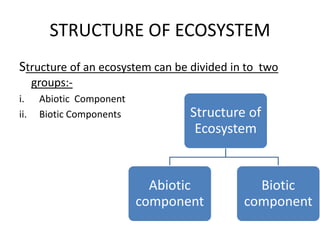
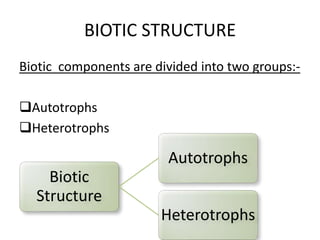
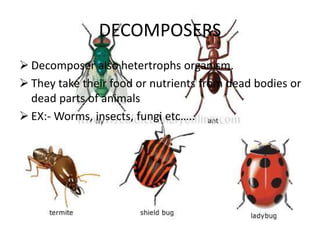
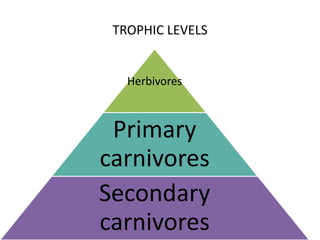
This document discusses the key components and structure of ecosystems. It begins by defining ecology as the study of relationships between life forms, and ecosystems as communities of organisms within a shared environment. Ecosystems have both abiotic (non-living) components like soil and air, as well as biotic (living) components including producers, consumers, and decomposers. Producers, mainly plants, are autotrophs that produce their own food through photosynthesis. Consumers are heterotrophs that depend on producers and each other for food and include herbivores, primary carnivores, and secondary carnivores. Decomposers also rely on other organisms for nutrients and help recycle materials within the ecosystem