This PowerPoint presentation discusses the history, advantages, and concerns of using social media in higher education. It defines social media as web services that allow users to create profiles, connect with others, and view connections. Some key advantages discussed are using social media for communication, marketing, classroom collaboration, and engaging alumni. Potential downsides addressed include distraction, privacy issues, and spreading misinformation. The presentation recommends educating students and faculty on best practices for social media use.













![References
Boyd, D. M. & Ellison, N. B. (2007). Social network sites: Definition, history, and scholarship. Journal of Computer-
Mediated Communication, 13(1), 210-230. DOI: 10.1111/j.1083-6101.2007.00393.x
Heiberger, G., & Harper, R. (2008). Have you Facebooked Astin lately? Using technology to increase student
involvement. In Junco, R., & Timm, D. M., eds. Using emerging technologies to enhance student
engagement. New Directions for Student Services Issue #124. San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass, pp. 19-35.
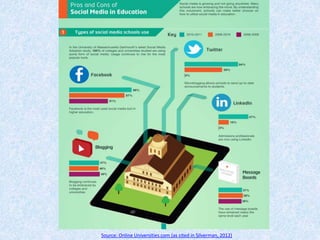
Silverman, M. (2012). How higher education uses social media [INFOGRAPHIC]. Retrieved from:
http://mashable.com/2012/02/03/higher-education-social-media/
Qualman, E. (2011). Socialnomics: How social media transforms the way we live and do business. Hoboken, NJ: John
Wiley & Sons.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2010casestudycompetition-150308123844-conversion-gate01/85/2010-case-study-competition-16-320.jpg)