This document summarizes an experimental study on reducing oxides of nitrogen (NOx) emissions in a single cylinder diesel engine converted to run in dual fuel mode with compressed natural gas (CNG). Experiments were conducted with varying CNG substitution levels, exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) rates, and fuel injection pressures. The results show that NOx emissions increased with higher CNG substitution levels but decreased with higher EGR rates and injection pressures. Increasing injection pressure was more effective at reducing NOx emissions while maintaining brake thermal efficiency compared to increasing EGR. The study aims to determine effective ways to control NOx emissions from a diesel engine operating in dual fuel mode with CNG.

![International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering and Technology (IJARET), ISSN 0976 – 6480(Print),
ISSN 0976 – 6499(Online) Volume 5, Issue 5, May (2014), pp. 66-74 © IAEME
67
I. INTRODUCTION
Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) has become a better option as a clean burning fuel of an IC
engine. In order to comply with the ever-stringent emission norms throughout the world and crunch
in petroleum reserves, the modern day automobile industry is compelled to hunt for new and
alternative means of fuel sources to keep the wheels spinning universally [1]. Paradoxical objectives
of attaining simultaneous reduction in emission along with high performance has provided with a
few alternative. Natural gas produces practically no particulates since it contains few dissolved
impurities (e.g. sulphur compounds). Moreover, natural gas can be used in compression ignition
engines (dual fuel diesel– natural gas engines) since the auto-ignition temperature of the gaseous fuel
is higher compared to the one of conventional liquid diesel fuel [3]. Dual fuel diesel–natural gas
engines feature essentially a homogeneous natural gas–air mixture compressed rapidly below its
auto-ignition conditions and ignited by the injection of an amount of liquid diesel fuel around top
dead center position. Natural gas is fumigated into the intake air and premixed with it during the
induction stroke. At constant engine speed, the fumigated gaseous fuel replaces an equal amount of
the inducted combustion air since the total amount of the inducted mixture has to be kept constant.
Furthermore, under fumigated dual fuel operating mode, the desired engine power output (i.e. brake
mean effective pressure) is controlled by changing the amounts of the fuels used. Thus, at a given
combination of engine speed and load, the change of the liquid fuel ‘‘supplementary ratio” leads to a
change of the inhaled combustion air, thus resulting to the alteration of the total relative air–fuel ratio
[1-3].
The fuel injection rate fuel nozzle design and fuel injection pressure all affect the
characteristics of the diesel fuel spray and its mixing with air in the combustion chamber [4-10]. The
increased injection pressure gave better results for brake specific fuel consumption and brake thermal
efficiency compared to the original and decreased injection pressures [11]. Injection pressures
decreased BSFC [12-14]. The peak cylinder pressure is reduced in the dual fuel operation mode
compared to the diesel single fuel operation mode. It has been reported that reductions in the
emissions of smoke and NOx can be achieved using DFC mode [6, 7]. By increasing fuel injection
pressure, pollution levels reduce due to complete combustion of fuel. Emissions are reduced at 200
bar with different manifold inclinations compared to other pressures. Finally, it is concluded that the
information obtained in this investigation is very much useful in reduction of pollution and
increasing the performance of the engine by varying the manifold inclination of the modern I.C
engines [15-19].
II. EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE
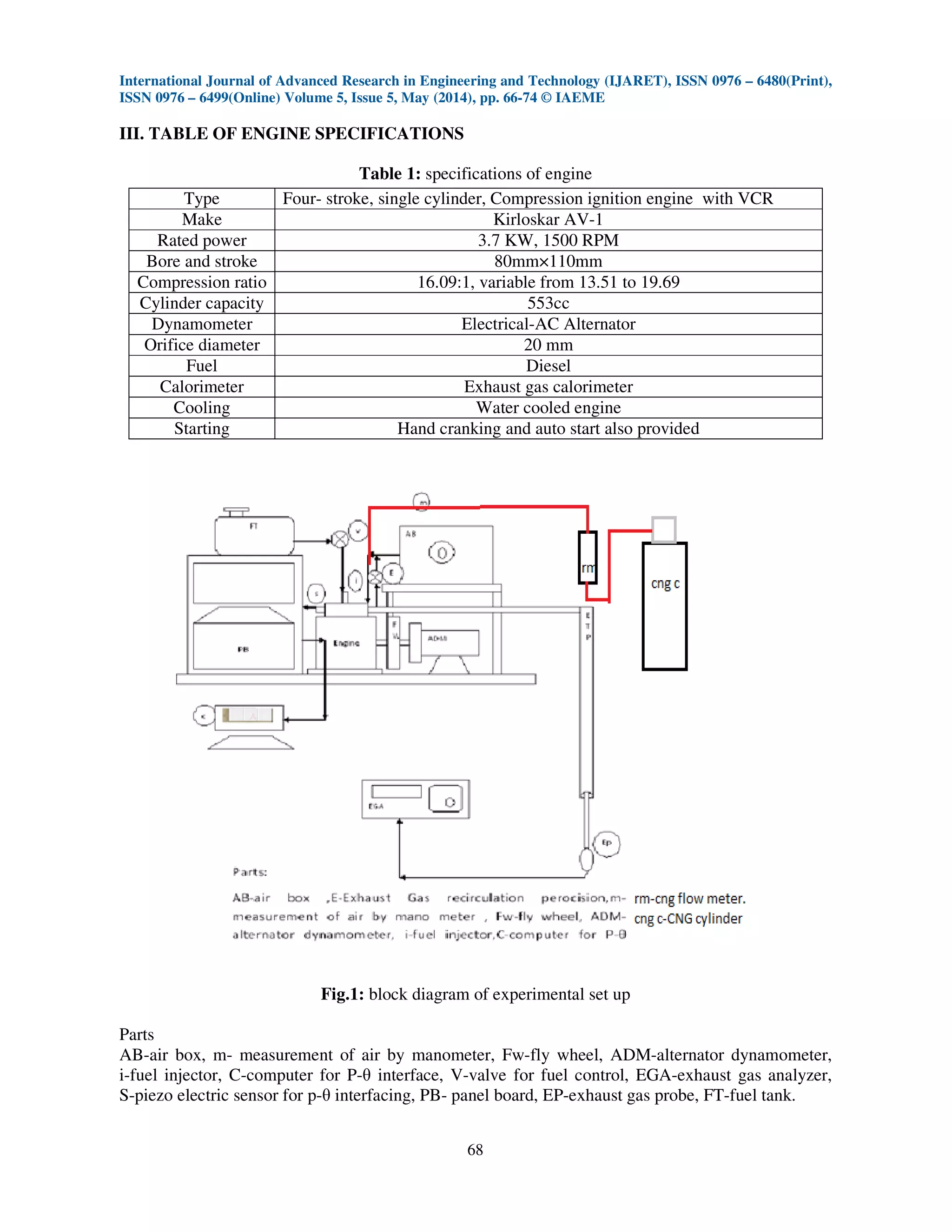
Series of several experimental cycles were conducted with varying CNG percentages and
iterations were done with varying exhaust gas recirculation and the results were compared. The
engine used in the present study is a Kirloskar AV-1, single cylinder direct injection, Water cooled
diesel engine with the specifications given in Table 1. Diesel injected with a nozzle hole of size
0.15mm.the engine is coupled to a dc dynamometer. Engine exhaust emission is measured. Load was
varied from 0.5 kilo watt to 3 kilo watts. The amount of exhaust gas sent to the inlet of the engine is
varied. At each cycle, the engine was operated at varying load and the efficiency of the engine has
been calculated simultaneously. The experiment is carried out by keeping the compression ratio
constant i.e., 16.09:1.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20120140505008-2-140611042324-phpapp02/75/20120140505008-2-2-2048.jpg)
![International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering and Technology (IJARET), ISSN 0976 – 6480(Print),
ISSN 0976 – 6499(Online) Volume 5, Issue 5, May (2014), pp. 66-74 © IAEME
72
Graph 7: Brake thermal efficiency Vs Nox at various EGR proportions
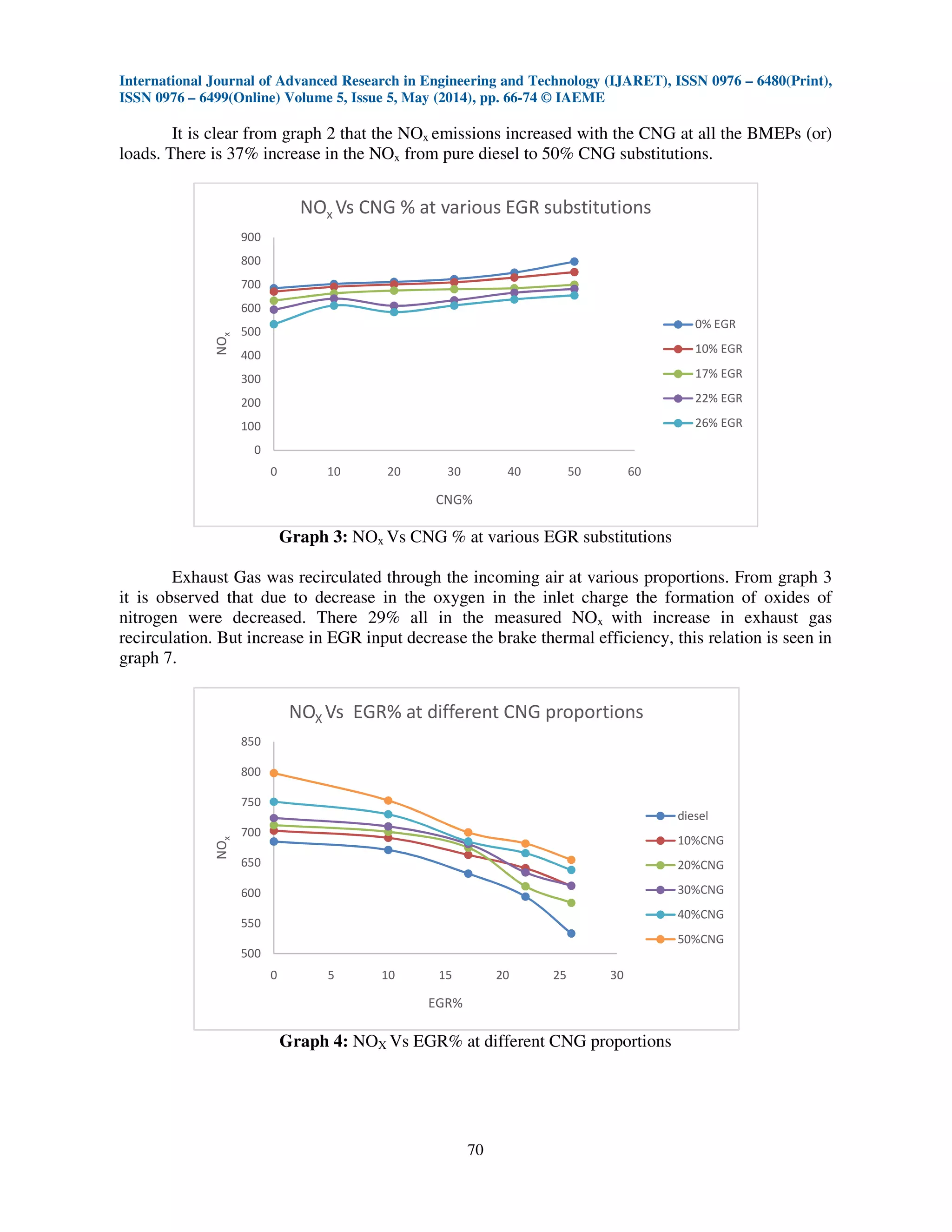
Graph 7 shows the cost of brake thermal efficiency at which the NOx was reduced by
increasing the exhaust gas recirculation. With increase in exhaust gas recirculation NOx decreased at
the cost of brake thermal efficiency. This makes increase in the injection pressure more feasible
when brake thermal efficiency is a constraint equally important to reduction of NOx.
V. CONCLUSION
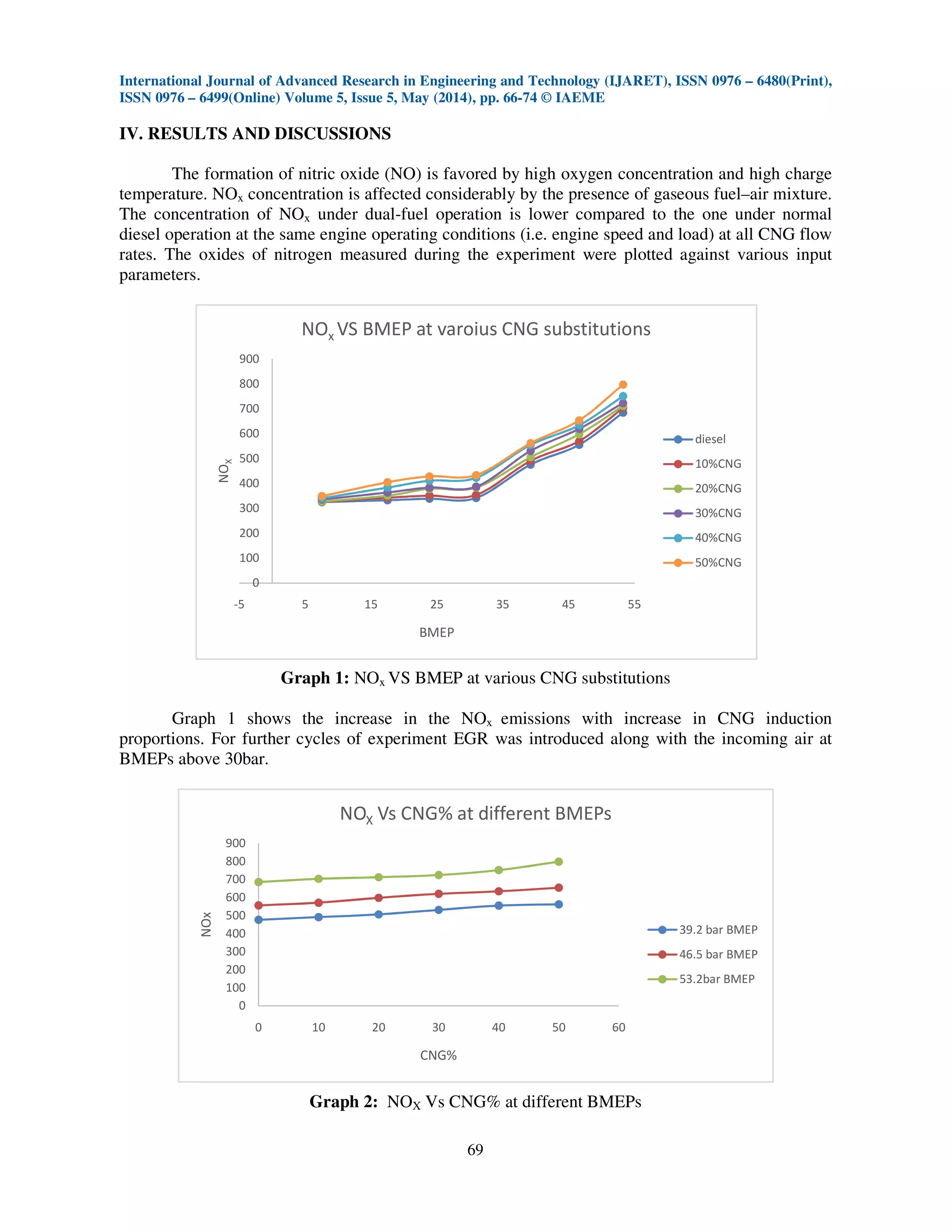
The NOx emissions increased with increase in CNG induction proportions at all the BMEPs
(or) loads. There is 37% increase in the NOx from pure diesel to 50% CNG substitutions. For further
cycles of experiment EGR was introduced along with the incoming air at BMEPs above 30bar.There
29% all in the measured NOx with increase in exhaust gas recirculation. But increase in EGR input
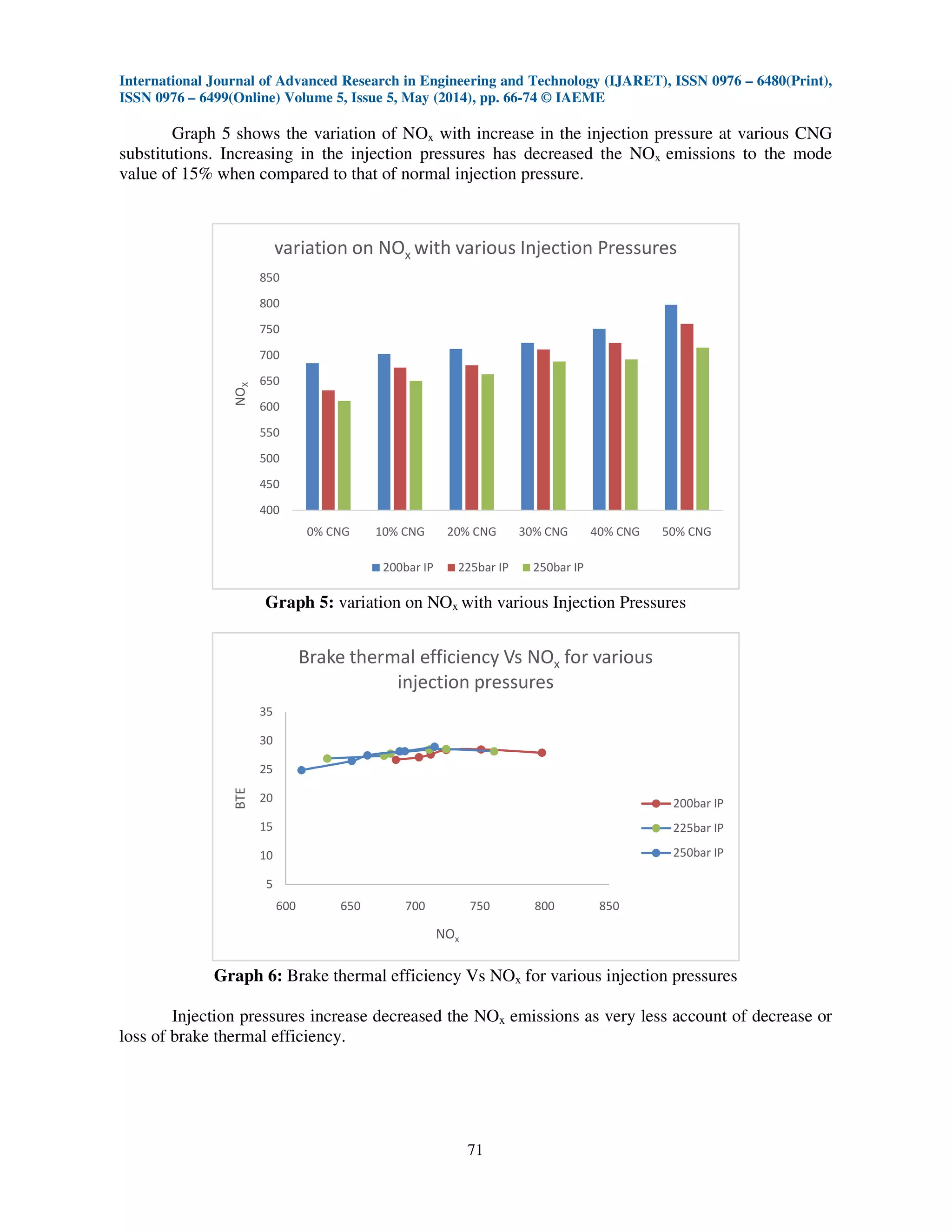
decrease the brake thermal efficiency. Increasing in the injection pressures has decreased the NOx
emissions to the mode value of 15% when compared to that of normal injection pressure. Injection
pressures increase decreased the NOx emissions as very less account of decrease or loss of brake
thermal efficiency. This makes increase in the injection pressure more feasible when brake thermal
efficiency is a constraint equally important to reduction of NOx.
REFERENCES
[1] R.G Papagiannakis, D.T Hountalas, “Experimental investigation concerning the effect of
natural gas percentage on performance and emissions of a DI dual fuel diesel engine”,
Applied Thermal Engineering, Volume 23, Issue 3, February 2003, Pages 353–365.
[2] S.K. Mahla, L.M. Das and M.K.G. Babu. “Effect of EGR on Performance and Emission
Characteristics of Natural Gas Fueled Diesel Engine”, Jordan Journal of Mechanical and
Industrial Engineering Volume 4, Number 4, September 2010, ISSN 1995-6665,
Pages: 523– 530.
5
10
15
20
25
30
500 550 600 650 700 750 800
BTE
NOx
Brake thermal efficiency Vs Nox at various EGR
proportions
10% EGR
17% EGR
22% EGR
26% EGR](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20120140505008-2-140611042324-phpapp02/75/20120140505008-2-7-2048.jpg)
![International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering and Technology (IJARET), ISSN 0976 – 6480(Print),
ISSN 0976 – 6499(Online) Volume 5, Issue 5, May (2014), pp. 66-74 © IAEME
73
[3] R.G. Papagiannakisa, P.N. Kotsiopoulosa, T.C. Zannisb, E.A. Yfantisb, D.T. Hountalasc and
C.D. Rakopoulosc, “Theoretical study of the effects of engine parameters on performance
and emissions of a pilot ignited natural gas diesel engine”, Energy, Volume 35, Issue 2,
February 2010, Pages 1129–1138, 21st International Conference, on Efficiency, Cost,
Optimization, Simulation and Environmental Impact of Energy Systems.
[4] N. Alagumurth, C.G. Saravanan K. Anandavelu, “Performance and Emission Evaluation of
Low Heat Rejection Direct Injection Diesel Engine Fueled by Diesel: Turpentine Oil Blends”
Proceedings of the ASME 2010 International Mechanical Engineering Congress &
Exposition, November 12-18, 2010, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada.
[5] Can Çinara, Tolga Topgüla, Murat Cinivizb, Can Haşimoğlu, “Effects of injection pressure
and intake CO2 concentration on performance and emission parameters of an IDI
turbocharged diesel engine”, Applied Thermal Engineering, Volume 25, Issues 11–12,
August 2005, Pages 1854–1862.
[6] Semin RAB. A technical review of compressed natural gas as an alternative fuelfor internal
combustion engines. Am J EngApplSci 2008;1(4):302–11.
[7] V. Pradeep, R.P. Sharma, “Use of HOT EGR for NOx control in a compression ignition
engine fuelled with bio-diesel from Jatropha oil”, Renewable Energy 32 pp 1136–1154, 2007.
[8] Ekrem Buyukkaya, Muhammet Cerit, “Experimental study of NOx emissions and injection
timing of a low heat rejection diesel engine”, International Journal of Thermal Sciences,
Volume 47, Issue 8, August 2008, Pages 1096–1106.
[9] Bakar, R. A., IsmailA. R., and Semin, “Fuel Injection Pressure Effect on Performance of
Direct Injection Diesel Engines Based on Experiment,” American Journal of Applied
Sciences, 5 (3), 2008, pp. 197–202.
[10] Keeler, B., and Shayler, P. J., 2008, “Constraints on Fuel Injection and EGR Strategies for
Diesel PCCI-Type Combustion,” SAE Paper No. 2008-01-1327.
[11] Bose PK, Banerjee R. Banerjee R. An experimental investigation the role of hydrogen in the
emission reduction and performance trade-off studies in an existing diesel engine operating in
dual fuel mode under exhaust gas recirculation. J Energy Resour Technol 2012;134(012601).
[12] Robert Kiplimoa, Eiji Tomitaa, Nobuyuki Kawaharaa, Sumito Yokobe, “Effects of spray
impingement, injection parameters, and EGR on the combustion and emission characteristics
of a PCCI diesel engine”, Applied Thermal Engineering, Volume 37, May 2012,
Pages 165–175.
[13] M.L.S Deva Kumar, S.Drakshayani, K.Vijaya Kumar Reddy, "Effect of Fuel Injection
Pressure on Performance of Single Cylinder Diesel Engine at Different Intake Manifold
Inclinations", International Journal of Engineering and Innovative Technology (IJEIT)
Volume 2, Issue 4, October 2012.
[14] Mahla SK, Das LM, Babu MKG. Effect of EGR on performance and Emission characteristics
of natural gas fueled diesel engine. Jordan J MechIndEng2010;4(4):523-3
[15] Junnian Zheng, erald A. Caton, “Second law analysis of a low temperature combustion diesel
engine: Effect of injection timing and exhaust gas recirculation”, Energy, Volume 38, Issue 1,
February 2012, Pages 78–84
[16] Muammer Özkan, Derya Burcu Özkan, Orkun Özener, Hasan Yılmaz, “Experimental study
on energy and exergy analyses of a diesel engine performed with multiple injection
strategies: Effect of pre-injection timing”, Applied Thermal Engineering, Volume 53, Issue 1,
29 April 2013, Pages 21–30.
[17] S. Saravanan, G. Nagarajan, S. Sampath, “Combined effect of injection timing, EGR and
injection pressure in NOx control of a stationary diesel engine fuelled with crude rice bran oil
methyl ester”, Fuel, Volume 104, February 2013, Pages 409–416.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20120140505008-2-140611042324-phpapp02/75/20120140505008-2-8-2048.jpg)
![International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering and Technology (IJARET), ISSN 0976 – 6480(Print),
ISSN 0976 – 6499(Online) Volume 5, Issue 5, May (2014), pp. 66-74 © IAEME
74
[18] Ying Wang, Yuwei Zhao, Fan Xiao, Dongchang Li, “Combustion and emission
characteristics of a diesel engine with DME as port premixing fuel under different injection
timing”, Energy Conversion and Management, Volume 77, January 2014, Pages 52–60.
[19] İsmet Çelıkten, “An experimental investigation of the effect of the injection pressure on
engine performance and exhaust emission in indirect injection diesel engines”, Applied
Thermal Engineering, Volume 23, Issue 16, November 2003, Pages 2051–2060.
[20] Shaik Magbul Hussain, Dr. B. Sudheer Prem Kumar and Dr. K. Vijaya Kumar Reddy,
“Biogas –Diesel Dual Fuel Engine Exhaust Gas Emissions” International Journal of
Advanced Research in Engineering & Technology (IJARET), Volume 4, Issue 3, 2013,
pp. 211 - 216, ISSN Print: 0976-6480, ISSN Online: 0976-6499.
[21] Shailaja M, V.Vijaya Kumar, Chandragiri Radha Charan and Dr. A V Sitarama Raju,
“Development of Back Propagation Neural Network Model to Predict Performance and
Emission Parameters of a Diesel Engine”, International Journal of Advanced Research in
Engineering & Technology (IJARET), Volume 4, Issue 3, 2013, pp. 85 - 92, ISSN Print:
0976-6480, ISSN Online: 0976-6499.
[22] Nandkishore D. Rao, Dr. B. Sudheer Premkumar and Jaganath.S, “Effect of Variation in
Compression Ratio on Characteristics of CI Engine Fuelled with Honge Oil-Ethanol Blend”,
International Journal of Mechanical Engineering & Technology (IJMET), Volume 4, Issue 4,
2013, pp. 357 - 365, ISSN Print: 0976 – 6340, ISSN Online: 0976 – 6359.
[23] S.H. Choi, Y.T. Oh and J. Azjargal, “Lard Biodiesel Engine Performance and Emissions
Characteristics with EGR Method”, International Journal of Mechanical Engineering &
Technology (IJMET), Volume 3, Issue 2, 2012, pp. 397 - 409, ISSN Print: 0976 – 6340,
ISSN Online: 0976 – 6359.
[24] Sharun Mendonca and John Paul Vas, “A Study of the Performance and Emission
Characteristics of a Compression Ignition Engine using Methyl Ester of Simarouba and
Jatropha at Different Injection Pressures”, International Journal of Advanced Research in
Engineering & Technology (IJARET), Volume 4, Issue 6, 2013, pp. 195 - 202, ISSN Print:
0976-6480, ISSN Online: 0976-6499.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20120140505008-2-140611042324-phpapp02/75/20120140505008-2-9-2048.jpg)