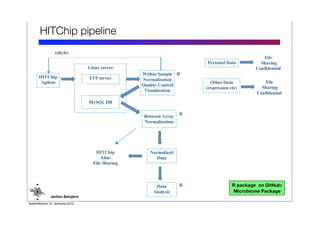
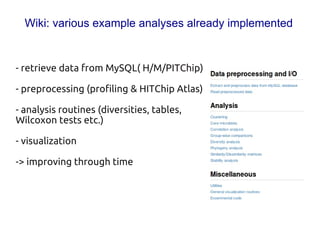
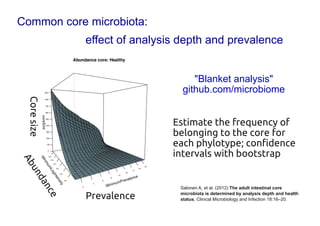
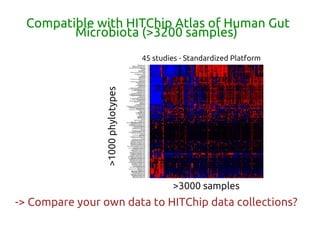
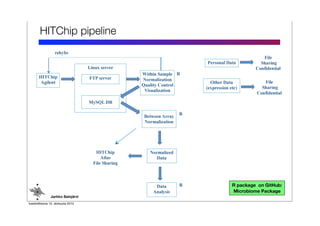
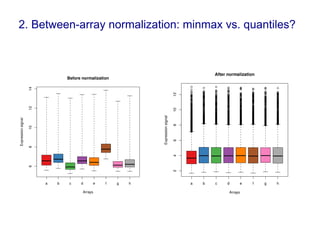
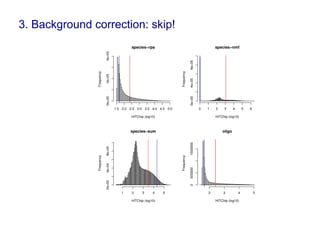
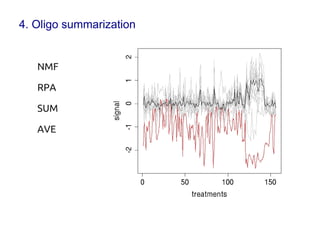
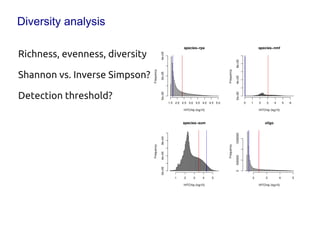
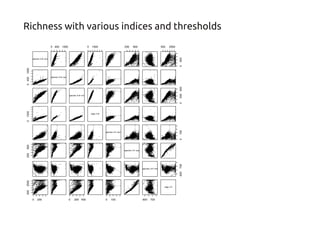
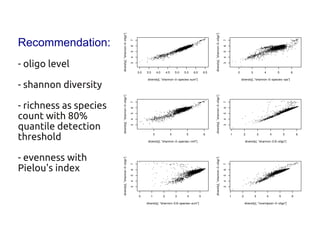
Code sharing for microbiomics analysis is proposed through standardized R packages and GitHub. This facilitates reproducible, efficient and collaborative analysis. Examples of standardized preprocessing, diversity analysis and visualization tools are provided. The microbiome package and wiki provide ready-made analysis examples to build upon.