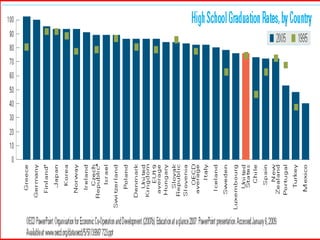
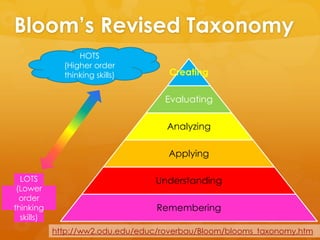
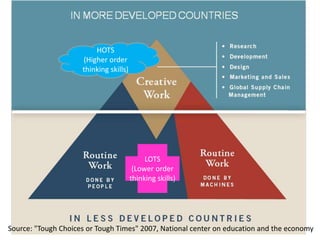
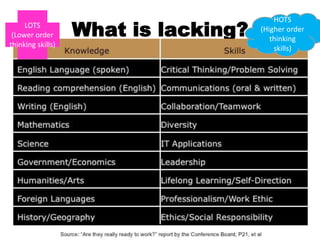
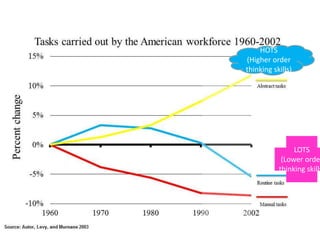
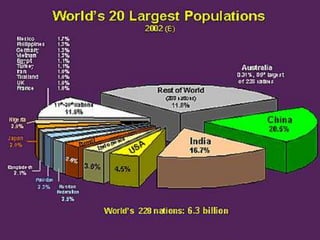
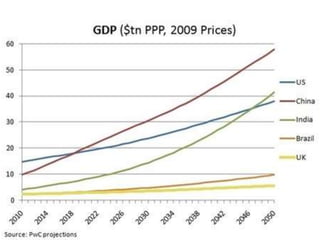
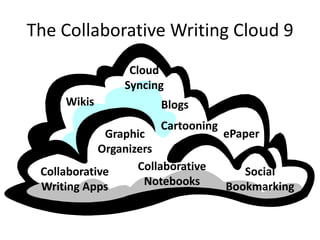
The document discusses collaborative writing and the Common Core writing standards. It defines collaborative writing as the process of writing, editing, and producing with a group of people. It notes that while wikis are collaborative platforms, most student wikis exhibit low levels of true collaboration where students meaningfully engage with each other's work. The benefits of collaborative writing mentioned include developing multiple perspectives, improved learning experiences, and skills needed for today's workplace. An overview of the Common Core writing standards is also provided.