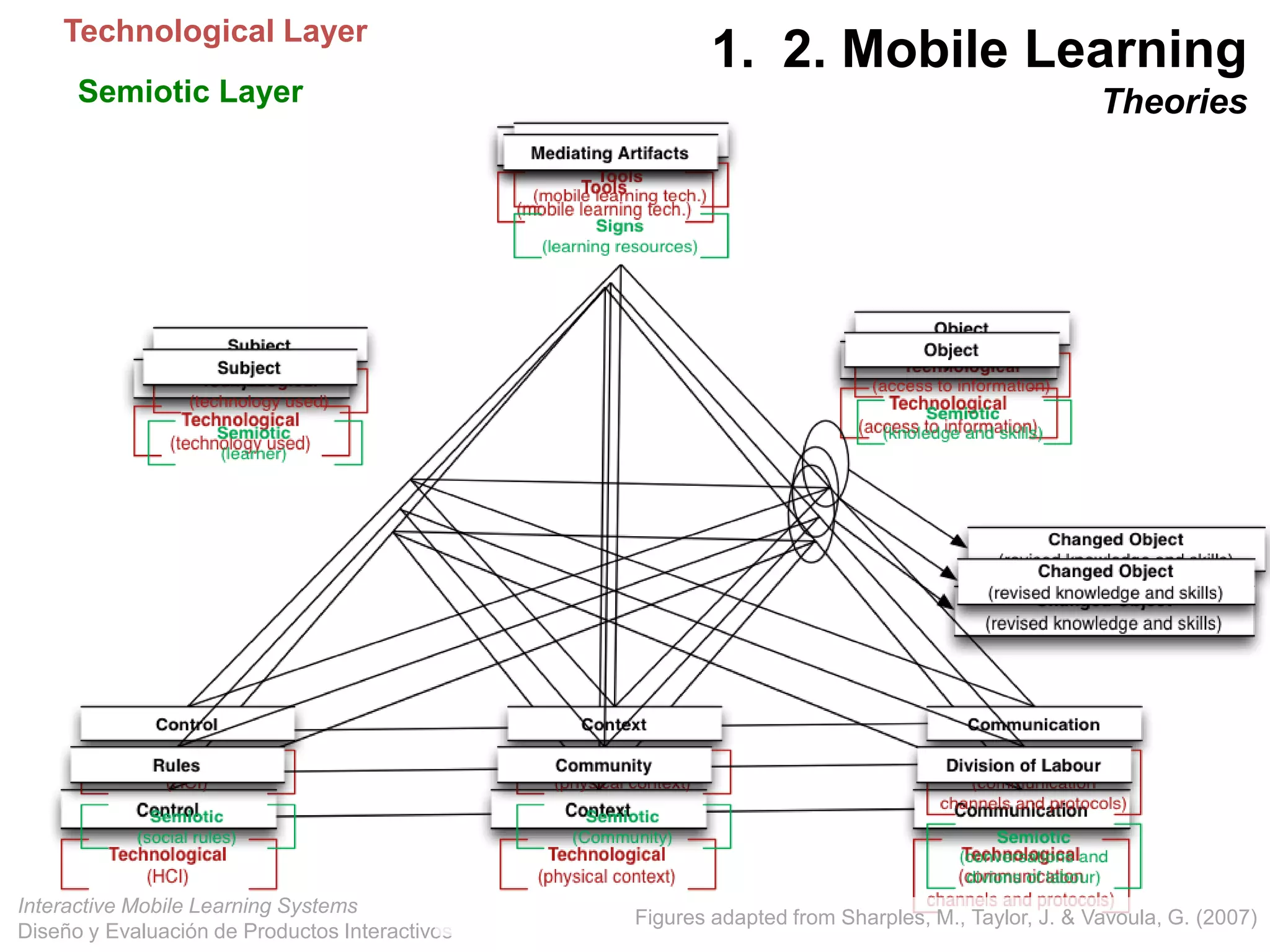
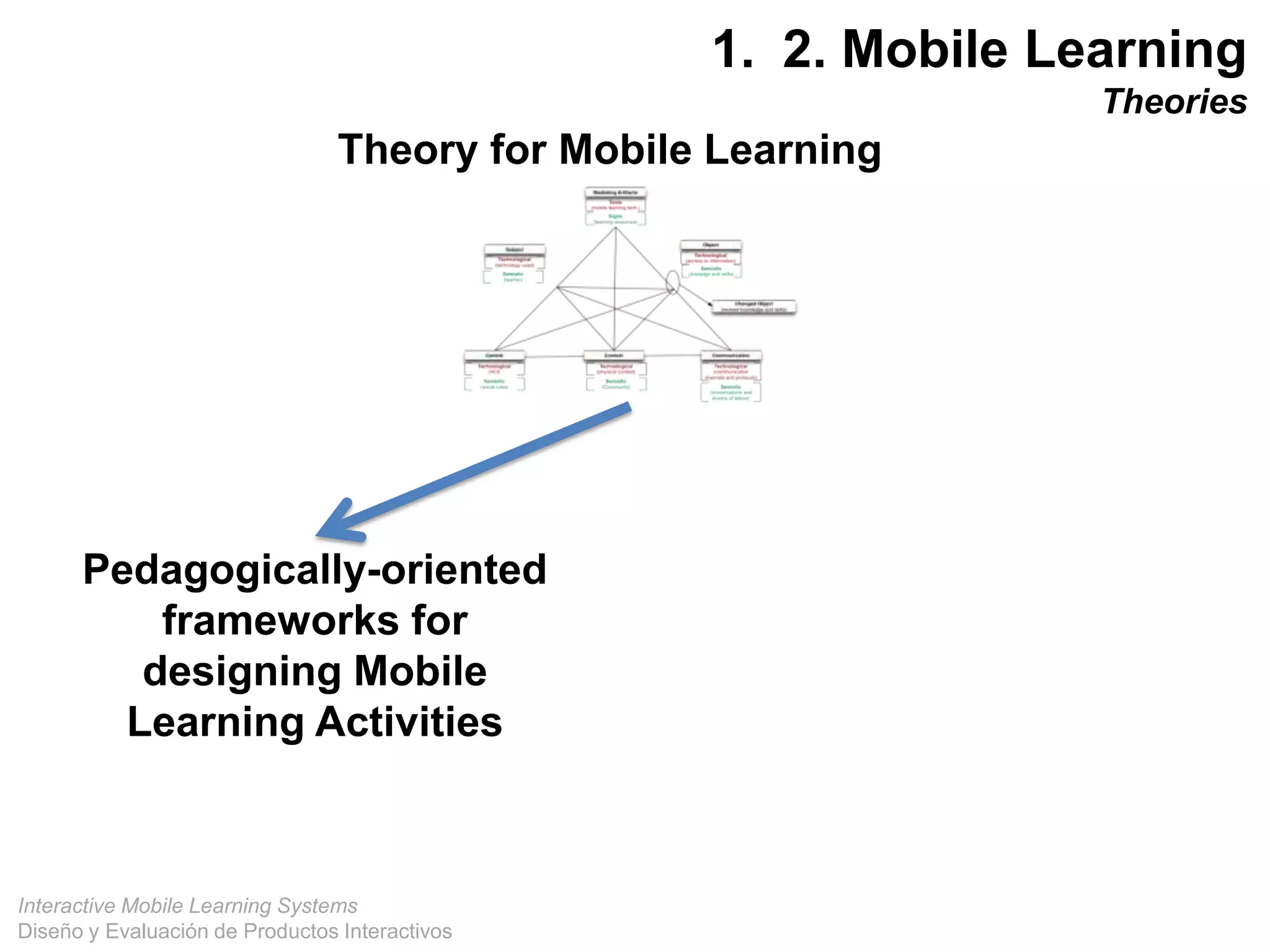
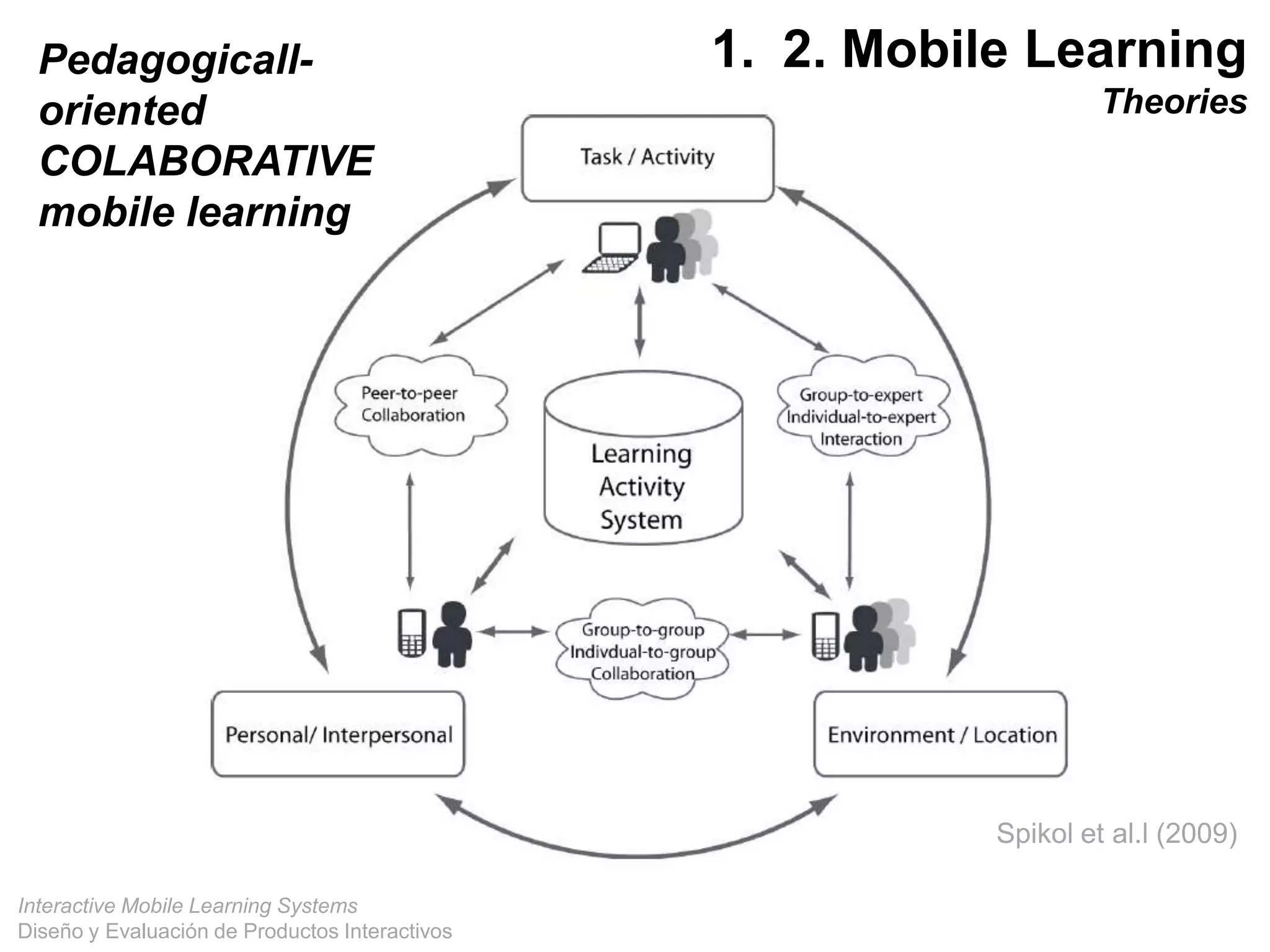
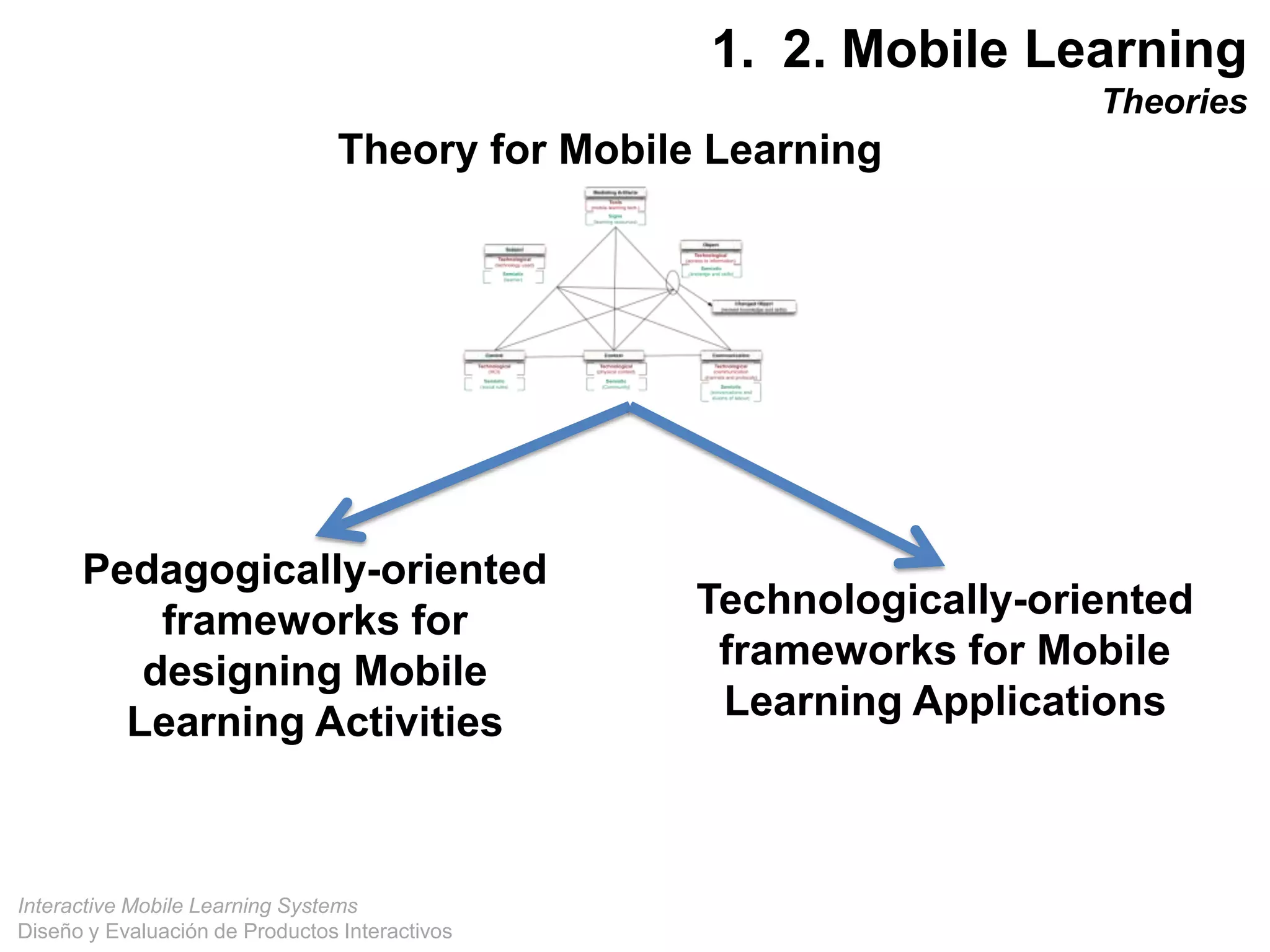
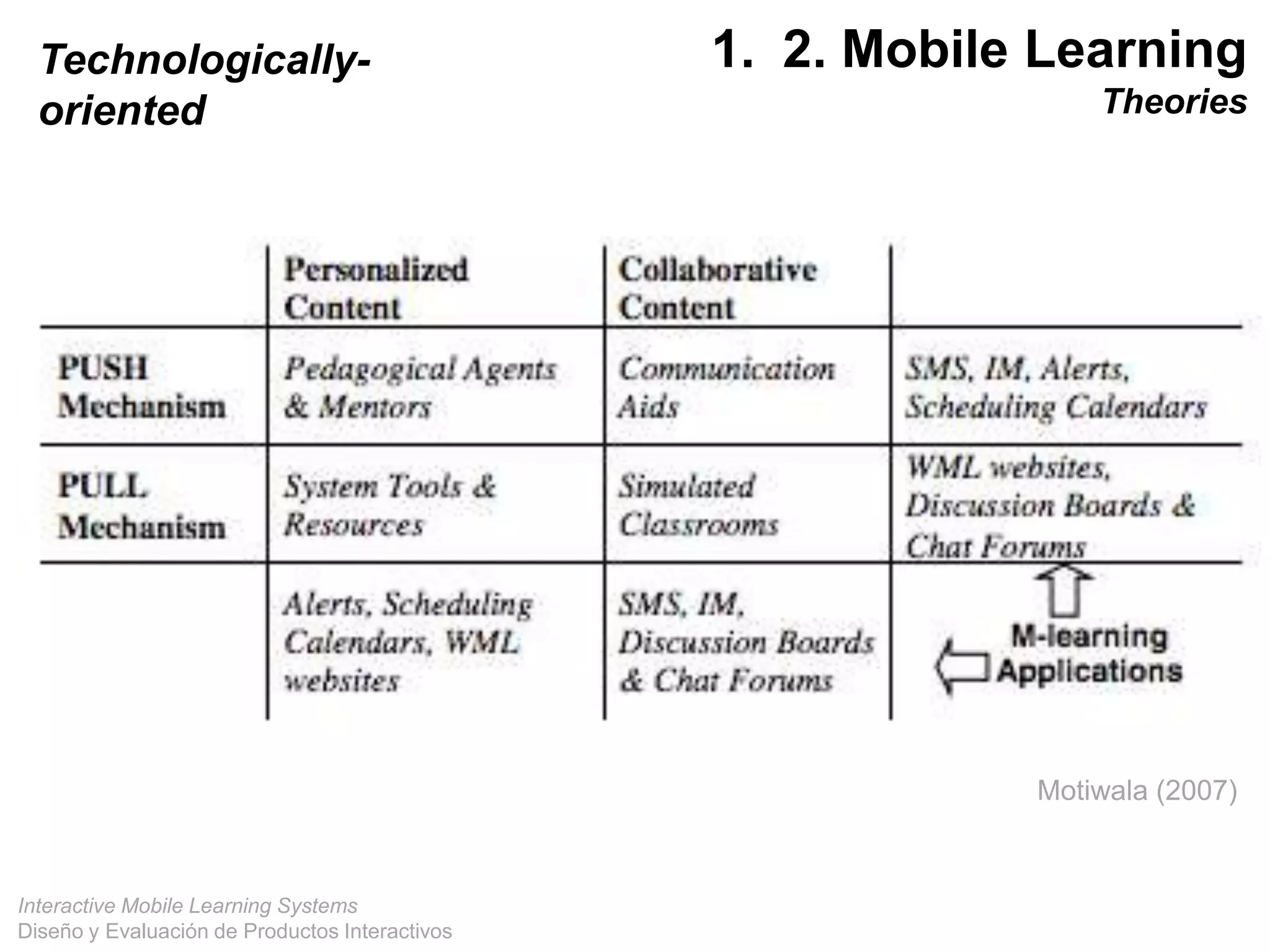
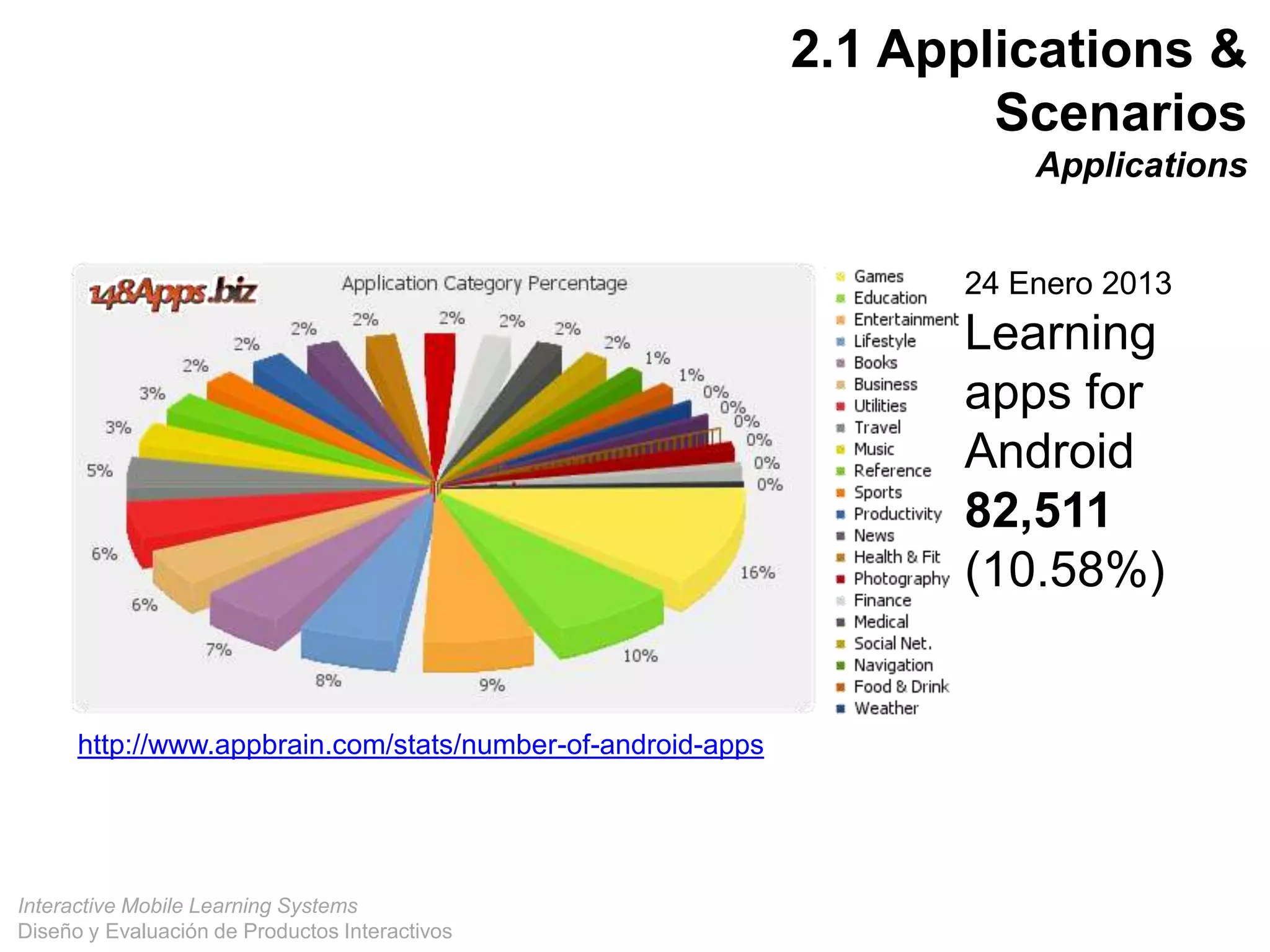
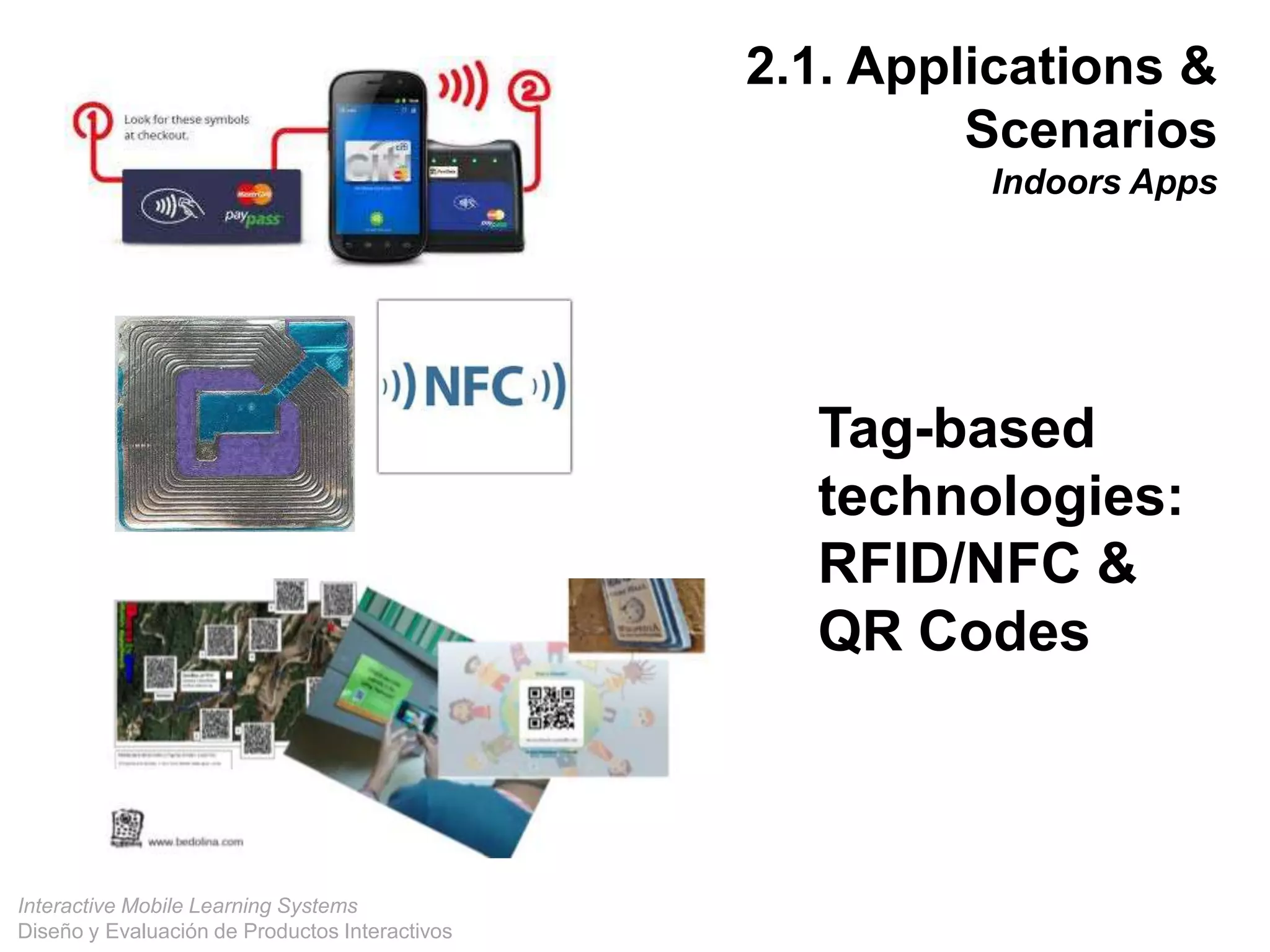
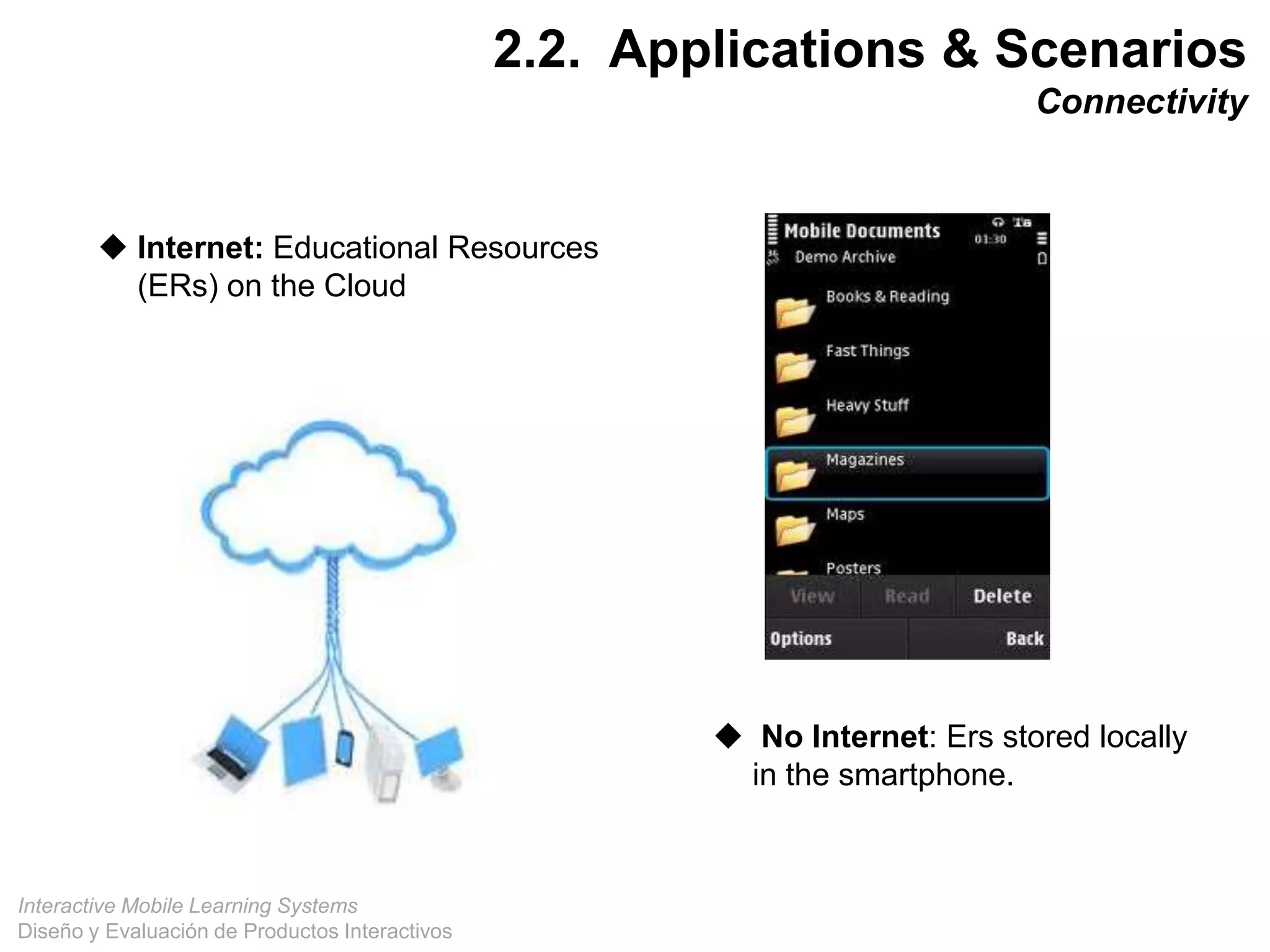
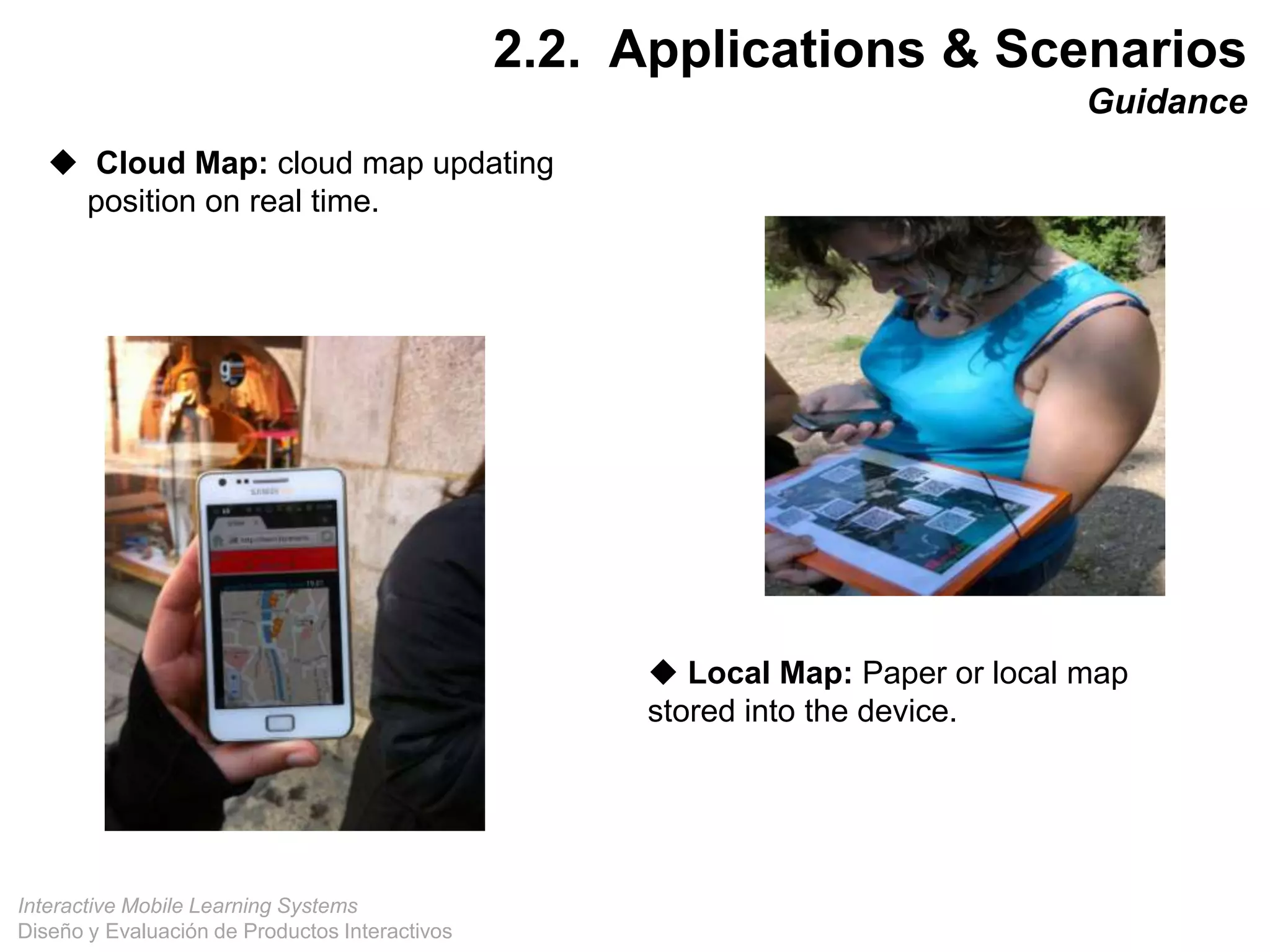
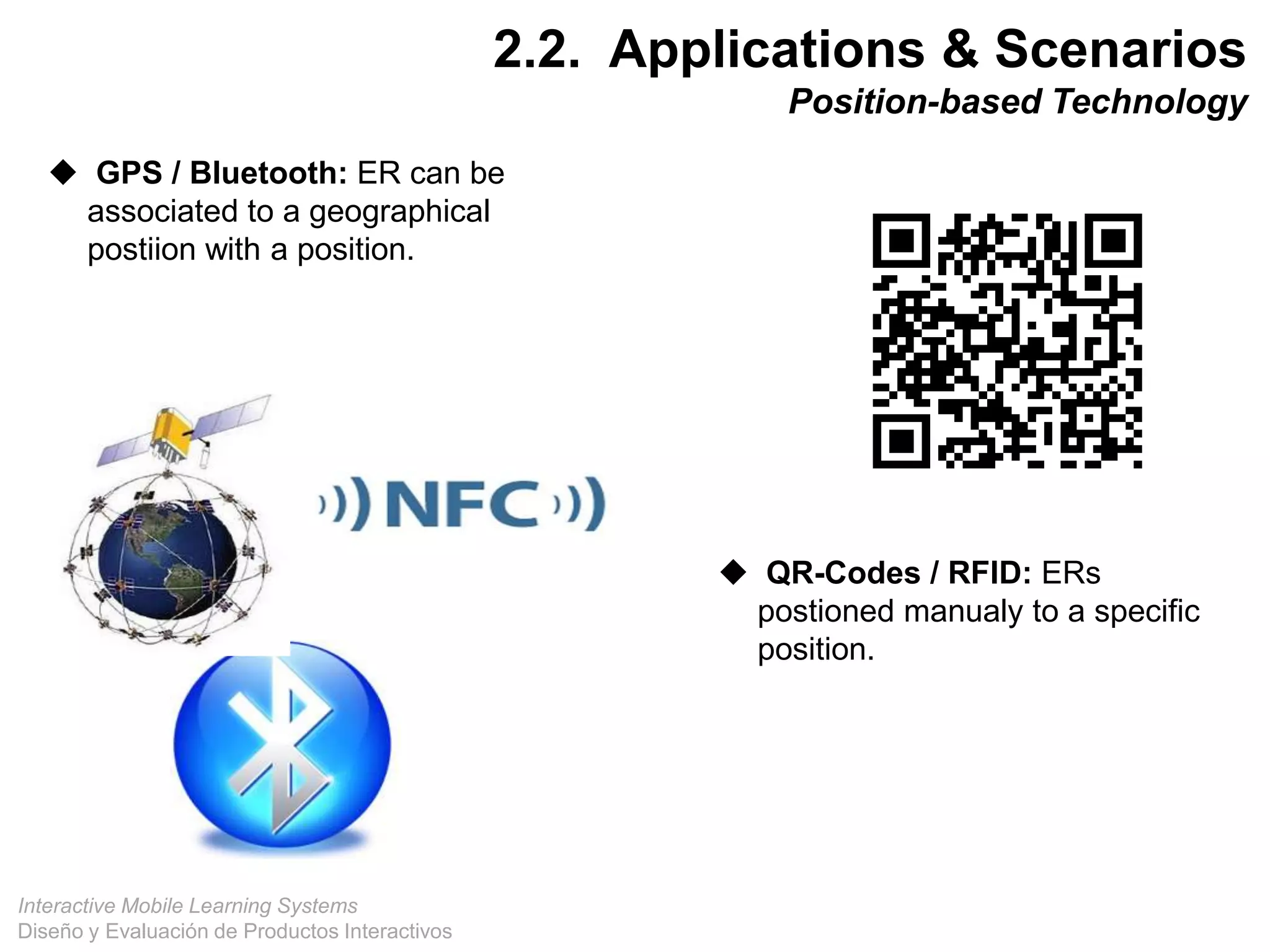
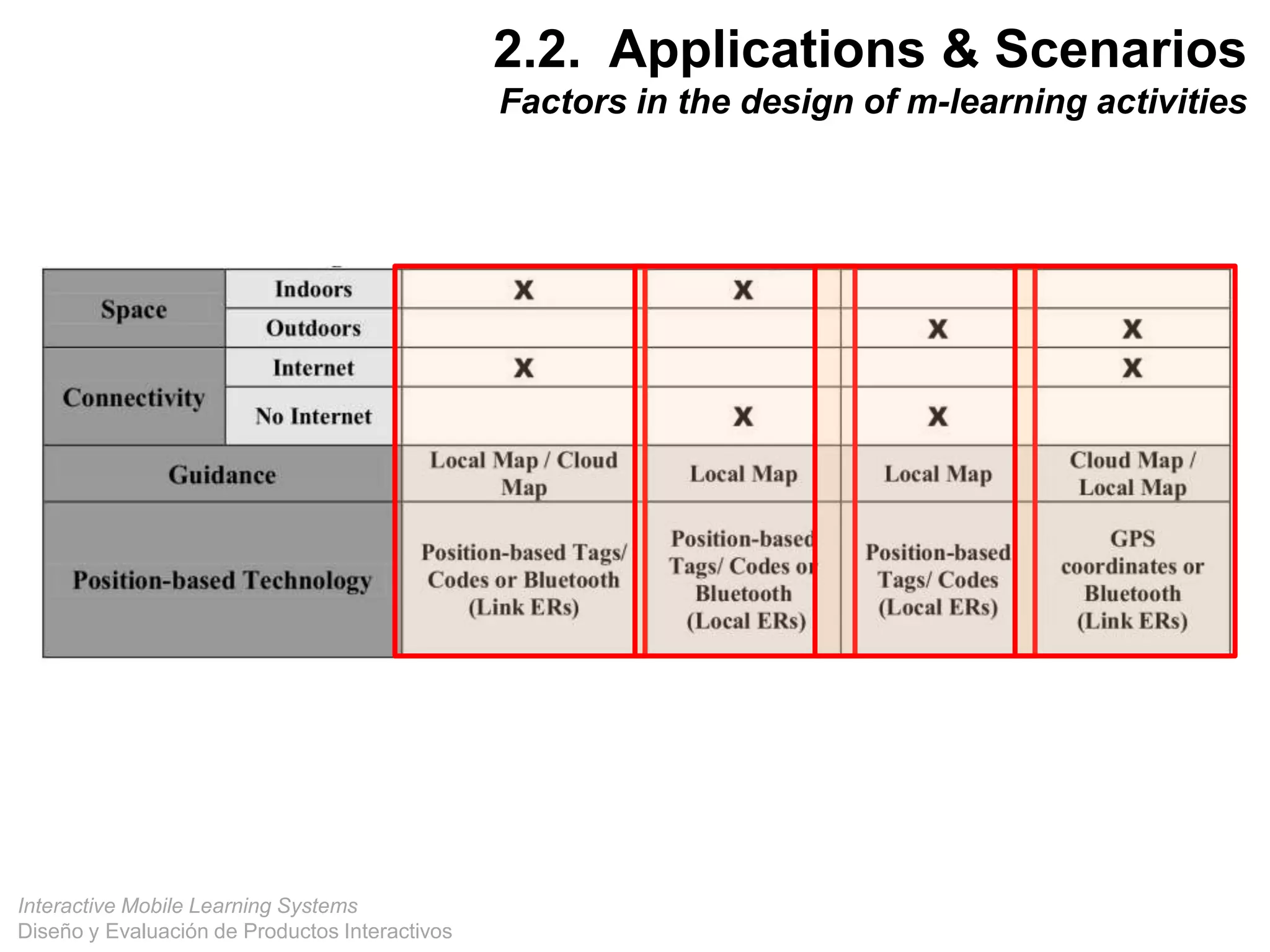
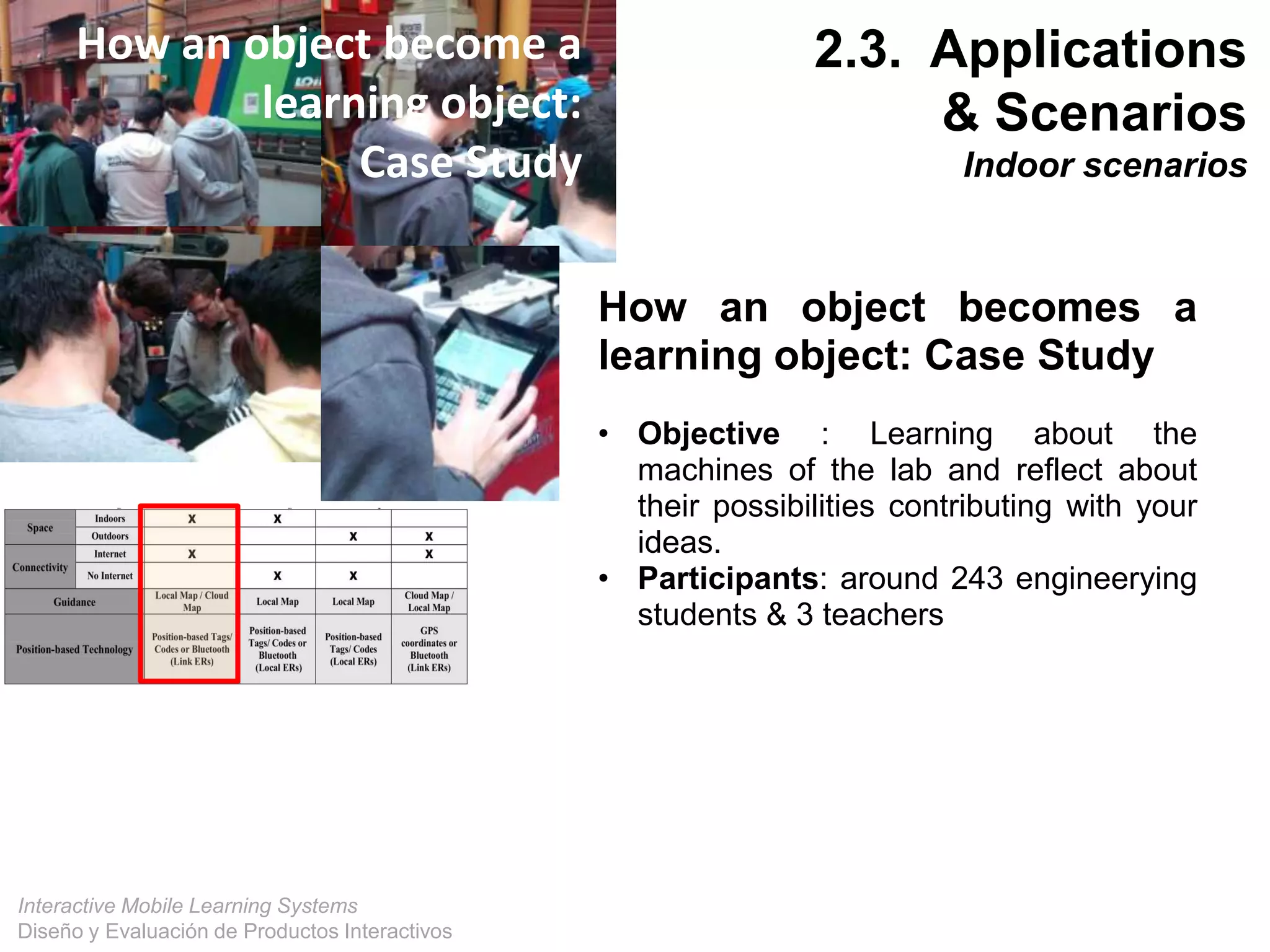
The document discusses the design and evaluation of interactive mobile learning systems, emphasizing the importance of teaching students how to use mobile devices for productive learning. It outlines various definitions, theories, and applications of mobile learning, particularly in smart city contexts, and highlights future challenges in integrating technology into educational practices. Conclusively, it describes mobile learning as a transformative approach to education that facilitates learning across different environments and contexts through the use of mobile technology.