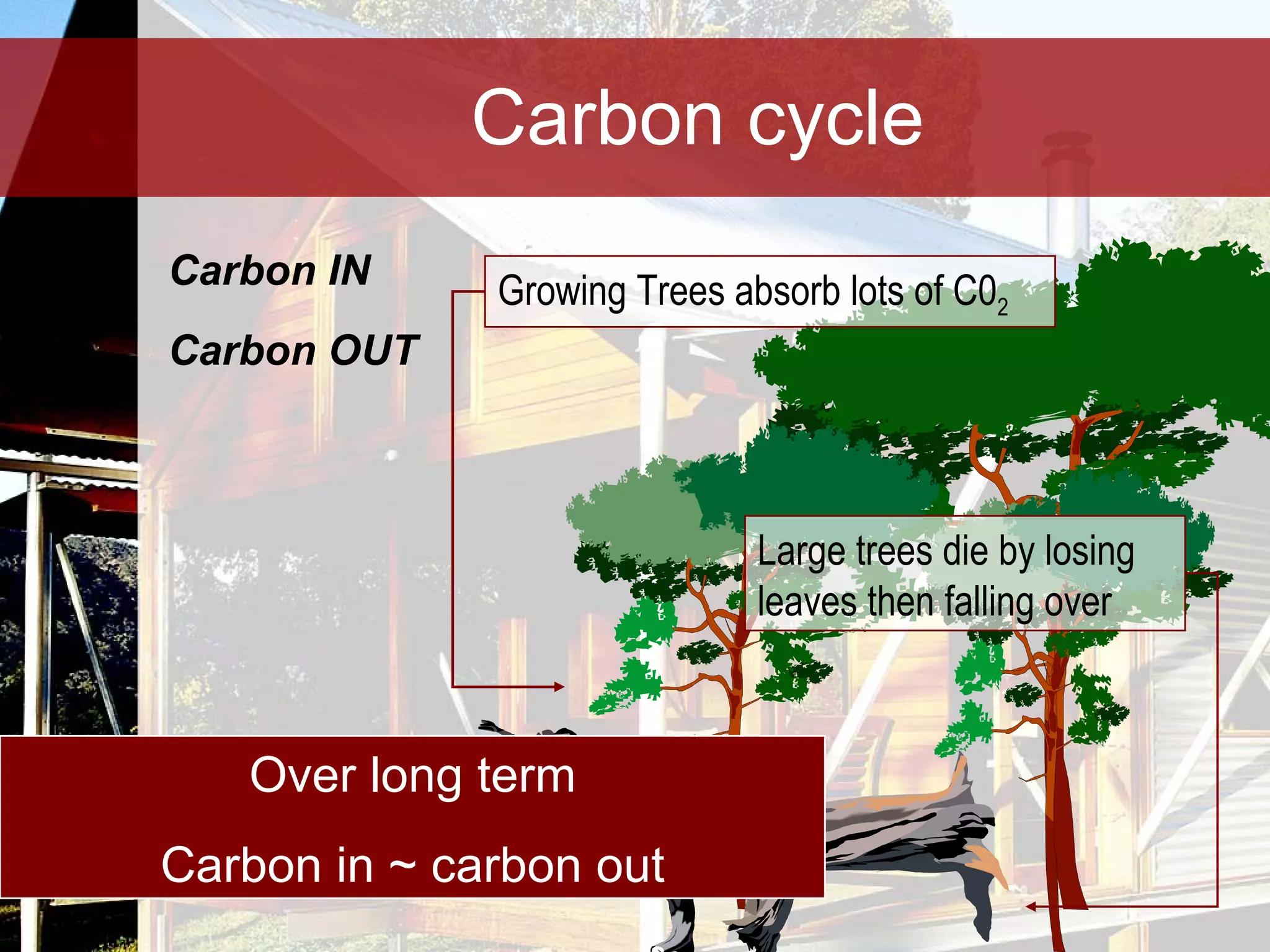
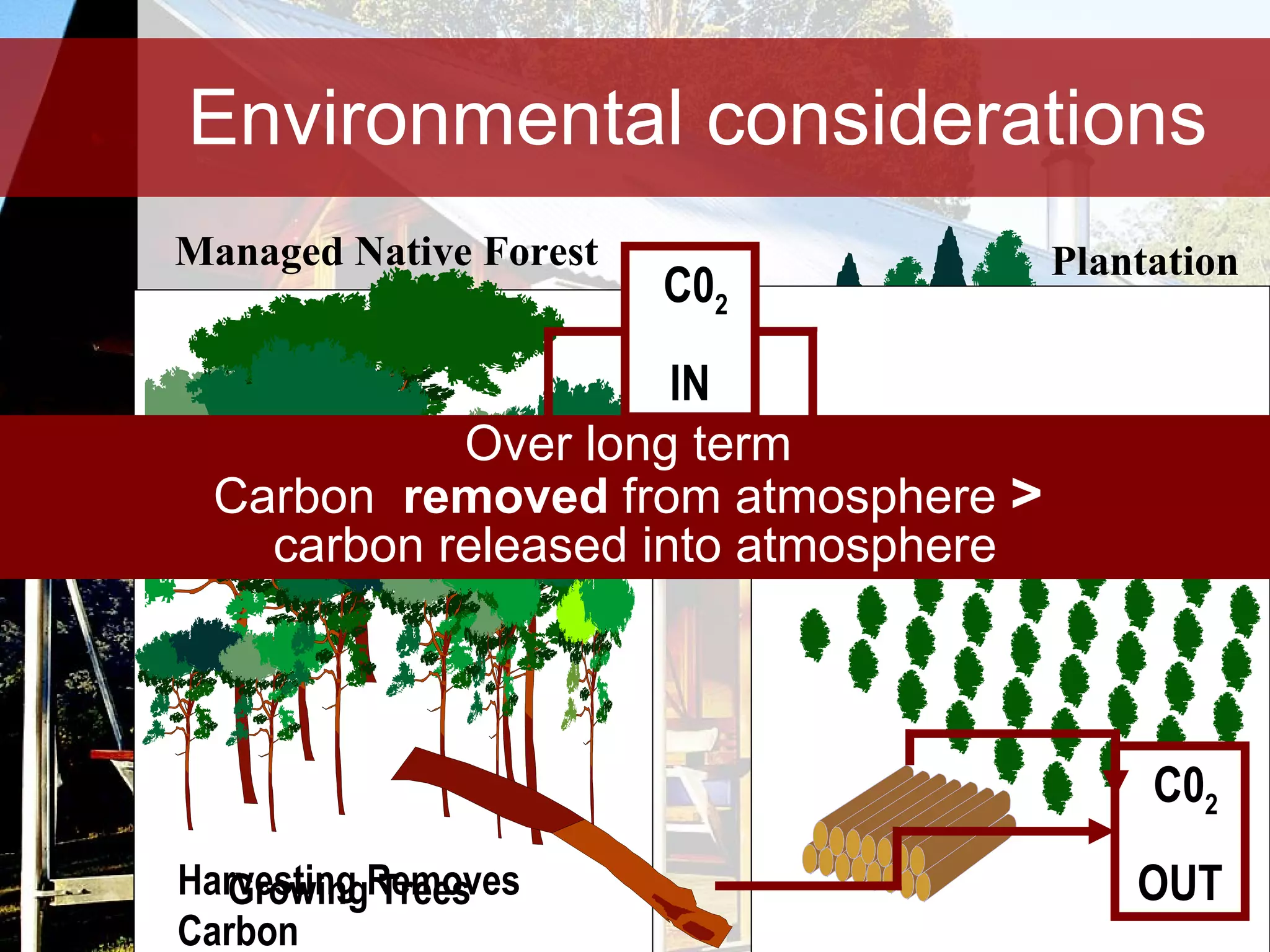
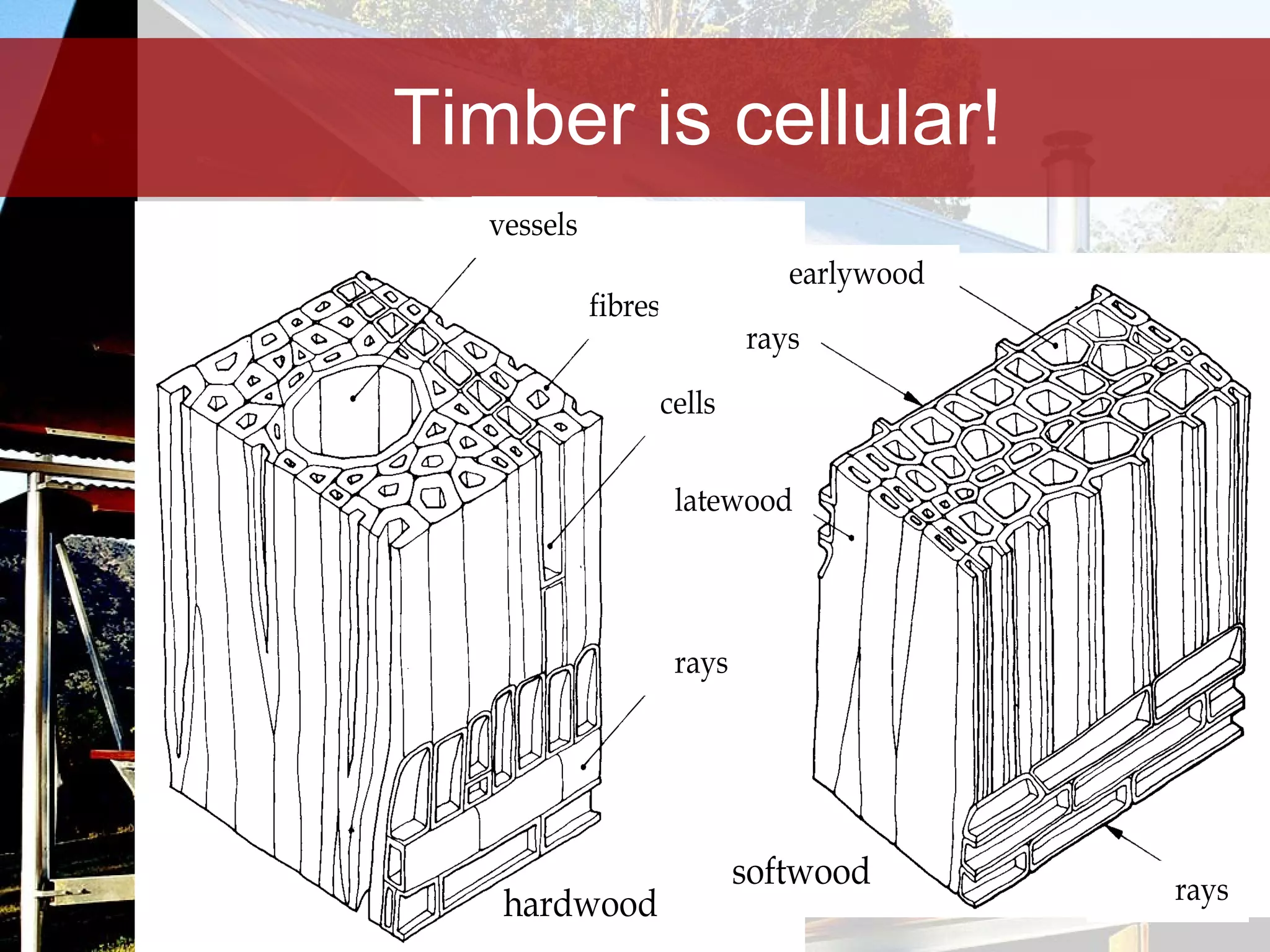
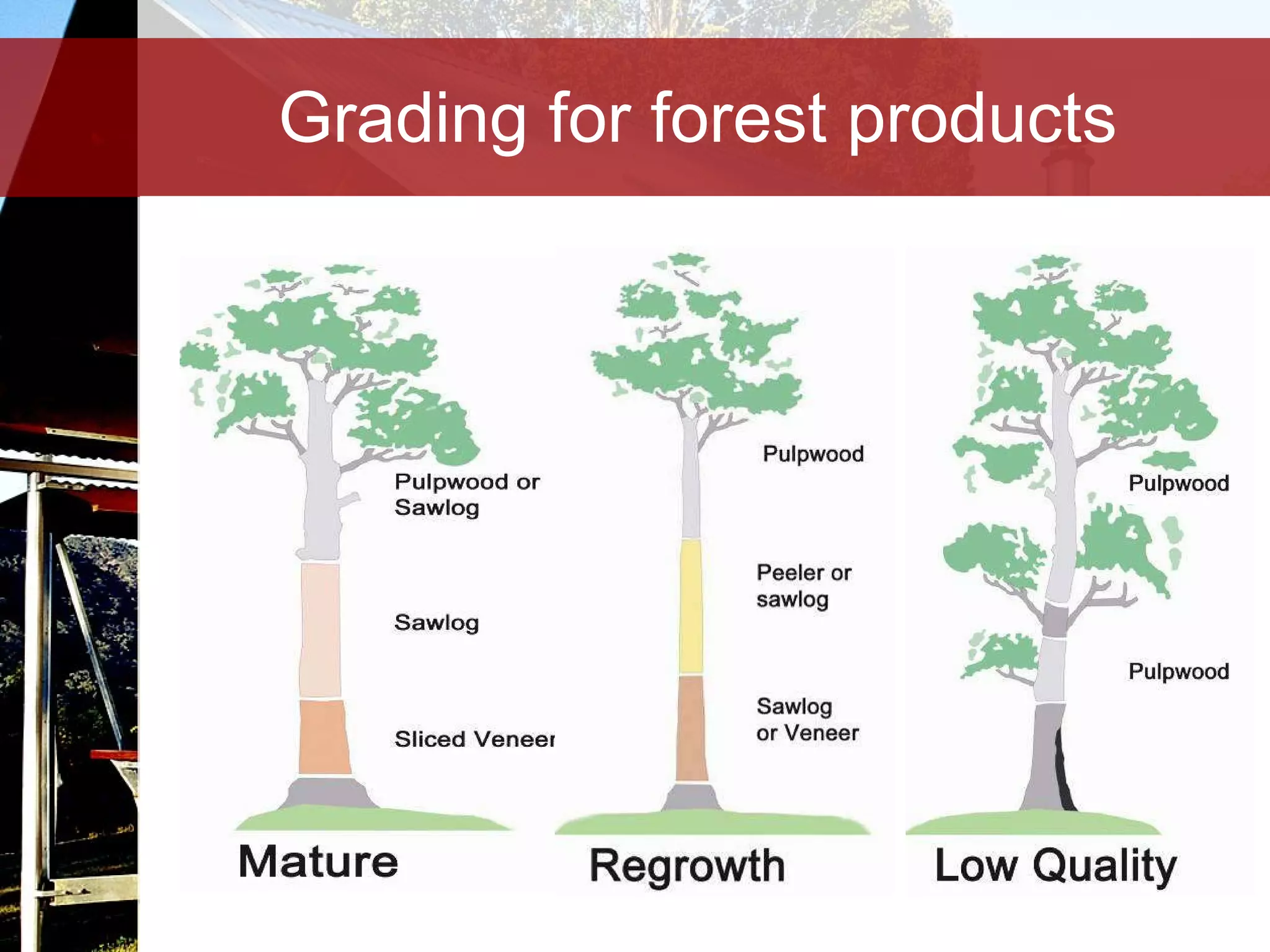
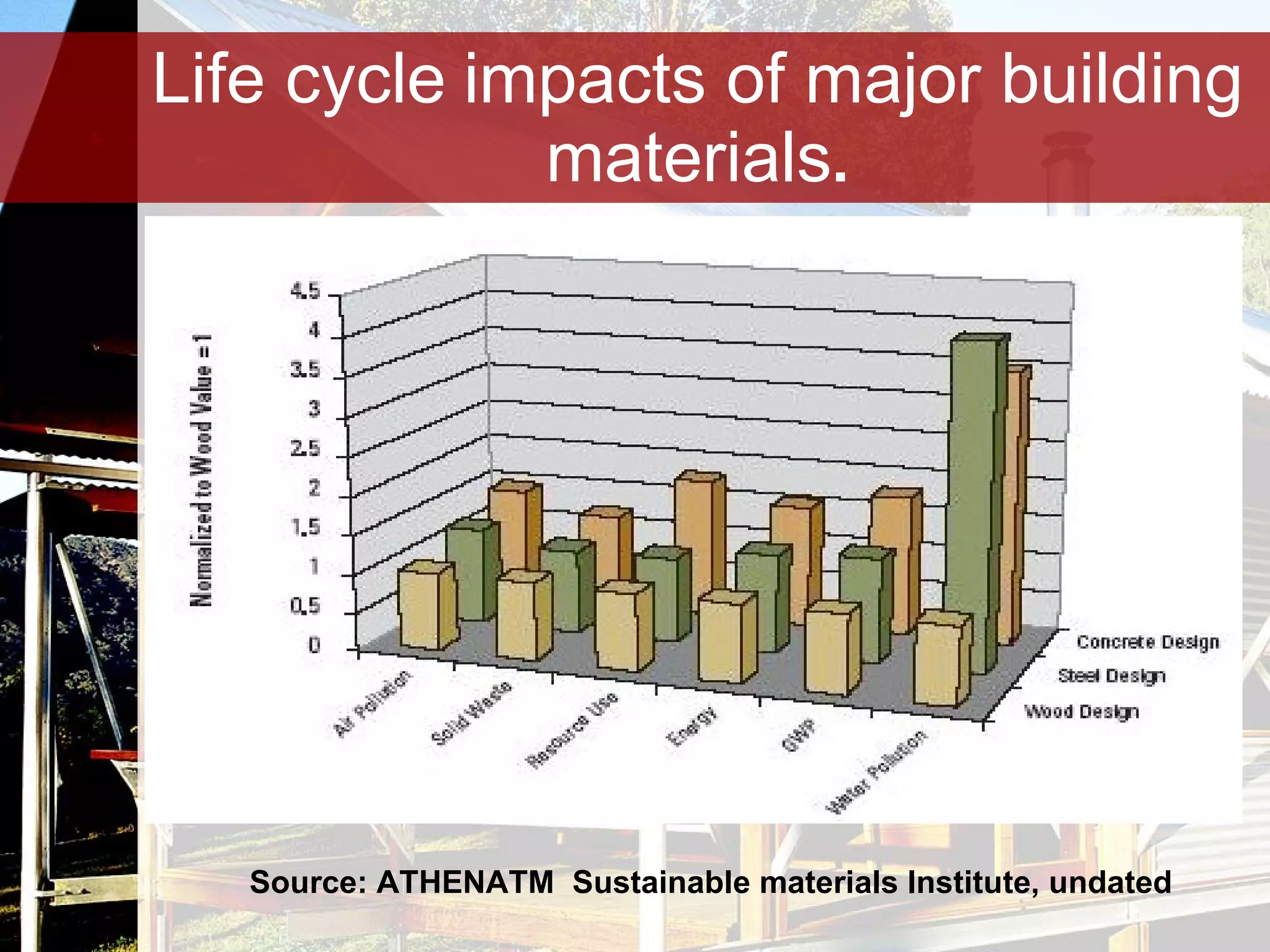
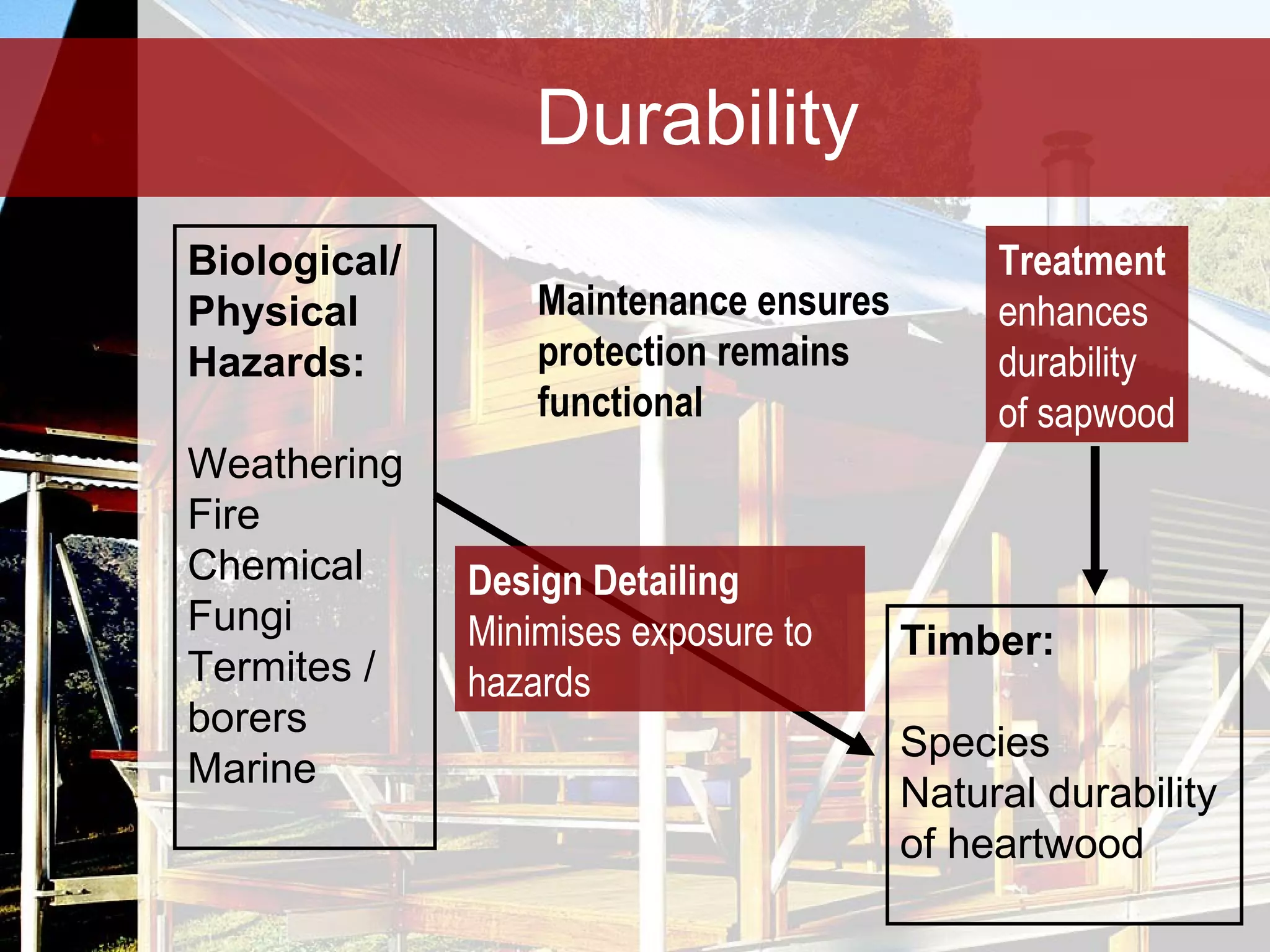
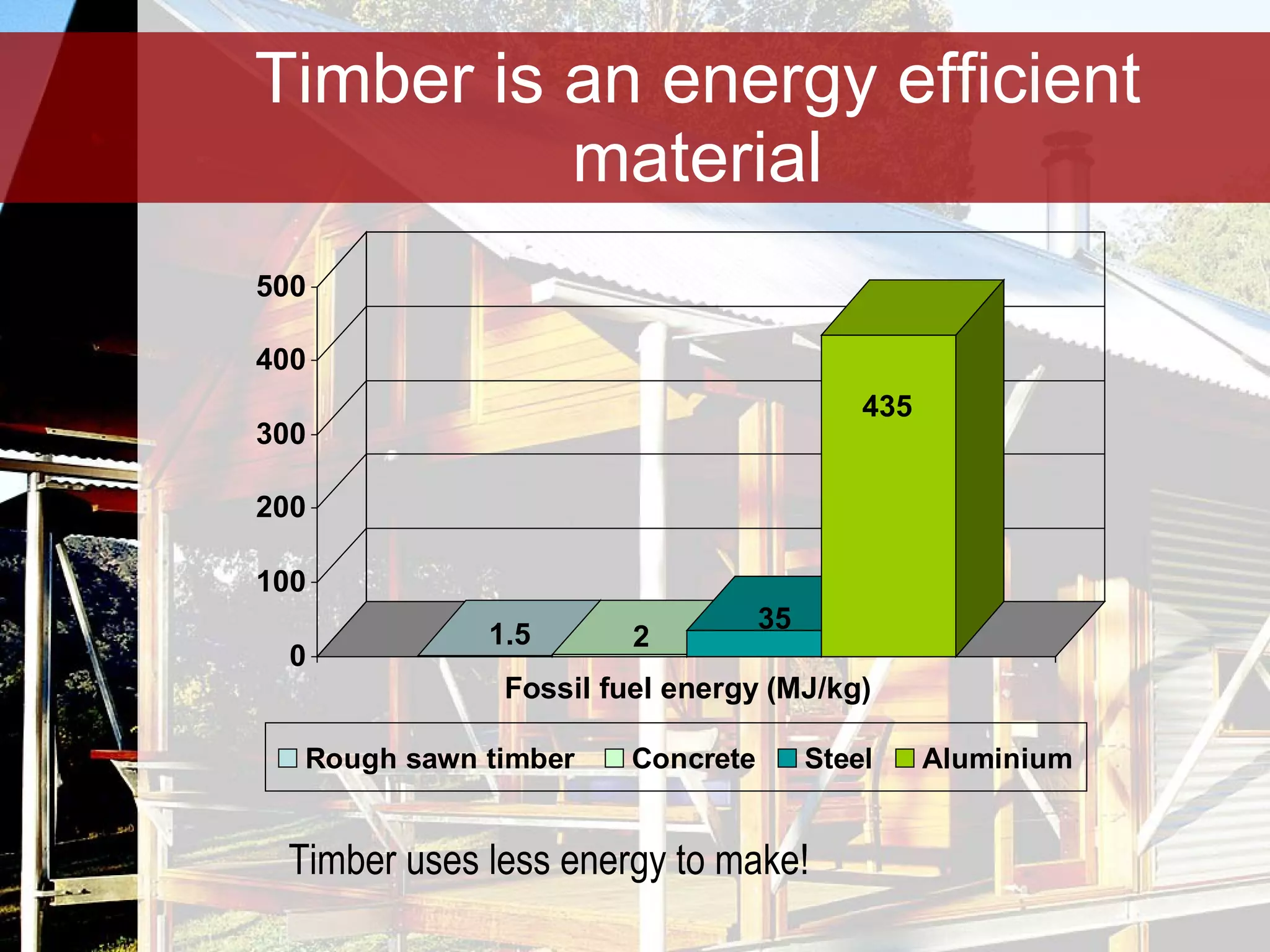
Timber is a renewable and sustainable building material that can be harvested from managed forests and plantations. It has low embodied energy, stores carbon, and has reuse and recycling options at the end of its life. When used properly through good design, detailing, and maintenance, timber can provide durable construction with low environmental impacts over its full life cycle.