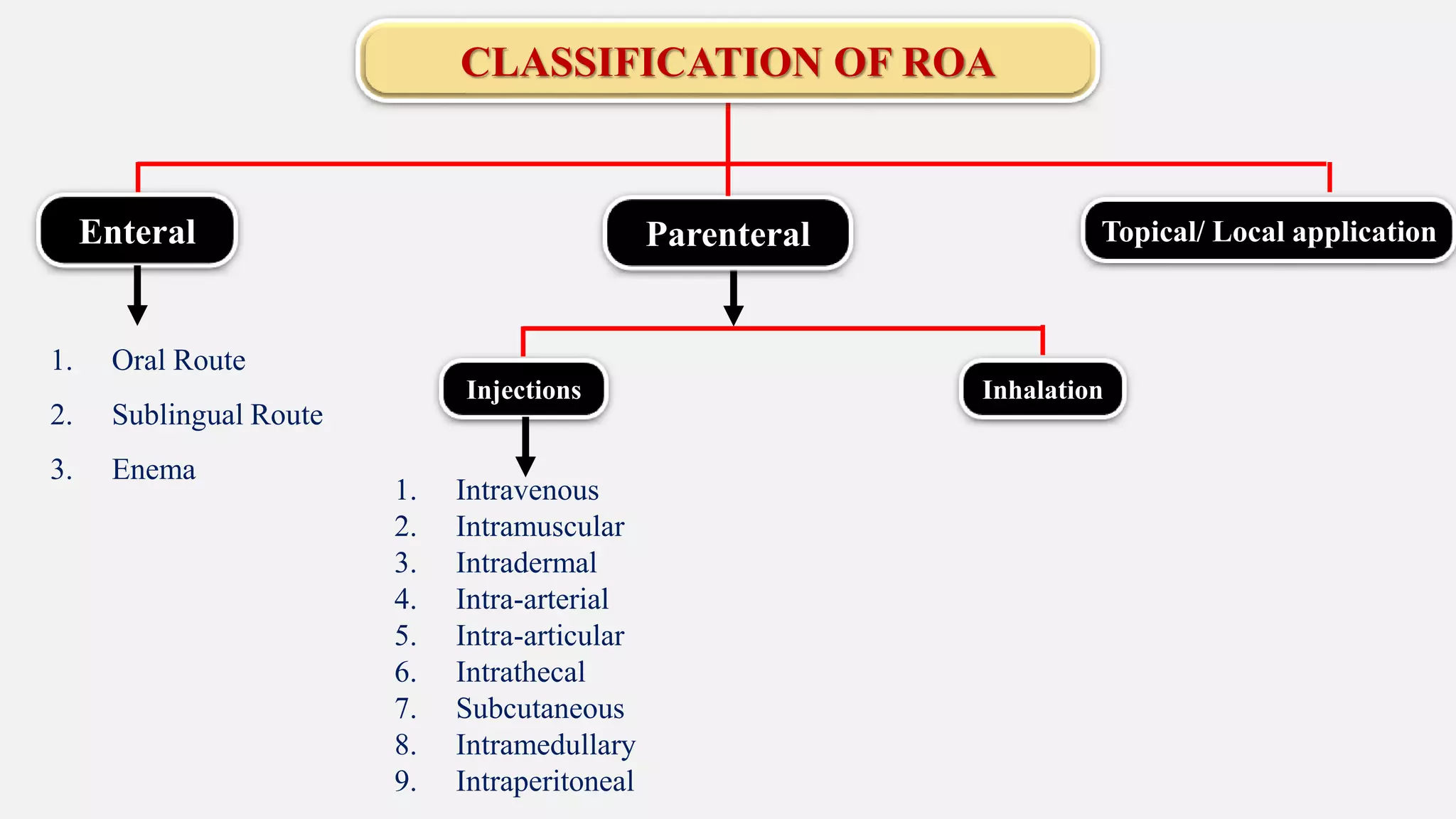
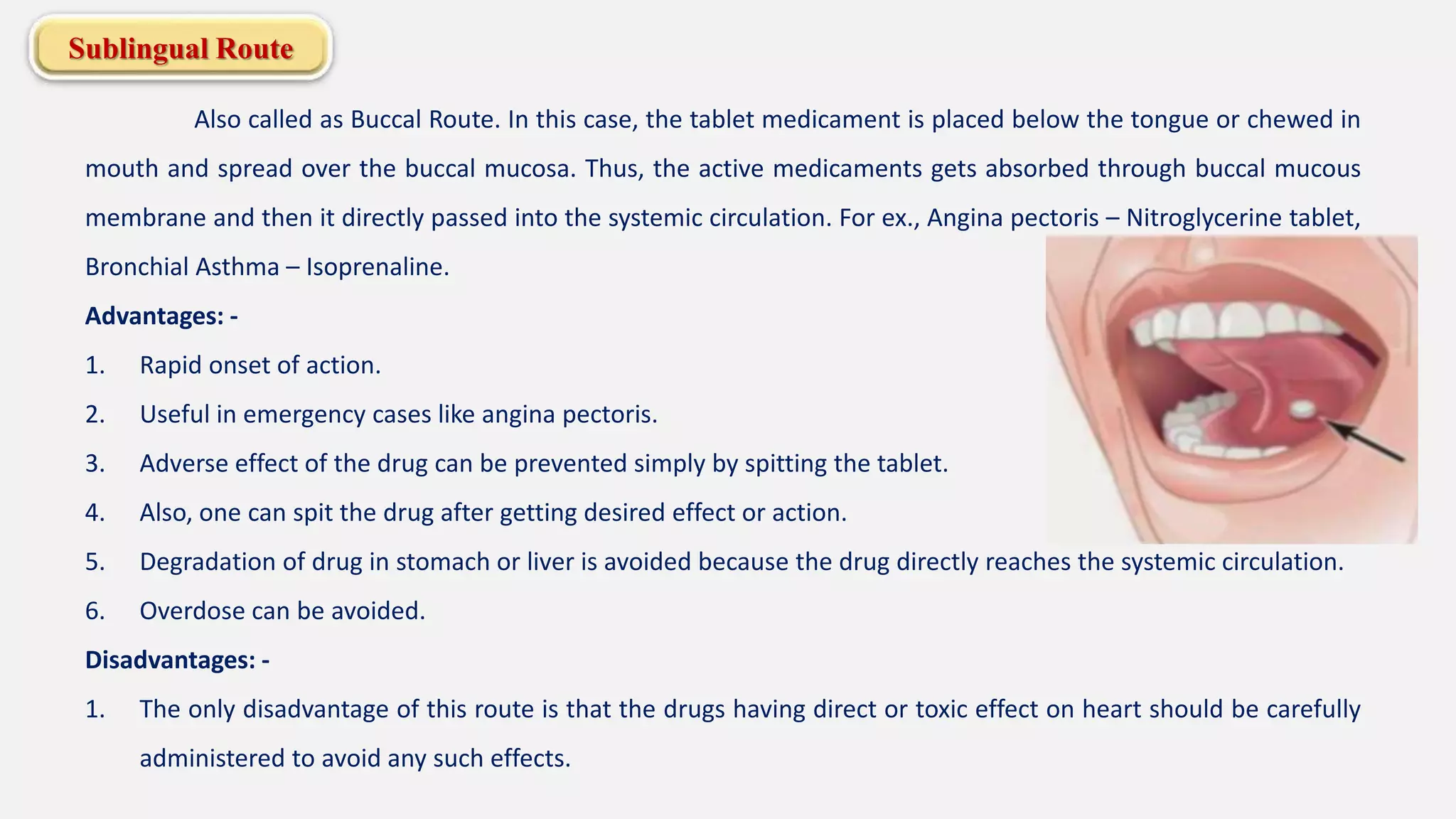
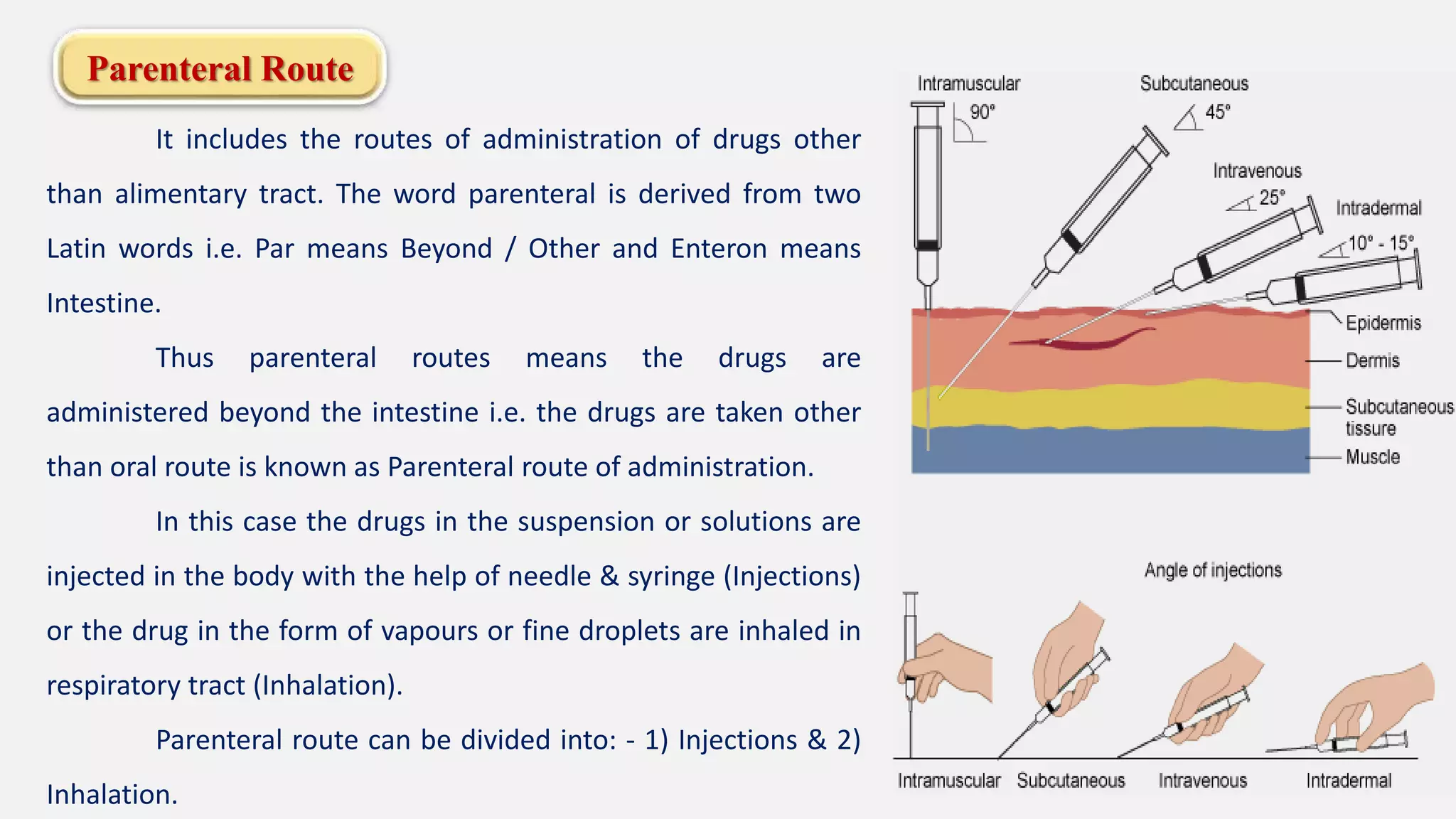
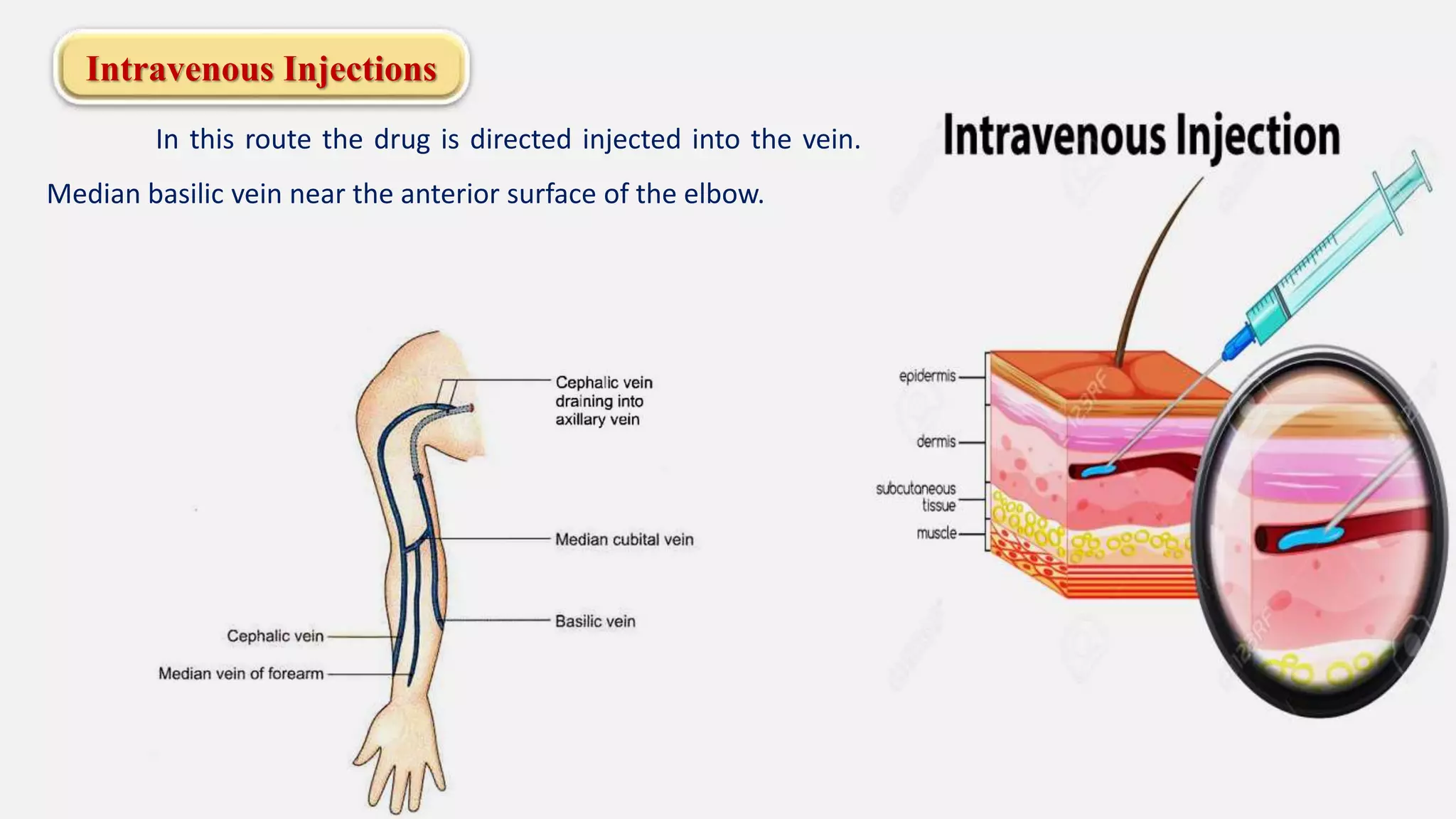
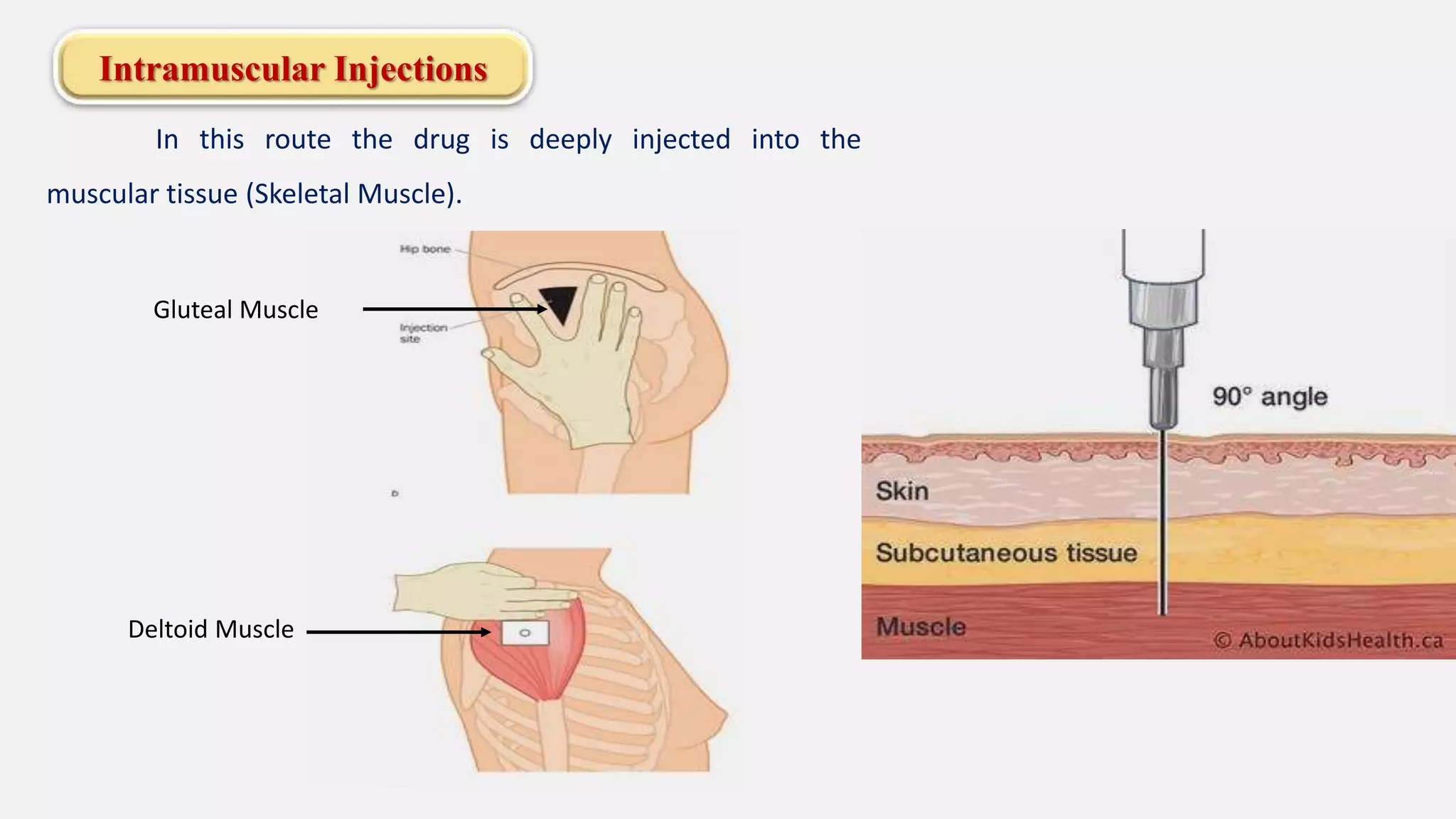
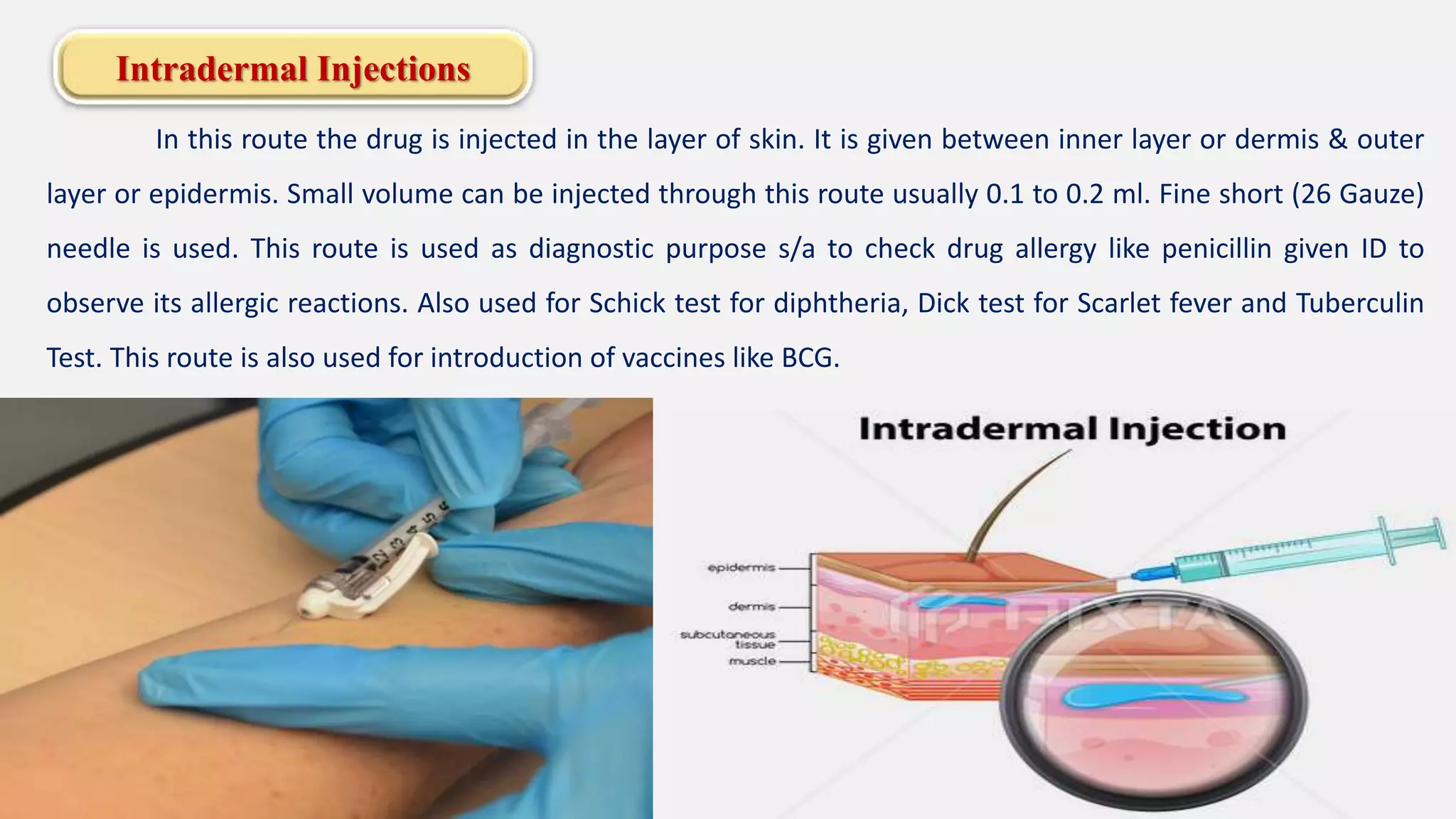
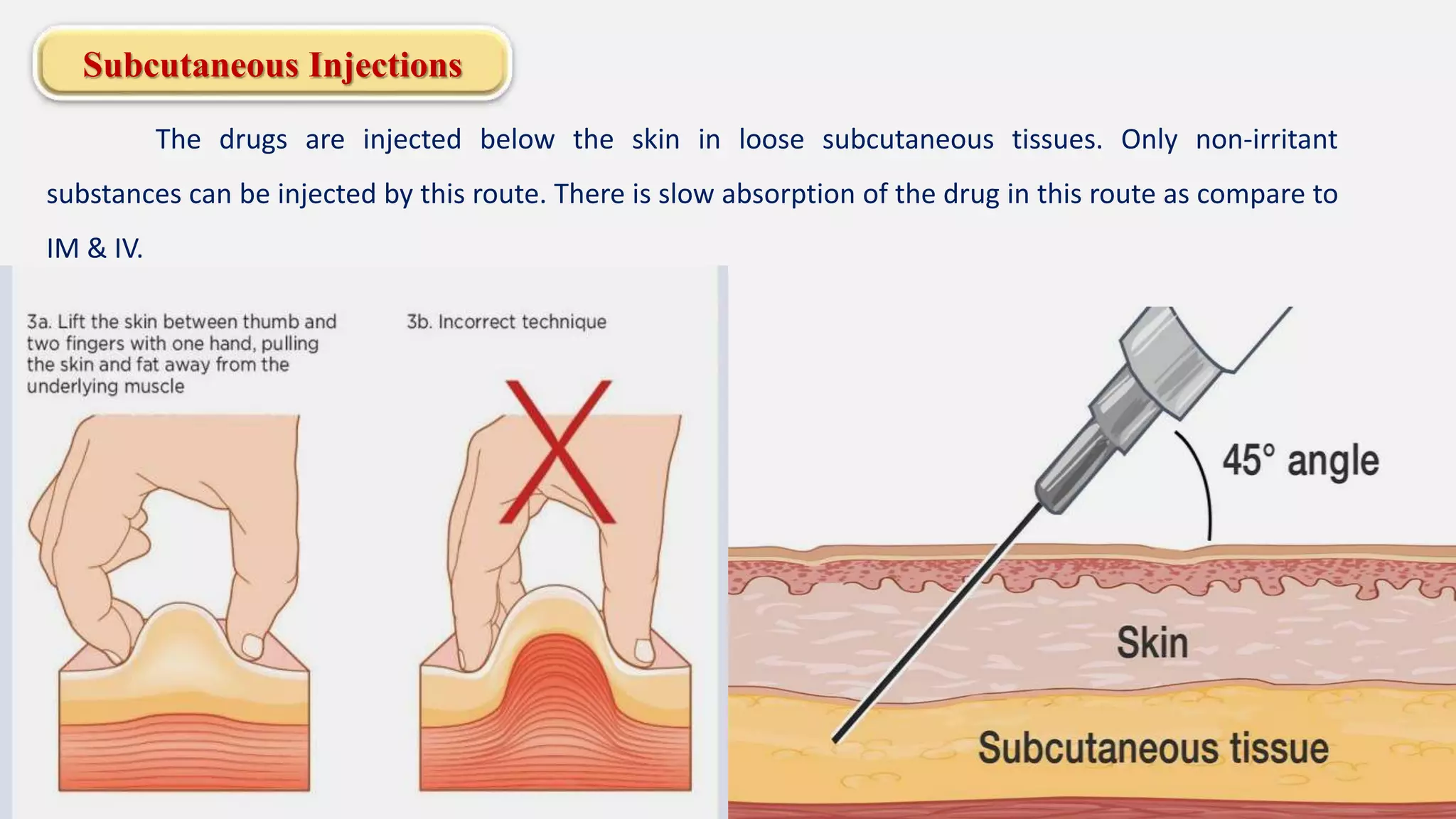
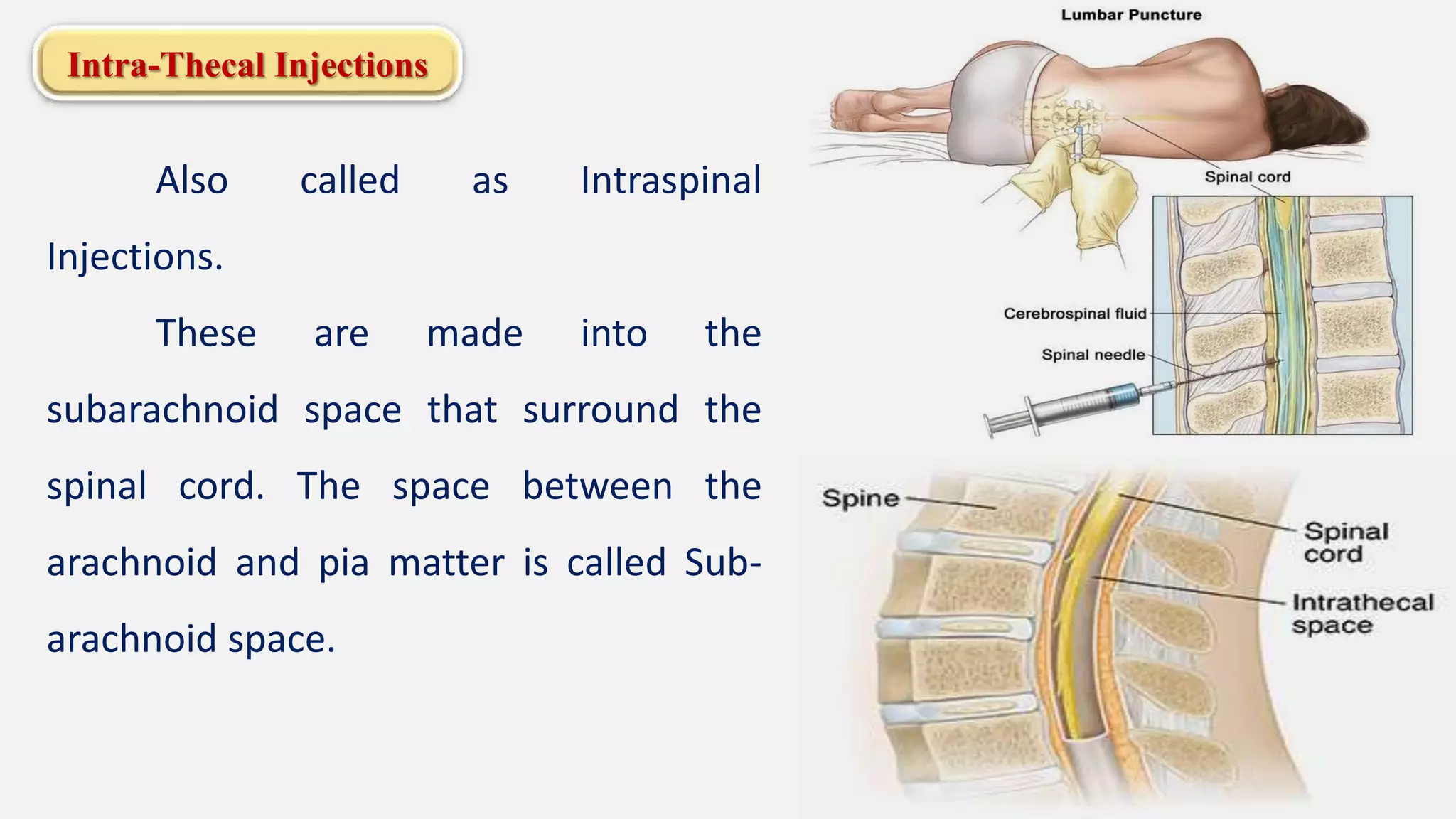
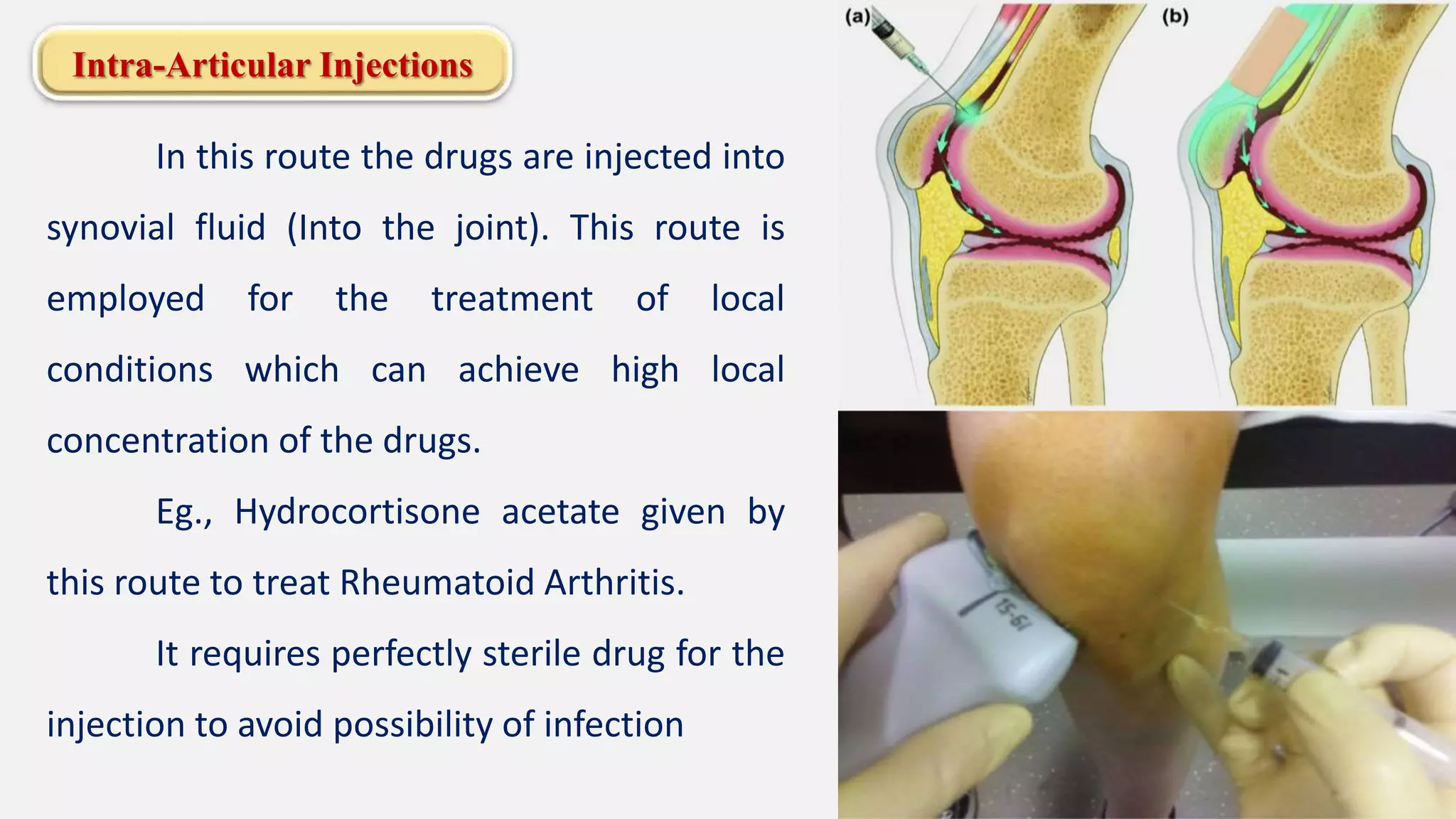
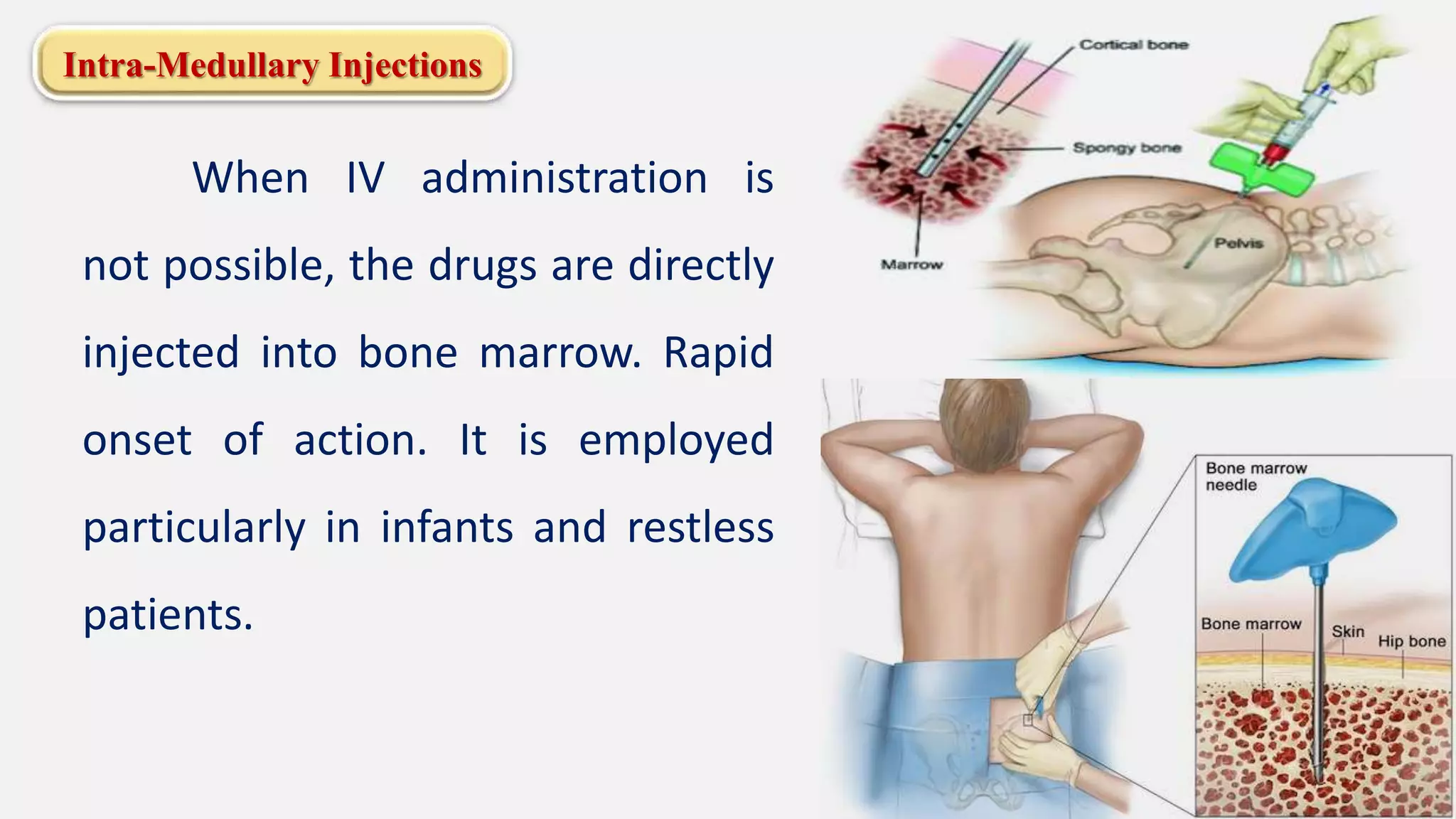
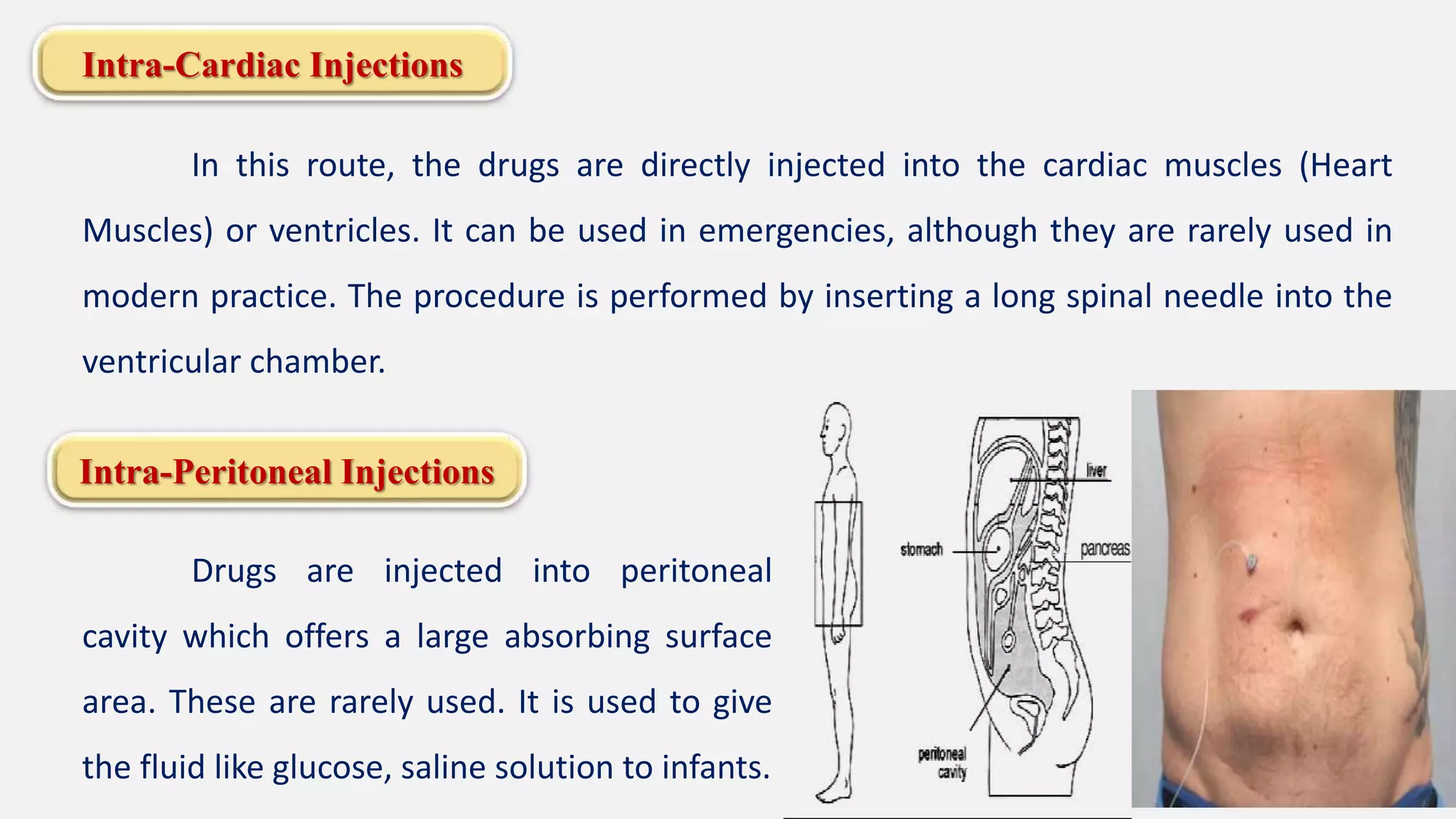
The document discusses various routes of drug administration including enteral, parenteral, and topical methods. Each route is classified, detailing advantages and disadvantages, such as the rapid action of parenteral routes versus the convenience of oral administration. It also highlights specific techniques like injections and inhalations, underscoring their applications in different medical scenarios.