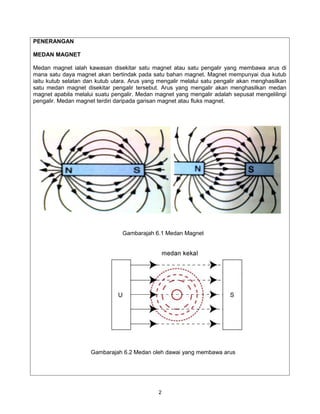
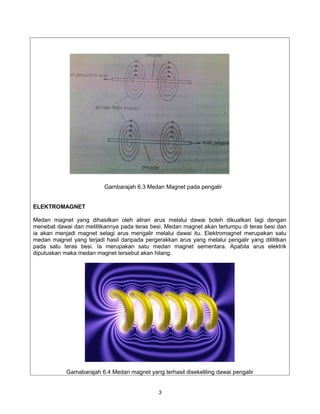
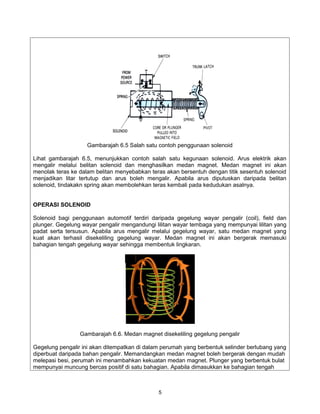
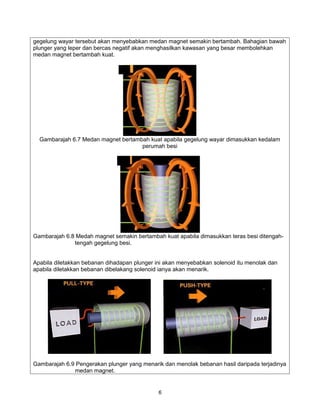
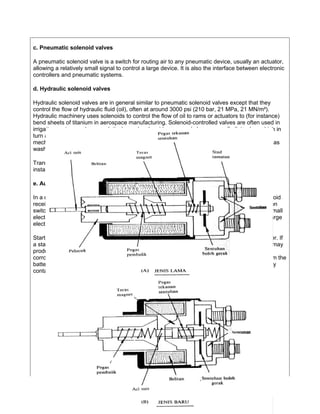
The document provides information on solenoids, including:
1. Solenoids produce a magnetic field when electric current flows through a coil wound around an iron core.
2. They are used to convert electrical energy to mechanical energy and can be used to engage or disengage components.
3. Common applications of solenoids include starters in vehicles, locks, and devices that control engine functions.