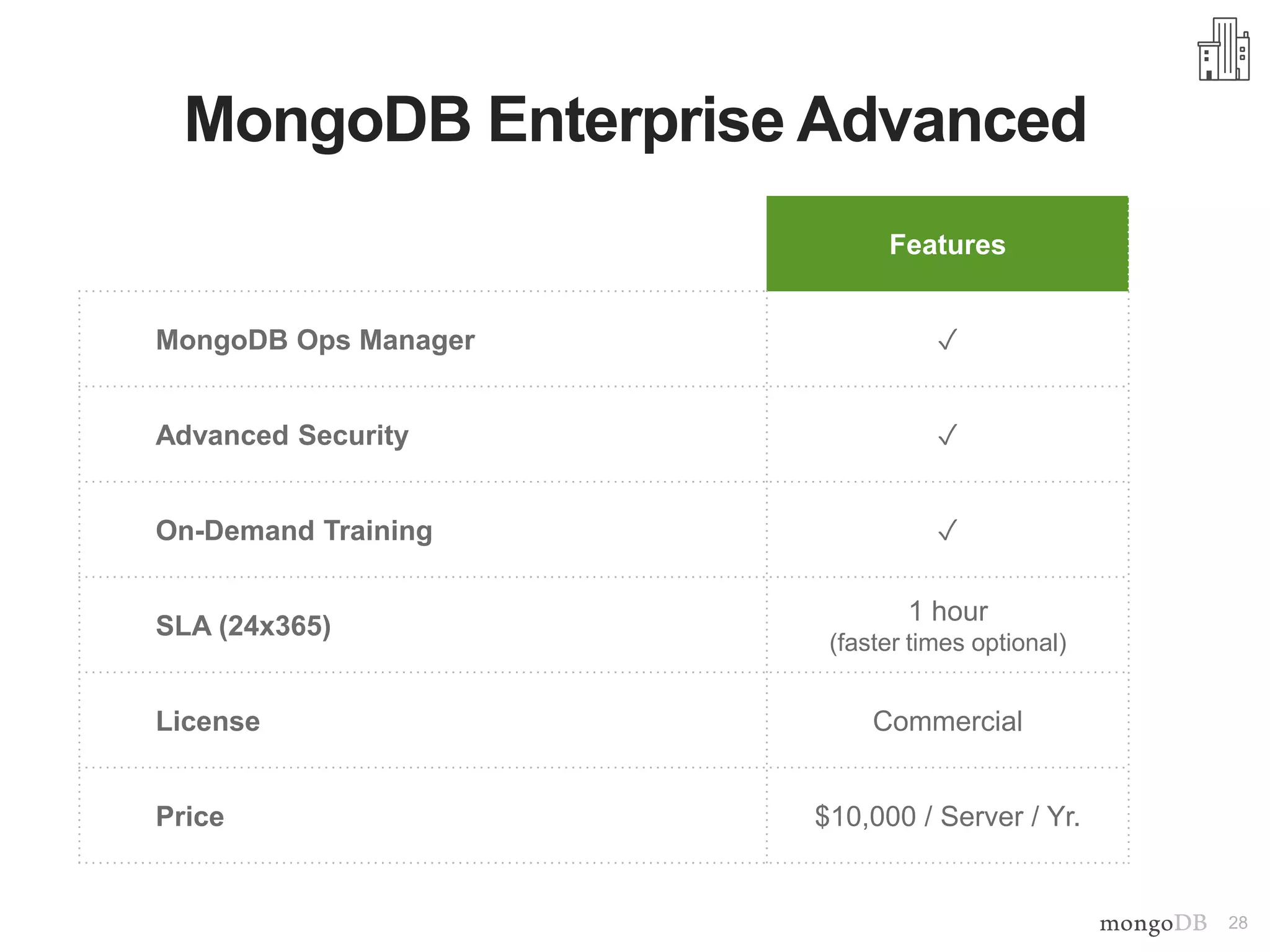
The document outlines strategies for securing MongoDB deployments, emphasizing the importance of access control, data protection, and security auditing. It discusses authentication methods, role-based access control, data encryption both in transit and at rest, and the significance of planning security from the onset of system design. Additionally, it highlights best practices and provides references for further reading on MongoDB security.